The Later Middle Ages
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
Student Information 8.2 Ancient Egypt and Its Rulers As in
... White Chapel at Karnak: Also known as the Jubilee Chapel Built to celebrate Senusret’s 30th year as ruler of Egypt. Made of alabaster, a hard white stone. Some historians believe that it was covered with a thin layer of gold. Artwork and hieroglyphics decorated the chapel’s pillars (columns) ...
... White Chapel at Karnak: Also known as the Jubilee Chapel Built to celebrate Senusret’s 30th year as ruler of Egypt. Made of alabaster, a hard white stone. Some historians believe that it was covered with a thin layer of gold. Artwork and hieroglyphics decorated the chapel’s pillars (columns) ...
Egypt Test
... provided. Note there will be two words not used. 1.The period of order and stability that lasted from 2050 BC until about 1750 BC was called the ...
... provided. Note there will be two words not used. 1.The period of order and stability that lasted from 2050 BC until about 1750 BC was called the ...
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE
... KEY LEARNING(S): Egypt achieved many accomplishments such as great architecture. hieroglyphics, medicine, religious beliefs, and military conquests due to its location along the Nile River. UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S): What were the many achievements throughout Egypt’s Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms ? ...
... KEY LEARNING(S): Egypt achieved many accomplishments such as great architecture. hieroglyphics, medicine, religious beliefs, and military conquests due to its location along the Nile River. UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S): What were the many achievements throughout Egypt’s Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms ? ...
File
... II. Belief in Afterlife - After death, the soul would be tested by Osiris. Osiris would weigh the heart (thought to be the soul in Ancient Egypt) would be weighed against a feather (which was the symbol of truth and justice). If the scale balanced, the soul would pass on to the afterlife, if there w ...
... II. Belief in Afterlife - After death, the soul would be tested by Osiris. Osiris would weigh the heart (thought to be the soul in Ancient Egypt) would be weighed against a feather (which was the symbol of truth and justice). If the scale balanced, the soul would pass on to the afterlife, if there w ...
New Kingdom: Pharaohs King Tut Tutankhamun was nine years old
... almost completely intact — the most complete ancient Egyptian royal tomb ever found. As Tutankhamun began his reign at such an early age, his vizier and eventual successor Ay was probably making most of the important political decisions during Tutankhamun's reign. ...
... almost completely intact — the most complete ancient Egyptian royal tomb ever found. As Tutankhamun began his reign at such an early age, his vizier and eventual successor Ay was probably making most of the important political decisions during Tutankhamun's reign. ...
Notes - Exodus: Out of Egypt
... me. Say it to me so that the poison might go out, for a man lives when one pronounces his name.” The poison burned with a burning, it was more powerful than flame or fire. Then the majesty of Ra said, “May you give to me your two ears, my daughter Isis, so that my name might go forth from my body to ...
... me. Say it to me so that the poison might go out, for a man lives when one pronounces his name.” The poison burned with a burning, it was more powerful than flame or fire. Then the majesty of Ra said, “May you give to me your two ears, my daughter Isis, so that my name might go forth from my body to ...
Name: Period: PHARAOHS
... unification of the two kingdoms. The Egyptians believed the crown had magic powers; it was the single item an Egyptian ruler could not take with him to the afterlife. A historian named Manetho reported that Menes ruled Egypt for 62 years and was killed by a hippopotamus. We cannot be certain of Mane ...
... unification of the two kingdoms. The Egyptians believed the crown had magic powers; it was the single item an Egyptian ruler could not take with him to the afterlife. A historian named Manetho reported that Menes ruled Egypt for 62 years and was killed by a hippopotamus. We cannot be certain of Mane ...
Who were the Egyptians? Egypt is a hot, dry country in the north of
... veins were filled with blood of the Sun God Re. It was important that this was not diluted. He must preserve its purity by marrying a member of his own family. Some Pharaohs even married their own daughters. A Pharaoh was the law and justice was defined as “what Pharaoh loves”. Wrongdoing was “what ...
... veins were filled with blood of the Sun God Re. It was important that this was not diluted. He must preserve its purity by marrying a member of his own family. Some Pharaohs even married their own daughters. A Pharaoh was the law and justice was defined as “what Pharaoh loves”. Wrongdoing was “what ...
First Civilizations: Africa and Asia 3200BCE – 500BCE
... ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into decline and fell to invaders from Assyria, Persia, Greece, and Rome. ...
... ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into decline and fell to invaders from Assyria, Persia, Greece, and Rome. ...
Egypt
... • Egyptian Entry to Eternal Life: 1. During life a person studies the “Book of the Dead” 2. After a person dies they stand before Osiris and Isis, their heart is placed on a scale and weighed against feathers, if the person studied the “Book of the Dead” and knew all the spells the scale balanced 3. ...
... • Egyptian Entry to Eternal Life: 1. During life a person studies the “Book of the Dead” 2. After a person dies they stand before Osiris and Isis, their heart is placed on a scale and weighed against feathers, if the person studied the “Book of the Dead” and knew all the spells the scale balanced 3. ...
First Civilizations: Africa and Asia 3200BCE – 500BCE
... ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into decline and fell to invaders from Assyria, Persia, Greece, and Rome. ...
... ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into decline and fell to invaders from Assyria, Persia, Greece, and Rome. ...
Ancient Egypt ABC Book
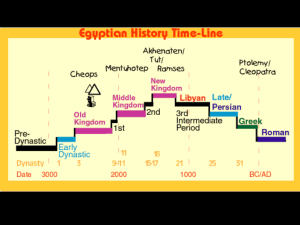
... Kingdoms, (old, middle, new) Ancient Egypt is broken down into 3 time periods: Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom. ...
... Kingdoms, (old, middle, new) Ancient Egypt is broken down into 3 time periods: Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom. ...
Egypt Test 1
... 27. Egyptians learned how to grind wheat into flour from the Mesopotamians. ________ 28. Egyptian social class was made up of 4 classes. __________ 29. Both Egyptians and Mesopotamians were Polytheistic. _____________ 30.Flooding was a very important part in both Egypt and Mesopotamia. ____________ ...
... 27. Egyptians learned how to grind wheat into flour from the Mesopotamians. ________ 28. Egyptian social class was made up of 4 classes. __________ 29. Both Egyptians and Mesopotamians were Polytheistic. _____________ 30.Flooding was a very important part in both Egypt and Mesopotamia. ____________ ...
Pharaoh
... Immortality of the Pharaoh Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death. He had an eternal spirit, or ka, that continued to take part in the governing of Egypt. The ka was a living spirit. Pharaoh’s Tomb needed the following: Eternal comforts: Artists decorated the walls of the ...
... Immortality of the Pharaoh Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death. He had an eternal spirit, or ka, that continued to take part in the governing of Egypt. The ka was a living spirit. Pharaoh’s Tomb needed the following: Eternal comforts: Artists decorated the walls of the ...
Egyptians Crossword Name
... Nile This is the longest river in the world and begins in the heart of Africa and empties into the Mediterranean Sea.45 Lower The area around the Nile Delta is called _____ Egypt.45 Upper The upstream area south of the Delta is called _____ Egypt.45 Flooding This yearly event is considered to be th ...
... Nile This is the longest river in the world and begins in the heart of Africa and empties into the Mediterranean Sea.45 Lower The area around the Nile Delta is called _____ Egypt.45 Upper The upstream area south of the Delta is called _____ Egypt.45 Flooding This yearly event is considered to be th ...
Egypt Notes
... A System of Writing Why is writing so important? Record keeping Communication ...
... A System of Writing Why is writing so important? Record keeping Communication ...
Chapter 4
... The army was made up of those who were drafted, professional Egyptian soldiers, and foreign mercenaries under the command of a general who answered to the Pharaoh. ...
... The army was made up of those who were drafted, professional Egyptian soldiers, and foreign mercenaries under the command of a general who answered to the Pharaoh. ...
CHAPTER 5 SECTION 3 GUIDED NOTES
... 17. Along the base, each side was ________________ feet long. 18. The tools used were __________ __________ and __________________. 19. Workers pulled stones slabs up long _____________ _____________ to their place on the pyramid. 20. Farmers worked during the Nile’s ____________ season. 21. The Gre ...
... 17. Along the base, each side was ________________ feet long. 18. The tools used were __________ __________ and __________________. 19. Workers pulled stones slabs up long _____________ _____________ to their place on the pyramid. 20. Farmers worked during the Nile’s ____________ season. 21. The Gre ...
Night at the Museum Final
... Egyptians Egypt is a country in North East Africa. The River Nile flows through the country and into the Mediterranean Sea. The River Nile was incredibly important for the Ancient Egyptians who lived along the riverbanks in Egypt. Farmers first settled in Egypt along the River Nile around 5000 B.C a ...
... Egyptians Egypt is a country in North East Africa. The River Nile flows through the country and into the Mediterranean Sea. The River Nile was incredibly important for the Ancient Egyptians who lived along the riverbanks in Egypt. Farmers first settled in Egypt along the River Nile around 5000 B.C a ...
Plagues of Egypt

The Plagues of Egypt (Hebrew: מכות מצרים, Makot Mitzrayim), also called the ten plagues (Hebrew: עשר המכות, Eser HaMakot) or the biblical plagues, were ten calamities that, according to the biblical Book of Exodus, the God of Israel inflicted upon Egypt to persuade the Pharaoh to release the ill-treated Israelites from slavery. Pharaoh capitulated after the tenth plague, triggering the Exodus of the Hebrew people. The plagues served to contrast the power of the God of Israel with the Egyptian gods, invalidating them. Some commentators have associated several of the plagues with judgment on specific gods associated with the Nile, fertility and natural phenomena. According to Exodus 12:12, all the gods of Egypt would be judged through the tenth and final plague: ""On that same night I will pass through Egypt and strike down every firstborn of both people and animals, and I will bring judgment on all the gods of Egypt. I am the LORD.""