Review sheet 2017
... Ancient Egypt and Its Rulers: Ancient Egypt enjoyed three periods of stability and unity under the rule of pharaohs. These periods were the Old Kingdom (Age of the Pyramids) from about 2700 to 2200 B.C.E.; the Middle Kingdom, (Period of Reunification) from about 2000 to 1800 B.C.E.; and the New Kin ...
... Ancient Egypt and Its Rulers: Ancient Egypt enjoyed three periods of stability and unity under the rule of pharaohs. These periods were the Old Kingdom (Age of the Pyramids) from about 2700 to 2200 B.C.E.; the Middle Kingdom, (Period of Reunification) from about 2000 to 1800 B.C.E.; and the New Kin ...
Summary: Ancient Egypt
... Scribes kept records with hieroglyphics. At times Egypt ruled a land called Nubia, to the south. It had many things Egyptians wanted, such as stones and gold. Meroe, one of Nubia’s largest cities, was built where the Nile met a trade route into Africa. ...
... Scribes kept records with hieroglyphics. At times Egypt ruled a land called Nubia, to the south. It had many things Egyptians wanted, such as stones and gold. Meroe, one of Nubia’s largest cities, was built where the Nile met a trade route into Africa. ...
Lesson 3 The Pyramid Builders
... • When a king died, he was usually replaced by one of his children - succession—order in which royal family members inherit a throne • Historians divided dynasties into Old, Middle, and New kingdoms - Old Kingdom began around 2575 B.C. as empire gained strength ...
... • When a king died, he was usually replaced by one of his children - succession—order in which royal family members inherit a throne • Historians divided dynasties into Old, Middle, and New kingdoms - Old Kingdom began around 2575 B.C. as empire gained strength ...
To a Word version
... leaders and their people, lest in case of war they should join themselves with the enemies of Egypt. Yet policy forbade their banishment from the country. Many of them were able and understanding workmen, and they added greatly to the wealth of the nation; the kings needed such labourers for the ere ...
... leaders and their people, lest in case of war they should join themselves with the enemies of Egypt. Yet policy forbade their banishment from the country. Many of them were able and understanding workmen, and they added greatly to the wealth of the nation; the kings needed such labourers for the ere ...
Ancient Egyptians and the Environment
... monuments (ex pyramids) for the pharaoh. (June to October) Crop yields increase so the pharaoh can tax the people more People are happy so they trust the Pharaoh- results in unity build his irrigation systems- increases productivity ...
... monuments (ex pyramids) for the pharaoh. (June to October) Crop yields increase so the pharaoh can tax the people more People are happy so they trust the Pharaoh- results in unity build his irrigation systems- increases productivity ...
Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs
... – Egypt’s Golden Age; increased trade during this time of peace and stability ...
... – Egypt’s Golden Age; increased trade during this time of peace and stability ...
CHAPTER 5 STUDY GUIDE (Answers in bold) How religion affected
... 54. Amenhotep: changed his name to Akhenaton. 55. The Egyptian god responsible for life, death, and rebirth was? Osiris. 56. Which Continent is Egypt located on? Africa 57. What was not one of the three kingdoms of ancient Egypt? Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom 58. For the most part, religi ...
... 54. Amenhotep: changed his name to Akhenaton. 55. The Egyptian god responsible for life, death, and rebirth was? Osiris. 56. Which Continent is Egypt located on? Africa 57. What was not one of the three kingdoms of ancient Egypt? Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom 58. For the most part, religi ...
Old Kingdom:
... The Hyksos invaded, they used weapons of Bronze and Iron to defeat the Egyptians. The power of the Pharaoh declined during the middle kingdom ...
... The Hyksos invaded, they used weapons of Bronze and Iron to defeat the Egyptians. The power of the Pharaoh declined during the middle kingdom ...
20131126151735
... Warrior-pharaoh who made Egypt an empire by extending Egyptian control into Syria Pharaoh who encouraged trade during her reign in the New Kingdom period Young pharaoh who succeeded Akhenaton Most powerful god worshiped during the New Kingdom period ...
... Warrior-pharaoh who made Egypt an empire by extending Egyptian control into Syria Pharaoh who encouraged trade during her reign in the New Kingdom period Young pharaoh who succeeded Akhenaton Most powerful god worshiped during the New Kingdom period ...
Class Notes / Learning Log / Textbook Notes
... Class Notes The Egyptian civilization began in the fertile Nile River Valley, where natural barriers discouraged invasions. The Egyptians depended on the Nile’s floods to grow their crops. Around 3100 B.C., Egypt’s two major kingdoms, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt, were combined into one Egyptian soci ...
... Class Notes The Egyptian civilization began in the fertile Nile River Valley, where natural barriers discouraged invasions. The Egyptians depended on the Nile’s floods to grow their crops. Around 3100 B.C., Egypt’s two major kingdoms, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt, were combined into one Egyptian soci ...
Ancient Egypt
... the weighing of the heart Evolution of Egyptian mythology known as a ruler in the Nile delta a local god ...
... the weighing of the heart Evolution of Egyptian mythology known as a ruler in the Nile delta a local god ...
Ch. 3 Reading Questions
... preparation of soil and then allowed their crops to mature over the winter, and during the early spring, they would harvest them. 3. How did the institution of the pharaoh evolve, and what was the nature of the pharaoh's power through the Old Kingdom period? After 3100 B.C.E. Egyptian rulers forged ...
... preparation of soil and then allowed their crops to mature over the winter, and during the early spring, they would harvest them. 3. How did the institution of the pharaoh evolve, and what was the nature of the pharaoh's power through the Old Kingdom period? After 3100 B.C.E. Egyptian rulers forged ...
File
... headstones undiscovered in the dirt, their very graves forgotten. But their fame lives on in their papyrus rolls composed while they were still alive; And the memory of those who wrote such books shall last to the end of time and for eternity. - John Lawrence Foster ...
... headstones undiscovered in the dirt, their very graves forgotten. But their fame lives on in their papyrus rolls composed while they were still alive; And the memory of those who wrote such books shall last to the end of time and for eternity. - John Lawrence Foster ...
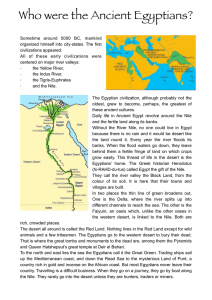
Geography and Early Egypt Chapter 11, Section 1
... • Longest river in the world • Southern region-Upper Egypt • Northern region-Lower Egypt ...
... • Longest river in the world • Southern region-Upper Egypt • Northern region-Lower Egypt ...
8th World History Egypt Notes Sumerians The ________fertile
... Earlier tombs were usually underground. Most tombs contained items that the ruler might want in the afterlife. During the Old Kingdom three enormous pyramids were built at ___giza__________. The Great Pyramid was the tallest building in the world for nearly ______4000_____________ years. The ____sph ...
... Earlier tombs were usually underground. Most tombs contained items that the ruler might want in the afterlife. During the Old Kingdom three enormous pyramids were built at ___giza__________. The Great Pyramid was the tallest building in the world for nearly ______4000_____________ years. The ____sph ...
File
... The Old Kingdom 2700-2200 B.C. The Old Kingdom was a period of great prosperity. This time is also called the pyramid age, because the great pyramids were built during this time. Egyptian kings came to be known as Pharaohs. The Pharaoh was seen as divine, or godlike. The people believed that the Ph ...
... The Old Kingdom 2700-2200 B.C. The Old Kingdom was a period of great prosperity. This time is also called the pyramid age, because the great pyramids were built during this time. Egyptian kings came to be known as Pharaohs. The Pharaoh was seen as divine, or godlike. The people believed that the Ph ...
Egyptian Timeline
... inscribed with a decree issued at Memphis in 196 BC on behalf of the Pharaoh. The decree appears in three scripts: the upper text is Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics, the middle portion Demotic (the stage of the Egyptian language after the New Kingdom) script, and the lowest Ancient Greek. Because it ...
... inscribed with a decree issued at Memphis in 196 BC on behalf of the Pharaoh. The decree appears in three scripts: the upper text is Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics, the middle portion Demotic (the stage of the Egyptian language after the New Kingdom) script, and the lowest Ancient Greek. Because it ...
File
... The Egyptians also believed pharaohs were gods in human form. They had absolute power over their subjects. After pharaohs died, huge stone pyramids were built as their tombs. Pharaohs were buried in chambers within the pyramids. A government ruled by a royal leader such as a pharaoh or king is calle ...
... The Egyptians also believed pharaohs were gods in human form. They had absolute power over their subjects. After pharaohs died, huge stone pyramids were built as their tombs. Pharaohs were buried in chambers within the pyramids. A government ruled by a royal leader such as a pharaoh or king is calle ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide: Egypt
... Nubia was located along the upper Nile River valley. The Nubians were among the first people to make ceramic pottery and offer it for trade. They also traded goods such as hardwoods and animal products that came from places in central and southern Africa. Why do you think Egyptians wanted to control ...
... Nubia was located along the upper Nile River valley. The Nubians were among the first people to make ceramic pottery and offer it for trade. They also traded goods such as hardwoods and animal products that came from places in central and southern Africa. Why do you think Egyptians wanted to control ...
Focus Question: What were the characteristics of the world`s first
... Unlike neighboring peoples, Israelites were monotheistic, believing in only one god. They believed every event reflected God’s plan. So, they recorded events and laws in the Torah, their holiest text. According to the Torah, about 2000 B.C., Abraham and his people moved to an area called Canaan. Abr ...
... Unlike neighboring peoples, Israelites were monotheistic, believing in only one god. They believed every event reflected God’s plan. So, they recorded events and laws in the Torah, their holiest text. According to the Torah, about 2000 B.C., Abraham and his people moved to an area called Canaan. Abr ...
Egypt Review Slideshow
... 3. “Weighing of the heart”: • Heart was center of intelligence and memory • Used this to weigh it against the “feather of truth” • If heart is lighter than the feather, than they were pure and could go to afterlife • If heart was heavier, they died a second death ...
... 3. “Weighing of the heart”: • Heart was center of intelligence and memory • Used this to weigh it against the “feather of truth” • If heart is lighter than the feather, than they were pure and could go to afterlife • If heart was heavier, they died a second death ...
Blue Nile and White Nile 2) How
... Mesopotamians developed their agriculture and then established settlements 9) Since Nubia had a shortage of farmland, how did the Nubians get the food that they needed? They added fish, ducks, and other birds to their diets. 10) Why was trade so popular and rich in Egypt? Trade flourished due to the ...
... Mesopotamians developed their agriculture and then established settlements 9) Since Nubia had a shortage of farmland, how did the Nubians get the food that they needed? They added fish, ducks, and other birds to their diets. 10) Why was trade so popular and rich in Egypt? Trade flourished due to the ...
Worksheet - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 9. As 'Lord of the Two Lands' the pharaoh was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned all of the ___________, made _________, __________________, and defended Egypt against ____________. 10. The most famous of all ancient Egyptian scripts is ______________. However, throughout three thousand ye ...
... 9. As 'Lord of the Two Lands' the pharaoh was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned all of the ___________, made _________, __________________, and defended Egypt against ____________. 10. The most famous of all ancient Egyptian scripts is ______________. However, throughout three thousand ye ...
The Middle and New Kingdoms
... time when Egypt was at its peak. • This era lasted from 1550 B.C. to 1050 B.C. • During this era, Egypt created its first army to take over new land and to keep people like the Hyksos from taking over again. ...
... time when Egypt was at its peak. • This era lasted from 1550 B.C. to 1050 B.C. • During this era, Egypt created its first army to take over new land and to keep people like the Hyksos from taking over again. ...
Plagues of Egypt

The Plagues of Egypt (Hebrew: מכות מצרים, Makot Mitzrayim), also called the ten plagues (Hebrew: עשר המכות, Eser HaMakot) or the biblical plagues, were ten calamities that, according to the biblical Book of Exodus, the God of Israel inflicted upon Egypt to persuade the Pharaoh to release the ill-treated Israelites from slavery. Pharaoh capitulated after the tenth plague, triggering the Exodus of the Hebrew people. The plagues served to contrast the power of the God of Israel with the Egyptian gods, invalidating them. Some commentators have associated several of the plagues with judgment on specific gods associated with the Nile, fertility and natural phenomena. According to Exodus 12:12, all the gods of Egypt would be judged through the tenth and final plague: ""On that same night I will pass through Egypt and strike down every firstborn of both people and animals, and I will bring judgment on all the gods of Egypt. I am the LORD.""