Ch 5.1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
Chemistry Standards Checklist
... b. Demonstrate appropriate techniques in all laboratory situations. c. Follow correct protocol for identifying and reporting safety problems and violations. SCSh5. Students will demonstrate the computation and estimation skills necessary for analyzing data and developing reasonable scientific ...
... b. Demonstrate appropriate techniques in all laboratory situations. c. Follow correct protocol for identifying and reporting safety problems and violations. SCSh5. Students will demonstrate the computation and estimation skills necessary for analyzing data and developing reasonable scientific ...
Study Guide – Unit Test (9-27-13)
... There will be other examples included on the test. (Look at notes/old quizzes and worksheets) ...
... There will be other examples included on the test. (Look at notes/old quizzes and worksheets) ...
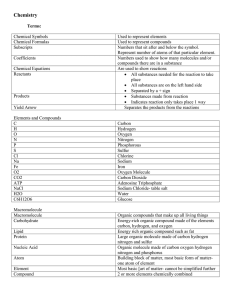
Chemical Equations
... • Chemical reactions are read left to right. • The starting substances are called the reactants • The substance that is made as a result of the chemical reaction are called products ...
... • Chemical reactions are read left to right. • The starting substances are called the reactants • The substance that is made as a result of the chemical reaction are called products ...
Chemical Reactions
... Pick up sock and board. Complete the Do Now via QR code or link I will be about 15-30 min late. This should be completed by the time I arrive. http://bit.ly/1LvB4ak ...
... Pick up sock and board. Complete the Do Now via QR code or link I will be about 15-30 min late. This should be completed by the time I arrive. http://bit.ly/1LvB4ak ...
Chapter One Outline
... The law of conservation of mass states that there is no detectable change in mass during an ordinary chemical reaction The law of constant composition states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass The Modern Atomic Theory ...
... The law of conservation of mass states that there is no detectable change in mass during an ordinary chemical reaction The law of constant composition states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass The Modern Atomic Theory ...
1 Types of Chemical Reactions
... Sudden dramatic changes in temperature occur. A new solid suddenly appears. ...
... Sudden dramatic changes in temperature occur. A new solid suddenly appears. ...
Gizmos: Types of Reactions
... Question: How are chemical reactions classified? 1. Match: Most chemical reactions can be classified as one of four types. Using the chemical equations in the Gizmo as a guide, match the following definitions to the type of reaction. ____ One reactant is broken down into two or more products. ...
... Question: How are chemical reactions classified? 1. Match: Most chemical reactions can be classified as one of four types. Using the chemical equations in the Gizmo as a guide, match the following definitions to the type of reaction. ____ One reactant is broken down into two or more products. ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
... attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
Job Description: Pre – Treatment Technologist
... managers within Hardide Coatings Ltd’s manufacturing staff. Reporting to the Operations Manager he/she will be responsible for the day-to-day working activities of their department and the pre-treatment of production components prior to Hardide coating in the CVD coating chambers. The Manager will b ...
... managers within Hardide Coatings Ltd’s manufacturing staff. Reporting to the Operations Manager he/she will be responsible for the day-to-day working activities of their department and the pre-treatment of production components prior to Hardide coating in the CVD coating chambers. The Manager will b ...
Unit 2 Test Review
... Organic molecule made of nucleotides; used for information storage Molecules that are ‘used’ in a chemical reaction; on the left side of the equation Fats and oils; used for long term energy storage Organic compound that is the building block of organisms; made of amino acids Number (from 0-14) meas ...
... Organic molecule made of nucleotides; used for information storage Molecules that are ‘used’ in a chemical reaction; on the left side of the equation Fats and oils; used for long term energy storage Organic compound that is the building block of organisms; made of amino acids Number (from 0-14) meas ...
Physical and Chemical Changes
... Physical changes to food while eating occur through chewing/teeth tearing and peristalsis (muscle contractions in esophagus and intestines). 8. Which element is found in abundance in both the human body and in the Earth? Oxygen is found in abundance (meaning there is a lot of it) in both the human b ...
... Physical changes to food while eating occur through chewing/teeth tearing and peristalsis (muscle contractions in esophagus and intestines). 8. Which element is found in abundance in both the human body and in the Earth? Oxygen is found in abundance (meaning there is a lot of it) in both the human b ...
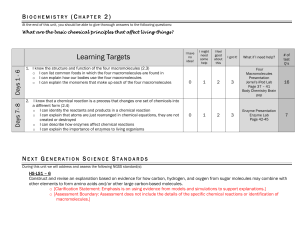
Chemistry Content Standards
... a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. b. Collect data and calculate the amount of heat given off or taken in by chemical or physical processes. c. Analyzing (both conceptually and quantitatively) flow of energy during change of state (phase). Teacher ...
... a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. b. Collect data and calculate the amount of heat given off or taken in by chemical or physical processes. c. Analyzing (both conceptually and quantitatively) flow of energy during change of state (phase). Teacher ...
Element - the simplest form of matter that can exist under normal
... Elements cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are the building blocks for all other substances There are now 117 known elements (as of 2006). All elements after uranium on the periodic table are man-made. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more differen ...
... Elements cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are the building blocks for all other substances There are now 117 known elements (as of 2006). All elements after uranium on the periodic table are man-made. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more differen ...
Headline Text 28 Point Color Text 2
... How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
... How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
2016-02 Chemical Depedency Rate Reform Project
... Chemical dependency rates reform project The 2009 Minnesota legislature directed the Alcohol and Drug Abuse Division (ADAD) to prepare for the 2011 legislature a statewide rate methodology for the Consolidated Chemical Treatment Fund (CCDTF). The methodology will replace county-negotiated rates with ...
... Chemical dependency rates reform project The 2009 Minnesota legislature directed the Alcohol and Drug Abuse Division (ADAD) to prepare for the 2011 legislature a statewide rate methodology for the Consolidated Chemical Treatment Fund (CCDTF). The methodology will replace county-negotiated rates with ...
Chemistry DCA Review Sheet
... 13. Label the following on the Periodic Table: periods, groups (families), metals, non-metals, metalloids, where protons and protons + neutrons can be found. ...
... 13. Label the following on the Periodic Table: periods, groups (families), metals, non-metals, metalloids, where protons and protons + neutrons can be found. ...
Slide 1
... • When one or more substances are changed into an new substance – Learn about chemical properties through chemical changes – Examples: ...
... • When one or more substances are changed into an new substance – Learn about chemical properties through chemical changes – Examples: ...
Chemical weapon

A chemical weapon (CW) is a munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on human beings. The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) states: The term chemical weapon may also be applied to any toxic chemical or its precursor that can cause death, injury, temporary incapacitation or sensory irritation through its chemical action. Munitions or other delivery devices designed to deliver chemical weapons, whether filled or unfilled, are also considered weapons themselves.They are classified as weapons of mass destruction (WMDs), though they are distinct from nuclear weapons, biological weapons (diseases), and radiological weapons (which use radioactive decay of elements). All may be used in warfare known by the military acronym NBC, for nuclear, biological, and chemical warfare. Weapons of mass destruction are distinct from conventional weapons, which are primarily effective due to their explosive, kinetic, or incendiary potential. Chemical weapons can be widely dispersed in gas, liquid and solid forms, and may easily afflict others than the intended targets. Nerve gas, tear gas and pepper spray are three modern examples.Lethal, unitary, chemical agents and munitions are extremely volatile and they constitute a class of hazardous chemical weapons that are now being stockpiled by many nations. (Unitary agents are effective on their own and require no mixing with other agents.) The most dangerous of these are nerve agents GA, GB, GD, and VX, and vesicant (blister) agents which are formulations of sulfur mustard such as H, HT, and HD. All are liquids at normal room temperature, but become gaseous when released. Widely used during the First World War, the effects of so-called mustard gas, phosgene gas and others caused lung searing, blindness, death and maiming.Pepper spray is of common use today. It is potentially lethal. There are no recent records of pepper spray being used in war, despite the fact that it inflicts fewer injuries and side-effects compared with impact and explosive weapons.Under the Chemical Weapons Convention (1993), there is a legally binding, world-wide ban on the production, stockpiling, and use of chemical weapons and their precursors. Notwithstanding, large stockpiles thereof continue to exist, usually justified as only a precaution against putative use by an aggressor.