Chapter #3
... There are N of the above equations, one for each element (atom type) in the reaction. Generally there are M coefficients to find using the N equations. Unfortunately, in most chemical equations, M > N. Usually, we have the case that M = N+1. Thus, we need to find one additional equation. One simple ...
... There are N of the above equations, one for each element (atom type) in the reaction. Generally there are M coefficients to find using the N equations. Unfortunately, in most chemical equations, M > N. Usually, we have the case that M = N+1. Thus, we need to find one additional equation. One simple ...
Matter Change
... Carbon – black, tasteless solid Oxygen – colorless, tasteless gas Hydrogen – colorless, tasteless gas ...
... Carbon – black, tasteless solid Oxygen – colorless, tasteless gas Hydrogen – colorless, tasteless gas ...
Balancing chemical equations notes
... Chemical equations can be viewed as recipes for chemical reactions. They give a description of what chemicals are combined together and what chemicals are made when a reaction occurs. The law of conservation of mass says that matter can neither be created nor destroyed, and this requires that all ch ...
... Chemical equations can be viewed as recipes for chemical reactions. They give a description of what chemicals are combined together and what chemicals are made when a reaction occurs. The law of conservation of mass says that matter can neither be created nor destroyed, and this requires that all ch ...
MATTER QUIZ: What to Study From: PHASE CHANGES
... Consists of elements from the periodic table. Is a pure substance Are combined physically Looks the same throughout Components can change in concentration or proportions Components are chemically combined. Are the following changes physical or chemical? (Mark P or C) 1. _______ Iodine reacts with st ...
... Consists of elements from the periodic table. Is a pure substance Are combined physically Looks the same throughout Components can change in concentration or proportions Components are chemically combined. Are the following changes physical or chemical? (Mark P or C) 1. _______ Iodine reacts with st ...
classification of chemical reactions
... Chemical change change in matter that produces new substances Example: rusting of iron burning of wood Physical change a change that does not produce a new substance a change in appearance or state Example: chopping wood ...
... Chemical change change in matter that produces new substances Example: rusting of iron burning of wood Physical change a change that does not produce a new substance a change in appearance or state Example: chopping wood ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... C. A mixture occurs when compounds can be separated by non-chemical means NO CHEMICAL BONDS FORM BETWEEN MOLECULES 1. Solution – translucent homogeneous mixture that does not settle out e.g. saltwater 2. Colloid – heterogeneous mixtures that appear milky 3. Suspensions – heterogeneous mixtures with ...
... C. A mixture occurs when compounds can be separated by non-chemical means NO CHEMICAL BONDS FORM BETWEEN MOLECULES 1. Solution – translucent homogeneous mixture that does not settle out e.g. saltwater 2. Colloid – heterogeneous mixtures that appear milky 3. Suspensions – heterogeneous mixtures with ...
Ch. 1-- Matter and Change
... They all take on the same qualities and for our purposes become one ...
... They all take on the same qualities and for our purposes become one ...
53 word equations
... the reactants come in front of the arrow the products come after the arrow ...
... the reactants come in front of the arrow the products come after the arrow ...
Reactive Materials - NC State University
... The reactivity of inorganic compounds may be frequently correlated with their “family” in the periodic table. Within a given family, similar types of behavior are observed with changes in the magnitude of reactivity varying consistently with atomic weight. The reactivity of chemical compounds shows ...
... The reactivity of inorganic compounds may be frequently correlated with their “family” in the periodic table. Within a given family, similar types of behavior are observed with changes in the magnitude of reactivity varying consistently with atomic weight. The reactivity of chemical compounds shows ...
Name__________________________________ Block______
... 2._____ a change during which one of the substances in a material changes into a different substance 3._____ can sometimes be a reversible change 4._____ a change that is not easily reversible 5._____ a melting ice cube 6._____ a broken piece of chalk 7._____ a burning cigarette 8._____ mixing sugar ...
... 2._____ a change during which one of the substances in a material changes into a different substance 3._____ can sometimes be a reversible change 4._____ a change that is not easily reversible 5._____ a melting ice cube 6._____ a broken piece of chalk 7._____ a burning cigarette 8._____ mixing sugar ...
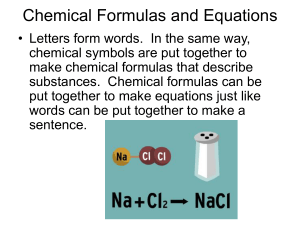
Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • A plus sign separates the formulas of two or more reactants or products ...
... • A plus sign separates the formulas of two or more reactants or products ...
Chapter 2 Introduction to Chemistry
... chemical reactions and to form new substances (i.e. flammability, rusting) – can only be observed during the change Chemical changes can’t be observed without altering the ...
... chemical reactions and to form new substances (i.e. flammability, rusting) – can only be observed during the change Chemical changes can’t be observed without altering the ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions
... Balancing Equations After you write a chemical equation you have to balance it to make sure that the same number of atoms of each element are on each side. How would you balance this equation? ...
... Balancing Equations After you write a chemical equation you have to balance it to make sure that the same number of atoms of each element are on each side. How would you balance this equation? ...
Balancing Equations
... the formulas of the reactants (on the left) are connected by an arrow with the formulas for the products (on the right). • Example: Reactants Products ...
... the formulas of the reactants (on the left) are connected by an arrow with the formulas for the products (on the right). • Example: Reactants Products ...
II. Classification of Matter
... Formulate a hypothesis (a testable if-then statement). The hypothesis serves as a basis for making predictions and for carrying out further experiments. Test your ______________________ – Requires experimentation that provides data to support or refute your hypothesis. ...
... Formulate a hypothesis (a testable if-then statement). The hypothesis serves as a basis for making predictions and for carrying out further experiments. Test your ______________________ – Requires experimentation that provides data to support or refute your hypothesis. ...
Docking
... Small Molecule/Ligand (Similarity) Predictive Methods (Kernel Methods) Why it is not hopeless ...
... Small Molecule/Ligand (Similarity) Predictive Methods (Kernel Methods) Why it is not hopeless ...
Discover Chemical Changes - gk-12
... I have listed above 9 possible chemical changes that can be used. Students should move from station to station and make observations in their journal of the chemical change: observations of how they know it’s a chemical change and the clue that tipped them off to why it was a chemical change and not ...
... I have listed above 9 possible chemical changes that can be used. Students should move from station to station and make observations in their journal of the chemical change: observations of how they know it’s a chemical change and the clue that tipped them off to why it was a chemical change and not ...
Physical and Chemical Changes
... For Example.... Add 3ml of the sodium iodate solution (solution A) to a test tube. Add 3ml of the sodium sulfate, citric acid and starch solution (solution B) to the test tube. Swirl the test tube around. ...
... For Example.... Add 3ml of the sodium iodate solution (solution A) to a test tube. Add 3ml of the sodium sulfate, citric acid and starch solution (solution B) to the test tube. Swirl the test tube around. ...
SNC2D – Science 10 Tuesday April 26th, 2010 Mr. Sourlis and Mr
... 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactants c. Equal to the total mass of the reactants d. Dependent on the type of reaction e. Impossible to determine 4. What is anothe ...
... 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactants c. Equal to the total mass of the reactants d. Dependent on the type of reaction e. Impossible to determine 4. What is anothe ...
SCIENCE 9
... has its own distinct properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change. COMPOUNDS- are pure substances that are made up of two or more elements chemically combined together. Compounds can be broken down into elements again by chemical means ...
... has its own distinct properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change. COMPOUNDS- are pure substances that are made up of two or more elements chemically combined together. Compounds can be broken down into elements again by chemical means ...
MSDS-U-200-B-ANG
... Clear amber liquid; characteristic amine odour. Can be pigmented, coloured. ...
... Clear amber liquid; characteristic amine odour. Can be pigmented, coloured. ...
Chemical Principles – by Steven Zumdahl (5 ) Chapter 1
... Substance is a material that cannot be separated by physical means into two or more materials. (with different properties) Elements are substances that cannot be decomposed by chemical reactions. Elements (atoms) are the simplest forms of matter (in chemistry). Each element is represented by a symbo ...
... Substance is a material that cannot be separated by physical means into two or more materials. (with different properties) Elements are substances that cannot be decomposed by chemical reactions. Elements (atoms) are the simplest forms of matter (in chemistry). Each element is represented by a symbo ...
Chemical weapon

A chemical weapon (CW) is a munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on human beings. The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) states: The term chemical weapon may also be applied to any toxic chemical or its precursor that can cause death, injury, temporary incapacitation or sensory irritation through its chemical action. Munitions or other delivery devices designed to deliver chemical weapons, whether filled or unfilled, are also considered weapons themselves.They are classified as weapons of mass destruction (WMDs), though they are distinct from nuclear weapons, biological weapons (diseases), and radiological weapons (which use radioactive decay of elements). All may be used in warfare known by the military acronym NBC, for nuclear, biological, and chemical warfare. Weapons of mass destruction are distinct from conventional weapons, which are primarily effective due to their explosive, kinetic, or incendiary potential. Chemical weapons can be widely dispersed in gas, liquid and solid forms, and may easily afflict others than the intended targets. Nerve gas, tear gas and pepper spray are three modern examples.Lethal, unitary, chemical agents and munitions are extremely volatile and they constitute a class of hazardous chemical weapons that are now being stockpiled by many nations. (Unitary agents are effective on their own and require no mixing with other agents.) The most dangerous of these are nerve agents GA, GB, GD, and VX, and vesicant (blister) agents which are formulations of sulfur mustard such as H, HT, and HD. All are liquids at normal room temperature, but become gaseous when released. Widely used during the First World War, the effects of so-called mustard gas, phosgene gas and others caused lung searing, blindness, death and maiming.Pepper spray is of common use today. It is potentially lethal. There are no recent records of pepper spray being used in war, despite the fact that it inflicts fewer injuries and side-effects compared with impact and explosive weapons.Under the Chemical Weapons Convention (1993), there is a legally binding, world-wide ban on the production, stockpiling, and use of chemical weapons and their precursors. Notwithstanding, large stockpiles thereof continue to exist, usually justified as only a precaution against putative use by an aggressor.