Directory - Humble ISD
... of the Declaration of the Rights of Man. Fearful that the nobles were recruiting criminals to terrorize them, the peasants banded together to destroy manor homes and feudal contracts. In the late hours of August 4 and the early hours of August 5, 1789, the National Assembly voted to abolish seigneur ...
... of the Declaration of the Rights of Man. Fearful that the nobles were recruiting criminals to terrorize them, the peasants banded together to destroy manor homes and feudal contracts. In the late hours of August 4 and the early hours of August 5, 1789, the National Assembly voted to abolish seigneur ...
Ch.9 The French Revolution and the Rise of Napoleon
... “We must suspend free speech and liberty so we can win the war. Otherwise, there will be nothing left to defend” “We must preserve the ideals of free speech and liberty at all costs. Otherwise the Revolution is not worth fighting for” ...
... “We must suspend free speech and liberty so we can win the war. Otherwise, there will be nothing left to defend” “We must preserve the ideals of free speech and liberty at all costs. Otherwise the Revolution is not worth fighting for” ...
review sheet for french revolution/napoleon/industrial revolution test
... NATIONAL CONVENTION – renamed from the National Assembly GUILLOTINE - France’s tool of execution; chopped off peoples’ heads including Louis XVI and Robespierre ...
... NATIONAL CONVENTION – renamed from the National Assembly GUILLOTINE - France’s tool of execution; chopped off peoples’ heads including Louis XVI and Robespierre ...
THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
... States basic principles of the Revolution – “liberty, equality, fraternity (brotherhood)”Did not extend to women Olympe de Gouges wrote a declaration of rights for women, she is later beheaded Women’s march to Versailles Louis remains at Versailles, refusing to accept the Declaration and the abol ...
... States basic principles of the Revolution – “liberty, equality, fraternity (brotherhood)”Did not extend to women Olympe de Gouges wrote a declaration of rights for women, she is later beheaded Women’s march to Versailles Louis remains at Versailles, refusing to accept the Declaration and the abol ...
Chapter 18 and 20-Political Revolutions
... 6. The Enlightenment – Ideas from this time period made French revolutionists think for themselves as opposed to trusting the authority of the monarchy and the Church. 7. Meeting of the Estates General – a general assembly meeting consisting of representatives from all three French estates. 8. Marie ...
... 6. The Enlightenment – Ideas from this time period made French revolutionists think for themselves as opposed to trusting the authority of the monarchy and the Church. 7. Meeting of the Estates General – a general assembly meeting consisting of representatives from all three French estates. 8. Marie ...
french revolution
... – Each estate would get one vote. (traditional) – 1st and 2nd Estate could outvote the 3rd ...
... – Each estate would get one vote. (traditional) – 1st and 2nd Estate could outvote the 3rd ...
mr. mounce - cloudfront.net
... Paris, where he reluctantly accepted the limited monarchy. French emigres tried to convince leaders of foreign governments that their own rule would be threatened unless they halted the revolution in France. French revolutionary leaders, fearing that Austria would try to reinstate Louis, declared wa ...
... Paris, where he reluctantly accepted the limited monarchy. French emigres tried to convince leaders of foreign governments that their own rule would be threatened unless they halted the revolution in France. French revolutionary leaders, fearing that Austria would try to reinstate Louis, declared wa ...
Unit 5: French Revolution
... France with the idea of Enlightment by its side. The National Assembly achieved a government based on enlightened ideals through their establishment of the Declaration of the Rights of Man, with its proclamations of men being born with equal rights with the government existing to protect those right ...
... France with the idea of Enlightment by its side. The National Assembly achieved a government based on enlightened ideals through their establishment of the Declaration of the Rights of Man, with its proclamations of men being born with equal rights with the government existing to protect those right ...
From Radical to Violent - Northside Middle School
... from the beginning but took control in 1792 Led the revolution during the “radical” period Chairman of the Committee of Public Safety Favored radical ideas from the Enlightenment Elimination of Religion Elimination of the Monarchy Favored democracy… Elimination of the Nobility ...
... from the beginning but took control in 1792 Led the revolution during the “radical” period Chairman of the Committee of Public Safety Favored radical ideas from the Enlightenment Elimination of Religion Elimination of the Monarchy Favored democracy… Elimination of the Nobility ...
French Revolution PPT
... -Robespierre is killed by the guillotine on July 28, 1794. -The National Convention is now controlled by a more moderate group and in 1795 another constitution is drafted creating a bicameral legislature and an executive body called the Directory. ...
... -Robespierre is killed by the guillotine on July 28, 1794. -The National Convention is now controlled by a more moderate group and in 1795 another constitution is drafted creating a bicameral legislature and an executive body called the Directory. ...
French Revolution Part 2 Reform, Radicals, and
... Anyone suspected of being an enemy of the Revolution was guillotine Even others that questioned Robespierre’s leadership were killed Thousands of Parisians were killed. 40,000 were killed through out the country ...
... Anyone suspected of being an enemy of the Revolution was guillotine Even others that questioned Robespierre’s leadership were killed Thousands of Parisians were killed. 40,000 were killed through out the country ...
C1 Overview of KI3
... Hoarders rooted out and punished. Food supplies would be secured by the army! ...
... Hoarders rooted out and punished. Food supplies would be secured by the army! ...
FrenchRevolution-2
... Brunswick Manifesto. The manifesto promised that if the French Royal family was not harmed, then the Allies would not harm French civilians or loot. However, if acts of violence or acts to humiliate the French Royal family were committed, the Allies threatened not only that they would take vengeance ...
... Brunswick Manifesto. The manifesto promised that if the French Royal family was not harmed, then the Allies would not harm French civilians or loot. However, if acts of violence or acts to humiliate the French Royal family were committed, the Allies threatened not only that they would take vengeance ...
The Reign of Terror
... the government. Members of the Committee, led by Maximilien Robespierre, took wartime control of the country. Robespierre ruled with the power of a dictator. Robespierre had just one goal in mind - to win the war. He believed that there was only one way to do that. He put it bluntly: "Liberty cannot ...
... the government. Members of the Committee, led by Maximilien Robespierre, took wartime control of the country. Robespierre ruled with the power of a dictator. Robespierre had just one goal in mind - to win the war. He believed that there was only one way to do that. He put it bluntly: "Liberty cannot ...
WC 3-3 - TeacherWeb
... that the blood about to be spilt will never fall upon the head of France…” ...
... that the blood about to be spilt will never fall upon the head of France…” ...
French Revolution
... power struggle in govt. • Maximilien Robespierre gains power & establish the republic of virtue • Wipes out all trace of monarchy and church ...
... power struggle in govt. • Maximilien Robespierre gains power & establish the republic of virtue • Wipes out all trace of monarchy and church ...
1793Louis XV Square was renamed the Square of the Revolution
... inflation. The Convention itself was bitterly divided between Jacobins and a rival group, the Girondins.Committee of Public Safety To deal with the threats to France, the Convention created the Committee of Public Safety. The 12-member committee had almost absolute power as it battled to save the re ...
... inflation. The Convention itself was bitterly divided between Jacobins and a rival group, the Girondins.Committee of Public Safety To deal with the threats to France, the Convention created the Committee of Public Safety. The 12-member committee had almost absolute power as it battled to save the re ...
chapter 3 section 3 notes
... -Government batled counterrevolutionaries under the hand of Maximilien Robespierre (a shrewd lawyer and politician) - leadership of the Committee of Public Safety -his dedication to the revolution gave him the nickname "the incorruptible", enemies called him a tyrant -embraced Rousseau's idea of gen ...
... -Government batled counterrevolutionaries under the hand of Maximilien Robespierre (a shrewd lawyer and politician) - leadership of the Committee of Public Safety -his dedication to the revolution gave him the nickname "the incorruptible", enemies called him a tyrant -embraced Rousseau's idea of gen ...
French Revolution
... War with Austria and Great Britain continued ; peace was made with Prussia and Spain Rising bread prices caused the sans-culottes to riot Some emigres threatened the power of the Directory because they favored a return of the former monarchy The emigres who fled previously supported the monarchy and ...
... War with Austria and Great Britain continued ; peace was made with Prussia and Spain Rising bread prices caused the sans-culottes to riot Some emigres threatened the power of the Directory because they favored a return of the former monarchy The emigres who fled previously supported the monarchy and ...
VIVE FRANCE!
... about: – No absolute rulers – No privilege (sorry, rich people) – Liberty – Political equality – Signed by Louis XVI on Oct. 5, 1791 ...
... about: – No absolute rulers – No privilege (sorry, rich people) – Liberty – Political equality – Signed by Louis XVI on Oct. 5, 1791 ...
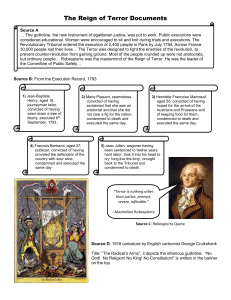
The Reign of Terror Documents Source A … The guillotine, the new
... The Reign of Terror Documents Source A … The guillotine, the new instrument of egalitarian justice, was put to work. Public executions were considered educational. Women were encouraged to sit and knit during trials and executions. The Revolutionary Tribunal ordered the execution of 2,400 people in ...
... The Reign of Terror Documents Source A … The guillotine, the new instrument of egalitarian justice, was put to work. Public executions were considered educational. Women were encouraged to sit and knit during trials and executions. The Revolutionary Tribunal ordered the execution of 2,400 people in ...
Enlightenment and French Revolution
... Factions split revolutionaries ◦ Radicals/Left: get rid of king, redo government ◦ Moderates/Center: wanted some changes in government ◦ Conservatives/Right: wanted to keep a limited monarchy with few changes in government ...
... Factions split revolutionaries ◦ Radicals/Left: get rid of king, redo government ◦ Moderates/Center: wanted some changes in government ◦ Conservatives/Right: wanted to keep a limited monarchy with few changes in government ...
Reign of Terror

The Reign of Terror (5 September 1793 – 28 July 1794), also known as The Terror (French: la Terreur), was a period of violence that occurred after the onset of the French Revolution, incited by conflict between two rival political factions, the Girondins and the Jacobins, and marked by mass executions of ""enemies of the revolution"". The death toll ranged in the tens of thousands, with 16,594 executed by guillotine (2,639 in Paris), and another 25,000 in summary executions across France.The guillotine (called the ""National Razor"") became the symbol of the revolutionary cause, strengthened by a string of executions: King Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette, the Girondins, Philippe Égalité (Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans), and Madame Roland, and others such as pioneering chemist Antoine Lavoisier, lost their lives under its blade. During 1794, revolutionary France was beset with conspiracies by internal and foreign enemies. Within France, the revolution was opposed by the French nobility, which had lost its inherited privileges. The Roman Catholic Church opposed the revolution, which had turned the clergy into employees of the state and required they take an oath of loyalty to the nation (through the Civil Constitution of the Clergy). In addition, the French First Republic was engaged in a series of wars with neighboring powers, and parts of France were engaging in civil war against the republican regime.The extension of civil war and the advance of foreign armies on national territory produced a political crisis and increased the already present rivalry between the Girondins and the more radical Jacobins. The latter were eventually grouped in the parliamentary faction called the Mountain, and they had the support of the Parisian population. The French government established the Committee of Public Safety, which took its final form on 6 September 1793, in order to suppress internal counter-revolutionary activities and raise additional French military forces.Through the Revolutionary Tribunal, the Terror's leaders exercised broad powers and used them to eliminate the internal and external enemies of the republic. The repression accelerated in June and July 1794, a period called la Grande Terreur (the Great Terror), and ended in the coup of 9 Thermidor Year II (27 July 1794), leading to the Thermidorian Reaction, in which several instigators of the Reign of Terror were executed, including Saint-Just and Robespierre.