Document
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Document
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Atoms, Electrons and Periodicity test - A
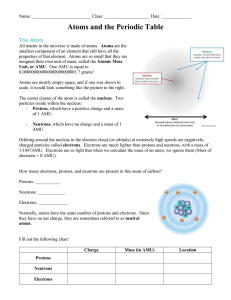
... Carbon is in the p-block of the Periodic Table. Naturally occurring carbon contains a mixture of two isotopes, 12C and 13C. Complete the table below for the atomic structure of the isotopes 12C and 13C. ...
... Carbon is in the p-block of the Periodic Table. Naturally occurring carbon contains a mixture of two isotopes, 12C and 13C. Complete the table below for the atomic structure of the isotopes 12C and 13C. ...
I. Atoms are the smallest forms
... Group 2 loses two electrons to become +2 ions Group 18 do not form ions at all Group 17 gain an electron to become negative ions Group 16 can gain 2 electrons to become -2 ions Groups 3 to 12 all form positive ions but the charge can ...
... Group 2 loses two electrons to become +2 ions Group 18 do not form ions at all Group 17 gain an electron to become negative ions Group 16 can gain 2 electrons to become -2 ions Groups 3 to 12 all form positive ions but the charge can ...
Atomic Structure and the Elements
... The largest number (with decimal) is the Atomic Mass # and is the weight of the atom and how many (+) and (n) are in the nucleus The smaller number (no decimal) is the Atomic # and is the number of (+) or (-). REMEMBER the number of (+) and (-) should always be ...
... The largest number (with decimal) is the Atomic Mass # and is the weight of the atom and how many (+) and (n) are in the nucleus The smaller number (no decimal) is the Atomic # and is the number of (+) or (-). REMEMBER the number of (+) and (-) should always be ...
Atomic Number
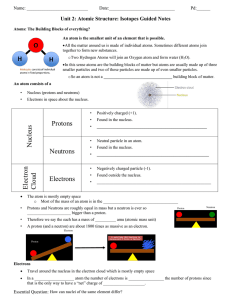
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 8.5 (B) Identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
... charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 8.5 (B) Identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... So why is Mendeleev called the “father of the modern periodic table” and not Meyer, or both? ...
... So why is Mendeleev called the “father of the modern periodic table” and not Meyer, or both? ...
Structure of Atoms
... 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). Most of the remaining 1% of carbon atoms have 7 neutrons (13C) while the rarest carbon isotope, with 8 neutrons, is 14C. Both 12C and 13C are stable isotopes while 14C is radioactive When 14C decays, one of its neutrons is converted to a proton and an ...
... 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). Most of the remaining 1% of carbon atoms have 7 neutrons (13C) while the rarest carbon isotope, with 8 neutrons, is 14C. Both 12C and 13C are stable isotopes while 14C is radioactive When 14C decays, one of its neutrons is converted to a proton and an ...
Chemical Element
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element (that is, with the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus), but having different numbers of neutrons. Most naturally-occurring elements have more than one isotope. Thus, for example, there are three main isotopes of carbon. All carbon atoms have 6 proto ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element (that is, with the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus), but having different numbers of neutrons. Most naturally-occurring elements have more than one isotope. Thus, for example, there are three main isotopes of carbon. All carbon atoms have 6 proto ...
File
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
gp - fc2009goran
... because it is radioactive, its presence can be detected. Iodine 131 thus became one of the earliest radioactive ...
... because it is radioactive, its presence can be detected. Iodine 131 thus became one of the earliest radioactive ...
Ch 17 Properties of Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... The organization of elements by their properties is the periodic table. Each small square on the periodic table shows the name of one element and the letter symbol for that element. The elements are arranged based on the number of protons an atom of that element has in its nucleus. Periodic la ...
... The organization of elements by their properties is the periodic table. Each small square on the periodic table shows the name of one element and the letter symbol for that element. The elements are arranged based on the number of protons an atom of that element has in its nucleus. Periodic la ...
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... Protons and Neutrons are roughly equal in mass but a neutron is ever so _____________________ bigger than a proton. ...
... Protons and Neutrons are roughly equal in mass but a neutron is ever so _____________________ bigger than a proton. ...
File
... amu). Based upon the average atomic mass of carbon (12.011 amu), which isotope of carbon do you think is the most abundant in nature? Explain your answer. An element has two naturally occurring isotopes. The mass of the first isotope is 64.9278 amu and the mass of the second isotope is 62.9296 amu. ...
... amu). Based upon the average atomic mass of carbon (12.011 amu), which isotope of carbon do you think is the most abundant in nature? Explain your answer. An element has two naturally occurring isotopes. The mass of the first isotope is 64.9278 amu and the mass of the second isotope is 62.9296 amu. ...
File - Cynthia Campbell
... Ninety-four are found naturally on Earth, and the rest are synthetic elements that have been produced artificially in particle accelerators. Elements 43 (technetium), 61 (promethium) and all elements greater than 83 (bismuth), beginning with 84 (polonium) have no stable isotopes. The atomic mass of ...
... Ninety-four are found naturally on Earth, and the rest are synthetic elements that have been produced artificially in particle accelerators. Elements 43 (technetium), 61 (promethium) and all elements greater than 83 (bismuth), beginning with 84 (polonium) have no stable isotopes. The atomic mass of ...
Atomic masses are weighted averages.
... What we know now of Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms are not indivisible – they are made of subatomic particles 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element ...
... What we know now of Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms are not indivisible – they are made of subatomic particles 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element ...
Chapter 17 - murraysphysical
... Unit of measurement of atomic particles is atomic mass unit. Atomic Number- the number of protons in an atom; number of protons also identifies the element. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is the mass number. ...
... Unit of measurement of atomic particles is atomic mass unit. Atomic Number- the number of protons in an atom; number of protons also identifies the element. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is the mass number. ...
Atom - Images
... • Step 1: Multiply the AMU for a single isotope by the % found in nature. • Cu 63 – AMU of 63 = 62.93 AMU; so 62.93 x 69.15% (nature) = 62.93 x .6915 = 43.52 AMU • Cu 65 – AMU of 65 = 64.93AMU; so 64.93 x 30.85% (nature) = 64.93 x .3085 = 20.03 AMU • Step 2: Add the all AMUs together. ...
... • Step 1: Multiply the AMU for a single isotope by the % found in nature. • Cu 63 – AMU of 63 = 62.93 AMU; so 62.93 x 69.15% (nature) = 62.93 x .6915 = 43.52 AMU • Cu 65 – AMU of 65 = 64.93AMU; so 64.93 x 30.85% (nature) = 64.93 x .3085 = 20.03 AMU • Step 2: Add the all AMUs together. ...
Masses of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
In 1869, Russia`s Dmitri Mendeleev and Germany`s Lothar Meyer
... are needed t o s ee thi s pi c ture. ...
... are needed t o s ee thi s pi c ture. ...