
EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
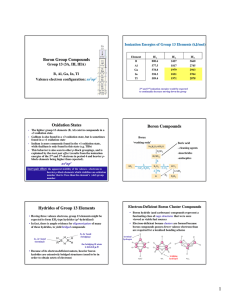
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • The name used to identify these electron-deficient cluster compounds involves several components. The proper name • indicates its shape (relative to a reference shape) • indicates the number of boron and hydrogen atoms • indicates the charge on anions ...
... • The name used to identify these electron-deficient cluster compounds involves several components. The proper name • indicates its shape (relative to a reference shape) • indicates the number of boron and hydrogen atoms • indicates the charge on anions ...
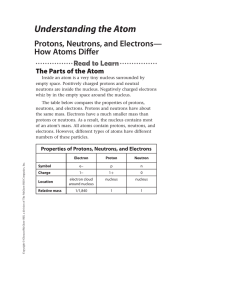
18 Chapter 2: The Atom An atom is the smallest particle of an element
... Proton – (symbol p+) a tiny subatomic particle having a positive electric charge, located in the center of the atom (nucleus). The electron and proton have equal sized, but opposite polarity, electric ...
... Proton – (symbol p+) a tiny subatomic particle having a positive electric charge, located in the center of the atom (nucleus). The electron and proton have equal sized, but opposite polarity, electric ...
Distinguishing Among Atoms Worksheet
... Each element has a unique atomic number, which is the number of protons the atom contains. Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. The number of neutrons in an atom can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. Isotopes Most elements contain se ...
... Each element has a unique atomic number, which is the number of protons the atom contains. Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. The number of neutrons in an atom can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. Isotopes Most elements contain se ...
Understanding the Atom
... Protons, Neutrons, and Mass Number The mass number of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. This is shown in the following equation. ...
... Protons, Neutrons, and Mass Number The mass number of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. This is shown in the following equation. ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Note Packet for Students
... To the casual observer, all pennies that you use seem to be identical in size, thickness, and composition. But just as elements have one or more isotopes with different masses, the pennies in circulation have different masses. In this investigation, you are going to use pennies with different masses ...
... To the casual observer, all pennies that you use seem to be identical in size, thickness, and composition. But just as elements have one or more isotopes with different masses, the pennies in circulation have different masses. In this investigation, you are going to use pennies with different masses ...
IT IS ELEMENTARY - the OLLI at UCI Blog
... and animal origin • These elements or their very simple compounds can kill—most commonly by interfering with cellular access to oxygen • Nitrogen N2 • Carbon dioxide CO2 • Carbon monoxide CO • Hydrogen cyanide HCN ...
... and animal origin • These elements or their very simple compounds can kill—most commonly by interfering with cellular access to oxygen • Nitrogen N2 • Carbon dioxide CO2 • Carbon monoxide CO • Hydrogen cyanide HCN ...
The atom: Isotopes (Grade 10) [NCS]
... elements as X-A where the X is the element symbol and the A is the atomic mass of that element. ...
... elements as X-A where the X is the element symbol and the A is the atomic mass of that element. ...
8b Isotopes and Ions2
... Ca atom has a mass of 40. (atomic # or #of P+’s = 20) The isotopes for Ca have masses of 42,43,44,46, & 48. To find the number of neutrons you subtract the atomic number from the mass number. 1.) How many neutrons are in a Ca atom and each of its isotopes? Number of Neutrons in each isotope: Ca40: 4 ...
... Ca atom has a mass of 40. (atomic # or #of P+’s = 20) The isotopes for Ca have masses of 42,43,44,46, & 48. To find the number of neutrons you subtract the atomic number from the mass number. 1.) How many neutrons are in a Ca atom and each of its isotopes? Number of Neutrons in each isotope: Ca40: 4 ...
Agenda/To Do - Perry Local Schools
... 1. Show and Tell-- Atom Models 2. Check homework/table 3. Periodic Table Notes 4. Periodic Table Basics (homework) 5. Atom Study Guide 6. Element Quiz-- FRIDAY! You will need to be able to identify the name or symbol for the elements in the following groups: ...
... 1. Show and Tell-- Atom Models 2. Check homework/table 3. Periodic Table Notes 4. Periodic Table Basics (homework) 5. Atom Study Guide 6. Element Quiz-- FRIDAY! You will need to be able to identify the name or symbol for the elements in the following groups: ...
Atomic Structure
... Atomic Mass. Step 1: Write out the mass number and % abundance as a multiplication problem with a ...
... Atomic Mass. Step 1: Write out the mass number and % abundance as a multiplication problem with a ...
Mystery Isotopes
... Teacher will monitor and prompt groups as needed. They will also check isotope models created before the exchange. ...
... Teacher will monitor and prompt groups as needed. They will also check isotope models created before the exchange. ...
Chemistry Unit 2 - Finding Patterns
... determines the atom’s identity. Average atomic mass reflects the relative abundance of these isotopes. The periodic table, arranged by atomic number, reveals a tendency for properties to repeat in a periodic pattern (periodicity), and can be used to predict the properties and uses of an element. The ...
... determines the atom’s identity. Average atomic mass reflects the relative abundance of these isotopes. The periodic table, arranged by atomic number, reveals a tendency for properties to repeat in a periodic pattern (periodicity), and can be used to predict the properties and uses of an element. The ...
CMC Chapter 04
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Chapter 4 power point notes
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
ch 4 ppt - Madison County Schools
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Chapter 4 PPT
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Vocabulary Review
... f. tiny bits of matter that are the building blocks of an atom Set Two----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. _____group of elements a. atoms of the same element which have different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus 2. _____perio ...
... f. tiny bits of matter that are the building blocks of an atom Set Two----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. _____group of elements a. atoms of the same element which have different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus 2. _____perio ...
ISN III: Building Atoms and Organizing Matter
... As of today, there are 117 known elements. Opinions differ, but about 93 occur naturally on earth (including technetium and plutonium), and 94 (including promethium) have been detected so far in the universe. The other elements not found on earth are made artificially; the first claim of a synthesiz ...
... As of today, there are 117 known elements. Opinions differ, but about 93 occur naturally on earth (including technetium and plutonium), and 94 (including promethium) have been detected so far in the universe. The other elements not found on earth are made artificially; the first claim of a synthesiz ...
C. - Taylor County Schools
... radioactive decay. • Atoms that contain too many or too few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. ...
... radioactive decay. • Atoms that contain too many or too few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. ...
Activity 2 - SSS Chemistry
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 18 Comparing Atoms Lab
... many marbles, and of as many colors as they need but must take at least as many total marbles as they put in. For example, a player can trade 2 yellows for 1 yellow, 1 blue, and 1 red. 11. Which particles are found in an atom’s nucleus? Which particles are found outside the nucleus? 12. What four el ...
... many marbles, and of as many colors as they need but must take at least as many total marbles as they put in. For example, a player can trade 2 yellows for 1 yellow, 1 blue, and 1 red. 11. Which particles are found in an atom’s nucleus? Which particles are found outside the nucleus? 12. What four el ...






![The atom: Isotopes (Grade 10) [NCS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016109524_1-1437871a54cd24e5ee13c27e98f0719d-300x300.png)














