hormones
... The hormones that guide reproductive processes come from the anterior pituitary and the gonads. During pregnancy, the placenta also makes hormones. The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetical ...
... The hormones that guide reproductive processes come from the anterior pituitary and the gonads. During pregnancy, the placenta also makes hormones. The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetical ...
Typical disorders of the endocrine system 1. Choose the correct
... 20. The development of diabetes insipidus is caused by a) the hypersecretion of vasopressin; + b) hyposecretion of vasopressin; c) aldosterone hypersecretion; d) hyposecretion of aldosterone; e) presence in blood insulin antagonists. 21. Damage of neurohypophysis is accompanied by impaired secretion ...
... 20. The development of diabetes insipidus is caused by a) the hypersecretion of vasopressin; + b) hyposecretion of vasopressin; c) aldosterone hypersecretion; d) hyposecretion of aldosterone; e) presence in blood insulin antagonists. 21. Damage of neurohypophysis is accompanied by impaired secretion ...
Anatomy of the pituitary gland
... Anatomy of the pituitary gland The pituitary gland is sometimes called the "master" gland of the endocrine system, because it controls the functions of the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypot ...
... Anatomy of the pituitary gland The pituitary gland is sometimes called the "master" gland of the endocrine system, because it controls the functions of the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypot ...
Endocrinology
... a) --- Alfa cells: which is secreted hormone (insulin). b) --- Beta cells: which is secreted glucogon. 7. Testes: they are two which produce male sex hormones or androgens. 8. Ovary: there are two ovaries produce female sex hormones which they are two types: a) Estrogen: secreted from the theca inte ...
... a) --- Alfa cells: which is secreted hormone (insulin). b) --- Beta cells: which is secreted glucogon. 7. Testes: they are two which produce male sex hormones or androgens. 8. Ovary: there are two ovaries produce female sex hormones which they are two types: a) Estrogen: secreted from the theca inte ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... Give two examples of hormones that are secreted in inactive forms, and are converted to the active form in the target tissue. Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond to each and every hormone? What is up-regulation, and what conditions lead to this ...
... Give two examples of hormones that are secreted in inactive forms, and are converted to the active form in the target tissue. Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond to each and every hormone? What is up-regulation, and what conditions lead to this ...
Endocrine System
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
Endocrine System
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
Assessing endocrine function
... The grey shaded area shows the range of responses measured in control subjects In hypopituitarism there is no response ...
... The grey shaded area shows the range of responses measured in control subjects In hypopituitarism there is no response ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation Causes ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
... Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation Causes ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
Endocrine System booklet
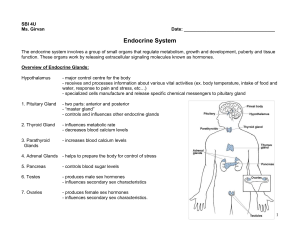
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
Endocrine System
... – Promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system – Required for sperm cell production ...
... – Promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system – Required for sperm cell production ...
02. Role of the central nervous system and endocrine glands
... luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. 3. GnRH also stimulates the release of LH from the anterior pituitary. 4. LH causes the release of additional estrogen from the ovary. The GnRH and LH levels in the blood increase because of this positive-feedback effect. ...
... luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. 3. GnRH also stimulates the release of LH from the anterior pituitary. 4. LH causes the release of additional estrogen from the ovary. The GnRH and LH levels in the blood increase because of this positive-feedback effect. ...
Cetrotide® 0.25 mg (cetrorelix acetate for injection)
... thus controls the release of LH and FSH in a dose-dependent manner. The onset of LH suppression is approximately one hour with the 3 mg dose and two hours with the 0.25 mg dose. This suppression is maintained by continuous treatment and there is a more pronounced effect on LH than on FSH. An initial ...
... thus controls the release of LH and FSH in a dose-dependent manner. The onset of LH suppression is approximately one hour with the 3 mg dose and two hours with the 0.25 mg dose. This suppression is maintained by continuous treatment and there is a more pronounced effect on LH than on FSH. An initial ...
Cetrotide® 0.25 mg
... thus controls the release of LH and FSH in a dose-dependent manner. The onset of LH suppression is approximately one hour with the 3 mg dose and two hours with the 0.25 mg dose. This suppression is maintained by continuous treatment and there is a more pronounced effect on LH than on FSH. An initial ...
... thus controls the release of LH and FSH in a dose-dependent manner. The onset of LH suppression is approximately one hour with the 3 mg dose and two hours with the 0.25 mg dose. This suppression is maintained by continuous treatment and there is a more pronounced effect on LH than on FSH. An initial ...
Cetrotide® 0.25 mg (cetrorelix acetate for injection) FOR
... thus controls the release of LH and FSH in a dose-dependent manner. The onset of LH suppression is approximately one hour with the 3 mg dose and two hours with the 0.25 mg dose. This suppression is maintained by continuous treatment and there is a more pronounced effect on LH than on FSH. An initial ...
... thus controls the release of LH and FSH in a dose-dependent manner. The onset of LH suppression is approximately one hour with the 3 mg dose and two hours with the 0.25 mg dose. This suppression is maintained by continuous treatment and there is a more pronounced effect on LH than on FSH. An initial ...
The Endocrine System
... Regulated by hormonal stimuli, mostly negative feedback Growth hormone General metabolic hormone Major effects are directed to growth of skeletal muscles and long bones Plays a role in determining final body size Causes amino acids to be built into proteins Causes fats to be broken down for a source ...
... Regulated by hormonal stimuli, mostly negative feedback Growth hormone General metabolic hormone Major effects are directed to growth of skeletal muscles and long bones Plays a role in determining final body size Causes amino acids to be built into proteins Causes fats to be broken down for a source ...
Hypothalamus - pituitary
... • suckling (stimulation of touch receptors in breast) • distension of uterus • pain 4. Neuroendocrine reflexes can be modified by emotional responses, stress, and other factors. 5. The target organs for pituitary hormones usually influence hormone release by negative feedback control. 6. Sometimes t ...
... • suckling (stimulation of touch receptors in breast) • distension of uterus • pain 4. Neuroendocrine reflexes can be modified by emotional responses, stress, and other factors. 5. The target organs for pituitary hormones usually influence hormone release by negative feedback control. 6. Sometimes t ...
Function of hypothalamo - pituitary
... suckling (stimulation of touch receptors in breast) distension of uterus pain 4. Neuroendocrine reflexes can be modified by emotional responses, stress, and other factors. 5. The target organs for pituitary hormones usually influence hormone release by negative feedback control. 6. Sometimes t ...
... suckling (stimulation of touch receptors in breast) distension of uterus pain 4. Neuroendocrine reflexes can be modified by emotional responses, stress, and other factors. 5. The target organs for pituitary hormones usually influence hormone release by negative feedback control. 6. Sometimes t ...
Endocrine System - Practicum-Health-II-2011-2012
... • In a woman, the breasts enlarge and fatty tissue is deposited around the hips • In both men and women height and weight increase ...
... • In a woman, the breasts enlarge and fatty tissue is deposited around the hips • In both men and women height and weight increase ...
File
... characteristics and sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in ...
... characteristics and sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in ...
Endocrine System
... • It is a “duct” less system. It gets secreted then heads directly to the blood stream. ...
... • It is a “duct” less system. It gets secreted then heads directly to the blood stream. ...
Endocrine System Endocrine System: Overview Types of Hormones
... Internal and external factors such as fever, hypoglycemia, and stressors can trigger the release of CRH ...
... Internal and external factors such as fever, hypoglycemia, and stressors can trigger the release of CRH ...