PPT14Chapter14TheEndocrineSystemPartI
... causes the glucose to move from the blood to the cell. As glucose enters the cells, blood glucose levels decrease. The information is fed back to the gland so it will decrease the insulin secretion. ...
... causes the glucose to move from the blood to the cell. As glucose enters the cells, blood glucose levels decrease. The information is fed back to the gland so it will decrease the insulin secretion. ...
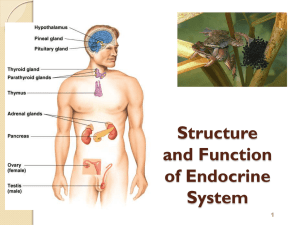
The Endocrine System
... 444. Sperm cells ___. A. start to migrate towards uterus immediately after being ejaculated into vagina B. are not able to fertilize an egg without capacitation C. can all find the egg ...
... 444. Sperm cells ___. A. start to migrate towards uterus immediately after being ejaculated into vagina B. are not able to fertilize an egg without capacitation C. can all find the egg ...
Medications available and illustrations Duration Starting dose Dose titration as per product
... Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic response vary from individual to individual. The clinician must use clinical judgement as to the duration of efficacy and not solely rely on reported values for PK and duration of effect. ...
... Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic response vary from individual to individual. The clinician must use clinical judgement as to the duration of efficacy and not solely rely on reported values for PK and duration of effect. ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
test review key - Hartland High School
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
ZUCLOPENTHIXOL tab, drops , amp: Class: Typical antipsychotic
... -Acute psychosis: Initial: 10-50 mg/day in 2-3 divided doses; may titrate dose upward by 10-20 mg every 2-3 days; usual dosage range: 20-60 mg/day; maximum dose: 100 mg/day -Maintenance therapy: Maintain lowest effective dose; usual maintenance dose: 20-40 mg/day; may be given as a single dose -Acut ...
... -Acute psychosis: Initial: 10-50 mg/day in 2-3 divided doses; may titrate dose upward by 10-20 mg every 2-3 days; usual dosage range: 20-60 mg/day; maximum dose: 100 mg/day -Maintenance therapy: Maintain lowest effective dose; usual maintenance dose: 20-40 mg/day; may be given as a single dose -Acut ...
ANATOMIA FUNCTIONALA/ FIZIOPATOLOGIA HIPOTALAMUSULUI
... or potassium content and the assumption that the body composition can be divided into fat and fat-free or lean body mass with certain characteristics. These techniques are relatively costly, time-consuming and do not give information on the distribution of the fat. Techniques such as bioelectrical i ...
... or potassium content and the assumption that the body composition can be divided into fat and fat-free or lean body mass with certain characteristics. These techniques are relatively costly, time-consuming and do not give information on the distribution of the fat. Techniques such as bioelectrical i ...
ENDOCRINE - Wikispaces
... in epinephrine target cells, thus increasing the effectiveness of epinephrine. • Cortisol also increases the effectiveness of epinephrine. ...
... in epinephrine target cells, thus increasing the effectiveness of epinephrine. • Cortisol also increases the effectiveness of epinephrine. ...
BS1060
... • Hormones are only effective over a narrow concentration range • The EC50 value is the hormone concentration required to produce 50% of the maximal response ...
... • Hormones are only effective over a narrow concentration range • The EC50 value is the hormone concentration required to produce 50% of the maximal response ...
The Endocrine System
... Mostly ______________________ (male sex hormones) are made but some __________________ (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
... Mostly ______________________ (male sex hormones) are made but some __________________ (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
PTA/OTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 2
... Function of the Pineal Gland • Pineal secretion peaks between the ages of 1 and 5 and declines by 75% by the end of puberty. • Produces two hormones, serotonin and melatonin. • Melatonin increase at night, due to a light rate-limiting enzyme that converts serotonin to melatonin- serotonin N-acetyl- ...
... Function of the Pineal Gland • Pineal secretion peaks between the ages of 1 and 5 and declines by 75% by the end of puberty. • Produces two hormones, serotonin and melatonin. • Melatonin increase at night, due to a light rate-limiting enzyme that converts serotonin to melatonin- serotonin N-acetyl- ...
hGH - ISpatula
... • Hypothalamus is a major link between nervous and endocrine system • Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamu ...
... • Hypothalamus is a major link between nervous and endocrine system • Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamu ...
bioidentical hormones - CPD University of Toronto
... Early oral progesterone pdts were broken down in GI tract Therefore progestins were derived from progesterone or testosterone (19-nortestosterone) precursors After micronization was discovered, progesterone could be given orally Prescribed in HT for women with uterus to protect against uterine cance ...
... Early oral progesterone pdts were broken down in GI tract Therefore progestins were derived from progesterone or testosterone (19-nortestosterone) precursors After micronization was discovered, progesterone could be given orally Prescribed in HT for women with uterus to protect against uterine cance ...
Biochemistry of hormones derived from amino acids and proteins
... Gene expression in the anterior and intermediary pituitary, but also in other tissues (intestine, placenta, male reproductive system) Cleavage into peptides, further modification (glycosylation, acetylation, phosphorylation) ...
... Gene expression in the anterior and intermediary pituitary, but also in other tissues (intestine, placenta, male reproductive system) Cleavage into peptides, further modification (glycosylation, acetylation, phosphorylation) ...
The Endocrine System
... Because of its peripheral effects & the need for parenteral administration, dopamine is not useful in the control of hyperprolactinemia, but bromocrptine & other orally active ergot –derivatives (eg. Cabergoline, pergoline) are effective in reducing prolactin secretion from the normal glands as well ...
... Because of its peripheral effects & the need for parenteral administration, dopamine is not useful in the control of hyperprolactinemia, but bromocrptine & other orally active ergot –derivatives (eg. Cabergoline, pergoline) are effective in reducing prolactin secretion from the normal glands as well ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... problem of an imbalance in Na+, K+, and water in the blood because aldosterone is a key regulator of those variables. • The loss of salt and water balance may lead to hypotension (low blood pressure). • Primary adrenal insufficiency from any of these causes is also known as Addison’s disease. ...
... problem of an imbalance in Na+, K+, and water in the blood because aldosterone is a key regulator of those variables. • The loss of salt and water balance may lead to hypotension (low blood pressure). • Primary adrenal insufficiency from any of these causes is also known as Addison’s disease. ...
Biology 30 Notes October 3, 2014 Introduction Endocrine System
... Anterior Pituitary – is a true hormone gland. It produces and releases hGH (human growth hormone), PRL (prolactin), TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), and LH leutinizing hormone. Blood vessels carry releasing hormones from the h ...
... Anterior Pituitary – is a true hormone gland. It produces and releases hGH (human growth hormone), PRL (prolactin), TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), and LH leutinizing hormone. Blood vessels carry releasing hormones from the h ...
The Endocrine System
... -it triggers ovulation of an egg from ovary and causes the ruptured follicle to produce progesterone and some estrogen - In men … it stimulate testestrone production by the interstitial cells of the testes -HYPOSECRETION OF (LH) AND (FSH) lead to sterility ...
... -it triggers ovulation of an egg from ovary and causes the ruptured follicle to produce progesterone and some estrogen - In men … it stimulate testestrone production by the interstitial cells of the testes -HYPOSECRETION OF (LH) AND (FSH) lead to sterility ...
The Endocrine System
... Produces HCG in addition to estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones ...
... Produces HCG in addition to estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones ...
Neuro-Endocrine - Sinoe Medical Association
... Hypothalamus Below the thalamus, it caps the brainstem and forms the inferolateral walls of the third ventricle Mammillary bodies - small, small paired nuclei bulging anteriorly from the hypothalamus - relay stations for olfactory pathways Infundibulum – stalk of the hypothalamus connecting to the ...
... Hypothalamus Below the thalamus, it caps the brainstem and forms the inferolateral walls of the third ventricle Mammillary bodies - small, small paired nuclei bulging anteriorly from the hypothalamus - relay stations for olfactory pathways Infundibulum – stalk of the hypothalamus connecting to the ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... The general function of the endocrine system is to integrate body systems, in conjunction with the nervous system. Recall that glands are effectors or responsive body parts that are stimulated by motor impulses from the autonomic nervous system. Some of these glands, endocrine glands compose the end ...
... The general function of the endocrine system is to integrate body systems, in conjunction with the nervous system. Recall that glands are effectors or responsive body parts that are stimulated by motor impulses from the autonomic nervous system. Some of these glands, endocrine glands compose the end ...
B. Chemical signal sent between individual are called C. Survival
... between the hours of 6 A.M. to 9 A.M. B. Cancer patient s often develop endocrine disorders because cancer cells sometimes secrete ...
... between the hours of 6 A.M. to 9 A.M. B. Cancer patient s often develop endocrine disorders because cancer cells sometimes secrete ...
The Endocrine System - bananateachersworld
... gland. The islets of Langerhans serve its endocrine functions •Two types of cells, alpha and beta are produced by the islets of ...
... gland. The islets of Langerhans serve its endocrine functions •Two types of cells, alpha and beta are produced by the islets of ...