Silica Sulfuric Acid Promotes Aza-Michael Addition Reactions under
... performed by stirring an intimate mixture of PTEA (1.0 mmol), morpholine (1.2 mmol) and silica (240-400 mesh, 100 mg) at room temperature. No aza-Michael addition product was formed even after 24 h, which indicate that the requirement of SiO2-SO3H is key factor for the successful outcome of the reac ...
... performed by stirring an intimate mixture of PTEA (1.0 mmol), morpholine (1.2 mmol) and silica (240-400 mesh, 100 mg) at room temperature. No aza-Michael addition product was formed even after 24 h, which indicate that the requirement of SiO2-SO3H is key factor for the successful outcome of the reac ...
File - chemistryattweed
... production of ammonia because two molecules of gaseous ammonia occupy a smaller volume than the four molecules of gaseous reactants. High pressure also increases the reaction rate because the gas molecules are closer and at higher concentrations. However, high-pressure equipment is expensive and r ...
... production of ammonia because two molecules of gaseous ammonia occupy a smaller volume than the four molecules of gaseous reactants. High pressure also increases the reaction rate because the gas molecules are closer and at higher concentrations. However, high-pressure equipment is expensive and r ...
Mixtures
... oxygen, with smaller amounts of other gases, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor. Some days the air has more water vapor, or is more humid, than on other days. But regardless of the ratio of the components, air is still a mixture. ...
... oxygen, with smaller amounts of other gases, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor. Some days the air has more water vapor, or is more humid, than on other days. But regardless of the ratio of the components, air is still a mixture. ...
Power Point Presentation
... Negligible attractive forces between the particles: Also explains why a gas expands to fill its container ...
... Negligible attractive forces between the particles: Also explains why a gas expands to fill its container ...
158KB - NZQA
... Whereas HCOOH is a weak acid, it does not readily dissociate in water. HCOOH(aq) + H2O() H3O+(aq) + HCOO–(aq) [H3O+] = 0.00398mol L–1 In the resulting solutions, HCl has a higher concentration of H 3O+, and therefore a lower pH (1) than HCOOH, which has a lower concentration of H3O+, and therefor ...
... Whereas HCOOH is a weak acid, it does not readily dissociate in water. HCOOH(aq) + H2O() H3O+(aq) + HCOO–(aq) [H3O+] = 0.00398mol L–1 In the resulting solutions, HCl has a higher concentration of H 3O+, and therefore a lower pH (1) than HCOOH, which has a lower concentration of H3O+, and therefor ...
Reaction Rate Reading Packet
... For the same mass, many small particles have a greater total surface area than one large particle. For example, steel wool has a larger surface area than a block of steel of the same mass. This allows oxygen molecules to collide with many more iron atoms per unit of time. The more surface contact be ...
... For the same mass, many small particles have a greater total surface area than one large particle. For example, steel wool has a larger surface area than a block of steel of the same mass. This allows oxygen molecules to collide with many more iron atoms per unit of time. The more surface contact be ...
Example of Boltzmann distribution.
... Lagrange Undetermined Multipliers. The term is somewhat misleading because the multipliers can, in fact, be determined. In the following example it is not necessary to use this sophisticated method and you should solve the problem in a simple fashion. Consider the equation ax+by=0……………..(1) If y=y(x ...
... Lagrange Undetermined Multipliers. The term is somewhat misleading because the multipliers can, in fact, be determined. In the following example it is not necessary to use this sophisticated method and you should solve the problem in a simple fashion. Consider the equation ax+by=0……………..(1) If y=y(x ...
Chapter 7
... • Increasing the temperature of a substance causes its particles to move faster, on average. • Particles that move faster are both more likely to collide and more likely to react. • If the number of collisions that produce reactions increases, then the reaction rate increases ...
... • Increasing the temperature of a substance causes its particles to move faster, on average. • Particles that move faster are both more likely to collide and more likely to react. • If the number of collisions that produce reactions increases, then the reaction rate increases ...
Resumen Science I Trimestre II Parcial Definitions: Element: pure
... condensation to occur. Removing energy slows the movement of gas particles which allows them to clump together. Condensation point: is the temperature at which the gas becomes a liquid. Sublimation: is the change of sate from solid to gas, For sublimation to occur, the attractions between the partic ...
... condensation to occur. Removing energy slows the movement of gas particles which allows them to clump together. Condensation point: is the temperature at which the gas becomes a liquid. Sublimation: is the change of sate from solid to gas, For sublimation to occur, the attractions between the partic ...
Porous silicon-based nanostructured microparticles as degradable
... 1(3)): A solution of 11-undecenylamine (0.677 g, 4 mmol) in 30 mL of anhydrous CH2Cl2 was prepared and cooled in an ice bath. In a separate flask, 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl chloride (1.04 g, 4 mmol) was dissolved in a small amount of anhydrous CH2Cl2 and was slowly added to the solution of 11undece ...
... 1(3)): A solution of 11-undecenylamine (0.677 g, 4 mmol) in 30 mL of anhydrous CH2Cl2 was prepared and cooled in an ice bath. In a separate flask, 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl chloride (1.04 g, 4 mmol) was dissolved in a small amount of anhydrous CH2Cl2 and was slowly added to the solution of 11undece ...
A Feed-Forward/Feedback Run-to-Run Control of a Mixed Product
... 4.1. Single Product Control. If only one grade of product is produced, the diameter of the particle can be controlled from run to run by a simple EWMA controller. Simulation and experimental results of single product run-to-run control are shown in Figures 6(target ) 250 nm) and 7 (target ) 200 nm). ...
... 4.1. Single Product Control. If only one grade of product is produced, the diameter of the particle can be controlled from run to run by a simple EWMA controller. Simulation and experimental results of single product run-to-run control are shown in Figures 6(target ) 250 nm) and 7 (target ) 200 nm). ...
Chem 216 H W13 Notes - Dr. Masato Koreeda Thin
... are normally not detectable under the 254 nm UV lamp. O OH ...
... are normally not detectable under the 254 nm UV lamp. O OH ...
Chemical Reactions
... The limiting reactant is the reactant that determines the maximum amount of product that is formed. The limiting reactant will be completely used up in a reaction. This makes the reaction stop. The other reactant will have some unchanged so it is said to be the excess reactant. For example, if you n ...
... The limiting reactant is the reactant that determines the maximum amount of product that is formed. The limiting reactant will be completely used up in a reaction. This makes the reaction stop. The other reactant will have some unchanged so it is said to be the excess reactant. For example, if you n ...
KHSO4-SiO2-MeOH – An efficient selective solid
... zeolite3c, acid resin4, etc that are generally in use suffer from certain limitations such as requirement in large volume, pore size dependency, substrate specificity, etc. Recently selective cleavage of only prenyl esters using silica-supported sodium hydrogen sulphate in a nonprotic solvent was re ...
... zeolite3c, acid resin4, etc that are generally in use suffer from certain limitations such as requirement in large volume, pore size dependency, substrate specificity, etc. Recently selective cleavage of only prenyl esters using silica-supported sodium hydrogen sulphate in a nonprotic solvent was re ...
Chemistry 116: General Chemistry
... As a gas molecule, N2 does not often collide with other reactants. The lone pairs on N do react but only reversibly. Reactions with N2 are indeed thermodynamically favorable, but they are just slow. ...
... As a gas molecule, N2 does not often collide with other reactants. The lone pairs on N do react but only reversibly. Reactions with N2 are indeed thermodynamically favorable, but they are just slow. ...
States of Matter
... Distinguish among kinetic, potential, and other forms of energy Apply the theory of conservation of matter in balancing chemical reactions. Classify changes of state in terms of endothermic and exothermic processes Classify mixtures as being homogenous or heterogeneous ...
... Distinguish among kinetic, potential, and other forms of energy Apply the theory of conservation of matter in balancing chemical reactions. Classify changes of state in terms of endothermic and exothermic processes Classify mixtures as being homogenous or heterogeneous ...
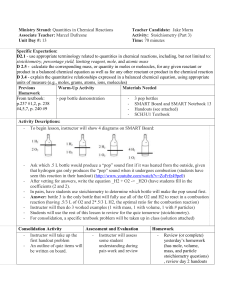
Ministry Strand: Quantities in Chemical Reactions Teacher
... coefficients (2 and 2). In pairs, have students use stoichiometry to determine which bottle will make the pop sound first. Answer: bottle 3 is the only bottle that will fully use all of the O2 and H2 to react in a combustion reaction (having .5/3 L of O2 and 2*.5/3 L H2, the optimal ratio for the co ...
... coefficients (2 and 2). In pairs, have students use stoichiometry to determine which bottle will make the pop sound first. Answer: bottle 3 is the only bottle that will fully use all of the O2 and H2 to react in a combustion reaction (having .5/3 L of O2 and 2*.5/3 L H2, the optimal ratio for the co ...
Jon Abbatt - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Physics
... Gas-to-particle conversion of low volatility gases, e.g. sulfuric acid vapour (free troposphere), highly oxidized organics (remote continental sites), higher oxidation states of iodine (coastal marine regions), leads to new particle formation events. This nucleation process is not understood at the ...
... Gas-to-particle conversion of low volatility gases, e.g. sulfuric acid vapour (free troposphere), highly oxidized organics (remote continental sites), higher oxidation states of iodine (coastal marine regions), leads to new particle formation events. This nucleation process is not understood at the ...
Silica supported zinc chloride catalyzed acetylation of amines
... In the area of green chemistry, the development of heterogeneous catalysts has played an important role, since they offer several advantages such as clean reaction conditions, easy separation of the catalyst from the reaction medium, greater selectivity and generally give higher yield of products an ...
... In the area of green chemistry, the development of heterogeneous catalysts has played an important role, since they offer several advantages such as clean reaction conditions, easy separation of the catalyst from the reaction medium, greater selectivity and generally give higher yield of products an ...