The Parallel Postulate
... 5. Given a straight line and a point not on the line, there is exactly one line through the given point parallel to the given line. The fifth is called the Parallel Postulate and was the object of much study in geometry from as early as 100 years after the Elements. Many geometers thought only the f ...
... 5. Given a straight line and a point not on the line, there is exactly one line through the given point parallel to the given line. The fifth is called the Parallel Postulate and was the object of much study in geometry from as early as 100 years after the Elements. Many geometers thought only the f ...
Geometry - spssailors.org
... MA 12.2.1 (a) Identify and explain the necessity of and give examples of definitions and theorems. MA 12.2.1 (b) Analyze properties and relationships among classes of two and three-dimensional geometric objects using inductive reasoning and counterexamples. MA 12.2.1 (c) State and prove geometric th ...
... MA 12.2.1 (a) Identify and explain the necessity of and give examples of definitions and theorems. MA 12.2.1 (b) Analyze properties and relationships among classes of two and three-dimensional geometric objects using inductive reasoning and counterexamples. MA 12.2.1 (c) State and prove geometric th ...
Geometry Honors - Santa Rosa Home
... Determine the center of a given circle. Given three points not on a line, construct the circle that passes through them. Construct tangents to circles. Circumscribe and inscribe circles about and within triangles and regular polygons. ...
... Determine the center of a given circle. Given three points not on a line, construct the circle that passes through them. Construct tangents to circles. Circumscribe and inscribe circles about and within triangles and regular polygons. ...
Essential - Kyschools.us
... Students will understand that characteristics and properties of two-dimensional figures and three-dimensional objects describe the world and are used to develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships and to evaluate the arguments of others. ...
... Students will understand that characteristics and properties of two-dimensional figures and three-dimensional objects describe the world and are used to develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships and to evaluate the arguments of others. ...
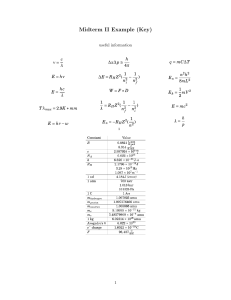
Midterm II Example (Key)
... (c) The repulsion due to a double bond is approximately equal to the repulsion due to a single bond. (d) The repulsion due to a double bond is always higher than the repulsion due to a single bond. ...
... (c) The repulsion due to a double bond is approximately equal to the repulsion due to a single bond. (d) The repulsion due to a double bond is always higher than the repulsion due to a single bond. ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)