Geometry
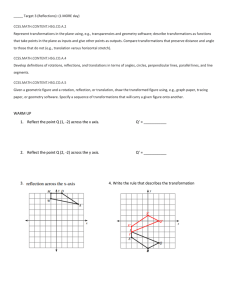
... 8.G.1.b Angles are taken to angles of the same measure. 8.G.1.c Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. Standard 8.G.2 Understand that a two-dimensional figure is congruent to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations; given tw ...
... 8.G.1.b Angles are taken to angles of the same measure. 8.G.1.c Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. Standard 8.G.2 Understand that a two-dimensional figure is congruent to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations; given tw ...
Analytic Geometry Review Notes Create a booklet with the students
... Create a booklet with the students using these key concepts. The review is organized into sections, probability, coordinate geometry, quadratics, numbers, circles, and triangles and theorems. The review is set up to go from the newest material to the oldest, so the first semester stuff should be fre ...
... Create a booklet with the students using these key concepts. The review is organized into sections, probability, coordinate geometry, quadratics, numbers, circles, and triangles and theorems. The review is set up to go from the newest material to the oldest, so the first semester stuff should be fre ...
Levels of Geometric Thinking
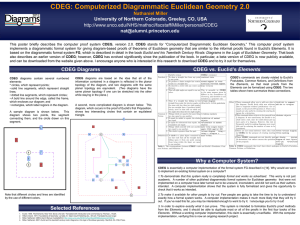
... About all we know concerning the man Euclid is that he was a professor of mathematics around 300 B.C., taught at the University of Alexandria in Greece, and was the author of the celebrated Elements. The stories told of Euclid show that he was a serious, uncompromising scholar. When asked by King Pt ...
... About all we know concerning the man Euclid is that he was a professor of mathematics around 300 B.C., taught at the University of Alexandria in Greece, and was the author of the celebrated Elements. The stories told of Euclid show that he was a serious, uncompromising scholar. When asked by King Pt ...
Molecular Geometry Practice Problems
... Advanced Chemistry I Molecular Geometry Practice Problems Basic Overview 1. According to VSEPR theory, how will the lone pairs and bonded atoms try to arrange themselves (close together, far apart, in a line, etc.)? ...
... Advanced Chemistry I Molecular Geometry Practice Problems Basic Overview 1. According to VSEPR theory, how will the lone pairs and bonded atoms try to arrange themselves (close together, far apart, in a line, etc.)? ...
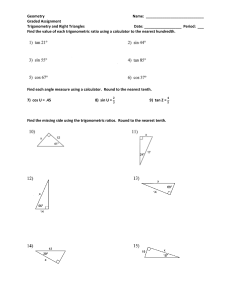
Graded Assignment - Trigonometry and Right Triangles
... Find the measure of the indicated angle using trigonometric ratios. Round to the nearest tenth of a degree. ...
... Find the measure of the indicated angle using trigonometric ratios. Round to the nearest tenth of a degree. ...
Sand Creek Zone Curriculum Map
... expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for of very large or very small quantities. ...
... expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for of very large or very small quantities. ...
Study Guide - U.I.U.C. Math
... Pythaogoras’s theorem Exterior angle theorem (Th 2.6) The sum of interior angles in a Euclidean triangle is 2 right angles Euclid Proposition 27 and 28 (transversals and parallel lines) The angle subtended by an arc at the circumference is half the angle subtended at the center of the circle. A tang ...
... Pythaogoras’s theorem Exterior angle theorem (Th 2.6) The sum of interior angles in a Euclidean triangle is 2 right angles Euclid Proposition 27 and 28 (transversals and parallel lines) The angle subtended by an arc at the circumference is half the angle subtended at the center of the circle. A tang ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)