The Plant Cell
... • The Plant Cell consists of a more or less rigid cell wall and the protoplast - the contents of the cell • The protoplast consists of the cytoplasm and a nucleus • The cytoplasm includes distinct membrane-bound organelles such as plastids and mitochondria; systems of membranes (endoplasmic reticulu ...
... • The Plant Cell consists of a more or less rigid cell wall and the protoplast - the contents of the cell • The protoplast consists of the cytoplasm and a nucleus • The cytoplasm includes distinct membrane-bound organelles such as plastids and mitochondria; systems of membranes (endoplasmic reticulu ...
Cells and Cell Theory
... 1) All living things are made of cells. 2) Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3) All cells come from other cells. ...
... 1) All living things are made of cells. 2) Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3) All cells come from other cells. ...
Cells
... Cell growth, replication of DNA Prepares for mitosis Refer to the cell cycle pie graph on page 23 Mitosis is ____ h Rapid growth is ____ h Growth and DNA replication is ____h Growth and preparation for division is ____ h ...
... Cell growth, replication of DNA Prepares for mitosis Refer to the cell cycle pie graph on page 23 Mitosis is ____ h Rapid growth is ____ h Growth and DNA replication is ____h Growth and preparation for division is ____ h ...
Unit 1 - Elgin Academy
... Cell walls provide support to plant cells, are composed mainly of cellulose and are freely permeable. Cell membranes control the movement of materials into and out of cells and are selectively permeable, only allowing small molecules to pass through. Cell membranes have a fluid mosaic structure form ...
... Cell walls provide support to plant cells, are composed mainly of cellulose and are freely permeable. Cell membranes control the movement of materials into and out of cells and are selectively permeable, only allowing small molecules to pass through. Cell membranes have a fluid mosaic structure form ...
Unit 2: Basic Biological Principles - kromko
... membranes that assists in the processing and transportation of proteins and lipids. • Rough ER – Produces, processes and transports proteins (roughness is the attached ribosomes) • Smooth ER – Processes and transports lipids ...
... membranes that assists in the processing and transportation of proteins and lipids. • Rough ER – Produces, processes and transports proteins (roughness is the attached ribosomes) • Smooth ER – Processes and transports lipids ...
Unit 3 Chapter 7 A View of the Cell
... based solution that suspends all internal parts of the cell Ribosomes: produces proteins DNA: genetic material made of nucleic acids ...
... based solution that suspends all internal parts of the cell Ribosomes: produces proteins DNA: genetic material made of nucleic acids ...
cells - Cobb Learning
... • Get out your organizer from Friday • Complete the back using pages 68 & 69 in the textbook • Fill out the Venn Diagram…you don’t have to use “inside” and “organization” if you don’t want to…create your own ideas in the circles! ...
... • Get out your organizer from Friday • Complete the back using pages 68 & 69 in the textbook • Fill out the Venn Diagram…you don’t have to use “inside” and “organization” if you don’t want to…create your own ideas in the circles! ...
5.5 Stages of Mitosis Notes & Questions
... All living things are made up of one or more cells. The cell is the functional unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cell division, the process by which cells come from pre-existing cells, is the process that perpetuates life and allows species to continue. Just as cells reprod ...
... All living things are made up of one or more cells. The cell is the functional unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cell division, the process by which cells come from pre-existing cells, is the process that perpetuates life and allows species to continue. Just as cells reprod ...
evolutionary trends released questions2013
... multicellular organisms. Which of the following best summarizes an advantage of eukaryotic cells having internal membranes? (A) Eukaryotic cells are able to reproduce faster because of the presence of organelles. (B) Some organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplast, are similar to prokaryotic c ...
... multicellular organisms. Which of the following best summarizes an advantage of eukaryotic cells having internal membranes? (A) Eukaryotic cells are able to reproduce faster because of the presence of organelles. (B) Some organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplast, are similar to prokaryotic c ...
Name - Belle Vernon Area School District
... eubacteria cells cell theory enzymes deoxyribosenucleic acid adenosine triphosphate amino acids ...
... eubacteria cells cell theory enzymes deoxyribosenucleic acid adenosine triphosphate amino acids ...
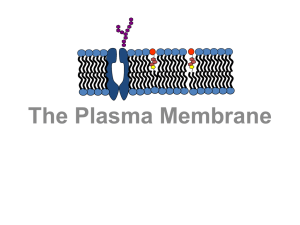
The Cell Membrane is a Fluid Mosaic
... different ends: a head and a tail. The head end contains a phosphate group and is hydrophilic. This means that is likes or is attracted to water molecules. The tail end is made up of two strings of hydrogen and carbon atoms called fatty acid chains. These chains are hydrophobic or do not like to min ...
... different ends: a head and a tail. The head end contains a phosphate group and is hydrophilic. This means that is likes or is attracted to water molecules. The tail end is made up of two strings of hydrogen and carbon atoms called fatty acid chains. These chains are hydrophobic or do not like to min ...
Cell Division
... During an investigation of a freshwater lake, a sad AP biology student discovers a previously unknown microscopic organism. Further study shows that the unicellular organism is eukaryotic. http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/apc/public/repository/ap11_biology_scoring_g uidelines.pdf a. Identify FOUR o ...
... During an investigation of a freshwater lake, a sad AP biology student discovers a previously unknown microscopic organism. Further study shows that the unicellular organism is eukaryotic. http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/apc/public/repository/ap11_biology_scoring_g uidelines.pdf a. Identify FOUR o ...
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 6: 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures
... • proteins destined to leave ER are transported to the Golgi where they are modified, sorted and sent to various destinations. • polysaccharides are produced in the Golgi apparatus as well ...
... • proteins destined to leave ER are transported to the Golgi where they are modified, sorted and sent to various destinations. • polysaccharides are produced in the Golgi apparatus as well ...
Slide 1 - gwbiology
... The ECM may help coordinate the behavior of all the cells within that tissue. ◦ Direct connections (intercellular junctions) between cells also function in this coordination. ...
... The ECM may help coordinate the behavior of all the cells within that tissue. ◦ Direct connections (intercellular junctions) between cells also function in this coordination. ...
Name: Date: Hour : _____ Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the
... 6. Centrioles are found inside of what type of cell?_______________________________________ 7. What additional layer is found around the outside of plant cells and bacteria ? ______________ 8. Centrioles are found at the center of __________________________ How do they help the cell? The nucleus in ...
... 6. Centrioles are found inside of what type of cell?_______________________________________ 7. What additional layer is found around the outside of plant cells and bacteria ? ______________ 8. Centrioles are found at the center of __________________________ How do they help the cell? The nucleus in ...
The World of Biology
... Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ ...
... Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ ...
2.-1
... • Cytology = study of cellular structure • Cell physiology = study of cellular function ...
... • Cytology = study of cellular structure • Cell physiology = study of cellular function ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.