Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... This particular eukaryotic cell happens to be an animal cell, but the cells of plants, fungi and protists are also eukaryotic. All bacteria have prokaryotic cells. Despite their apparent differences, these two cell types have a lot in common. They perform most of the same kinds of functions, and in ...
... This particular eukaryotic cell happens to be an animal cell, but the cells of plants, fungi and protists are also eukaryotic. All bacteria have prokaryotic cells. Despite their apparent differences, these two cell types have a lot in common. They perform most of the same kinds of functions, and in ...
Cell Structure and Function
... The cytoplasm is the cellular material inside the plasma membrane and outside the nucleus. The fluid portion of the cytoplasm contains various inorganic and organic chemicals that are dissolved and/or suspended. This fluid suspension is called the cytosol. ...
... The cytoplasm is the cellular material inside the plasma membrane and outside the nucleus. The fluid portion of the cytoplasm contains various inorganic and organic chemicals that are dissolved and/or suspended. This fluid suspension is called the cytosol. ...
TAP 121-3: Internal resistance of a C cell
... Start with the rheostat on its maximum resistance. Record V and I. Gradually reduce the rheostat to its lowest resistance (zero) measuring V and I a minimum of 7 times over the range. Don’t leave the circuit connected for long when the resistance is low (current high) because this will run the cell ...
... Start with the rheostat on its maximum resistance. Record V and I. Gradually reduce the rheostat to its lowest resistance (zero) measuring V and I a minimum of 7 times over the range. Don’t leave the circuit connected for long when the resistance is low (current high) because this will run the cell ...
how cells multiply, madison 2011
... Work in your groups to arrange the notes in the order that would make the cell divide… ...
... Work in your groups to arrange the notes in the order that would make the cell divide… ...
The cell wall
... What is photosynthesis? The process by which light energy and CO2 and water produce O2 and energy What is cellular respiration? The process by which O2 and sugar produce CO2, H2O and energy How are the two processes related? Plants use our CO2 and we use their O2 What is diffusion? When something go ...
... What is photosynthesis? The process by which light energy and CO2 and water produce O2 and energy What is cellular respiration? The process by which O2 and sugar produce CO2, H2O and energy How are the two processes related? Plants use our CO2 and we use their O2 What is diffusion? When something go ...
File
... • Carry protein and other materials from one part of the cell to another • Found in BOTH plant and ...
... • Carry protein and other materials from one part of the cell to another • Found in BOTH plant and ...
STUDY GU STUDY GUIDE QUESTIONS
... • I CAN compare and contrast the differences between plant and animal cells • I CAN describe and explain how living things are classified. ...
... • I CAN compare and contrast the differences between plant and animal cells • I CAN describe and explain how living things are classified. ...
Flash cards unit 1
... of oxygen and the pyruvic acid from glycolysis is broken down to Carbon dioxide, water and 36molecules of ATP. Anaerobic respiration happens in the absence of oxygen. Pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid (in animals) or alcohol and carbon dioxide (in plants) ...
... of oxygen and the pyruvic acid from glycolysis is broken down to Carbon dioxide, water and 36molecules of ATP. Anaerobic respiration happens in the absence of oxygen. Pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid (in animals) or alcohol and carbon dioxide (in plants) ...
Eukaryotic Origins
... Allows our cells to grow bigger, do more things and build more complex structures ...
... Allows our cells to grow bigger, do more things and build more complex structures ...
The Cell in Its Environment
... How is Osmosis Related to Diffusion? • Molecules tend to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Water molecules move by diffusion from an area where they are highly concentrated through the cell membrane to an area where they are less ...
... How is Osmosis Related to Diffusion? • Molecules tend to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Water molecules move by diffusion from an area where they are highly concentrated through the cell membrane to an area where they are less ...
Introduction
... • The fibers act like a geodesic dome to stabilize a balance between opposing forces. • The cytoskeleton provides anchorage for many organelles and cytosolic enzymes. • The cytoskeleton is dynamic, dismantling in one part and reassembling in another to change cell shape. ...
... • The fibers act like a geodesic dome to stabilize a balance between opposing forces. • The cytoskeleton provides anchorage for many organelles and cytosolic enzymes. • The cytoskeleton is dynamic, dismantling in one part and reassembling in another to change cell shape. ...
Cells Unit - Warren County Public Schools
... • Is a phospholipid bilayer with some proteins & carbohydrates associated with it. • Integral proteins form channels & pumps to pass substances across the membrane. • Represented by the “Fluid Mosaic Model”. ...
... • Is a phospholipid bilayer with some proteins & carbohydrates associated with it. • Integral proteins form channels & pumps to pass substances across the membrane. • Represented by the “Fluid Mosaic Model”. ...
Cells and Organelles!
... Eukaryotic Cells ▫ Contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. ▫ They are large and complex. They are found in the most complex life forms called eukaryotes. ▫ Examples: plant, animal, fungi and protist ...
... Eukaryotic Cells ▫ Contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. ▫ They are large and complex. They are found in the most complex life forms called eukaryotes. ▫ Examples: plant, animal, fungi and protist ...
PDF Steady State of Living Cells and Donnan Equilibrium
... The previous PDF handout points out that since the Nernst potential, Vi Nernst ≠ ΔV is ...
... The previous PDF handout points out that since the Nernst potential, Vi Nernst ≠ ΔV is ...
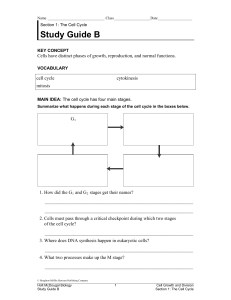
Study Guide B
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
The Cell Membrane
... How is diffusion going to take place? What happens with continued shaking? Is equilibrium reached? (Has homeostasis been reached?) ...
... How is diffusion going to take place? What happens with continued shaking? Is equilibrium reached? (Has homeostasis been reached?) ...
Week 3 Agenda and Notes
... Fimbriae – bristle-like appendages that help in adhesion of cell to surface Inclusion bodies – for storage of nutrients Nucleoid – area where bacterial chromosome are found (usually toward the center of the cell) (bacteria: have one chromosome, usually circular) Ribosomes – small particles suspended ...
... Fimbriae – bristle-like appendages that help in adhesion of cell to surface Inclusion bodies – for storage of nutrients Nucleoid – area where bacterial chromosome are found (usually toward the center of the cell) (bacteria: have one chromosome, usually circular) Ribosomes – small particles suspended ...
THE CELL
... They can be free floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum ...
... They can be free floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.