Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 5. During active transport molecules move from an area of _low___ concentration to an area of ___high_________ concentration. 6. ___Exocytosis______ is a form of active transport in which the cell sends materials out of the cell using vesicles, small storage structures that fuse to the cell membrane ...
... 5. During active transport molecules move from an area of _low___ concentration to an area of ___high_________ concentration. 6. ___Exocytosis______ is a form of active transport in which the cell sends materials out of the cell using vesicles, small storage structures that fuse to the cell membrane ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part B Classes of Compounds • Inorganic
... • Water, salts, and many acids and bases • Do not contain carbon ...
... • Water, salts, and many acids and bases • Do not contain carbon ...
What is a cell?
... _____________ in the cell membrane is used to stabilize the membrane and keep phospholipids from sticking together. _____________ on the surface help cells recognize each other. _____________ in the membrane are used for transporting molecules ...
... _____________ in the cell membrane is used to stabilize the membrane and keep phospholipids from sticking together. _____________ on the surface help cells recognize each other. _____________ in the membrane are used for transporting molecules ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Phospholipid molecules and proteins that are embedded in the membrane tend to drift sideways. This supports the idea of the cell membrane having a Fluid Consistency. ...
... Phospholipid molecules and proteins that are embedded in the membrane tend to drift sideways. This supports the idea of the cell membrane having a Fluid Consistency. ...
The Cell Cycle
... Cell Growth and Cell Division are carefully controlled Not all cells move through the cell cycle at the same rate ...
... Cell Growth and Cell Division are carefully controlled Not all cells move through the cell cycle at the same rate ...
Cell Organelles Graphic Organizer
... DNA (chromosomes) which contain instructions for traits & characteristics - Also contains a dark central ball called the nucleolus which makes ribosomes Function: Directs cell activities. Structure: - Not bound by a membrane. Each cell contains thousands. - Found on endoplasmic reticulum & freely fl ...
... DNA (chromosomes) which contain instructions for traits & characteristics - Also contains a dark central ball called the nucleolus which makes ribosomes Function: Directs cell activities. Structure: - Not bound by a membrane. Each cell contains thousands. - Found on endoplasmic reticulum & freely fl ...
Student Exploration: Cell Structure
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some ...
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some ...
CellStructureSE
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
Cell Structure Gizmo
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
cell structure and function 2010
... • Consists of all the contents between the nucleus and the cell membrane. • Made up of the cytosol and organelles such as mitochondria and ribosomes. • The fluid part of the cytoplasm is the Cytosol. It is clear in color and has a gel-like appearance. It is composed mainly of water and also contains ...
... • Consists of all the contents between the nucleus and the cell membrane. • Made up of the cytosol and organelles such as mitochondria and ribosomes. • The fluid part of the cytoplasm is the Cytosol. It is clear in color and has a gel-like appearance. It is composed mainly of water and also contains ...
Why do Cells Divide?
... You need the cell to remain small!! For example, if the cell size doubles it would need 8x more nutrients to survive and it would create 8x the waste to excrete!! The vol. increases faster than the surface area of the cell membrane!! ...
... You need the cell to remain small!! For example, if the cell size doubles it would need 8x more nutrients to survive and it would create 8x the waste to excrete!! The vol. increases faster than the surface area of the cell membrane!! ...
THE EUKARYOTIC CELL
... A eukaryotic cell contains complex structures enclosed within membranes. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, surrounded by a nuclear envelope, within which the genetic material is carried. Most eukaryotic cells also contain ot ...
... A eukaryotic cell contains complex structures enclosed within membranes. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, surrounded by a nuclear envelope, within which the genetic material is carried. Most eukaryotic cells also contain ot ...
Lecture 2
... eukaryotes. In addition, there are many other membrane-bound organelles of the cytoplasm that carry out specific functions, and these components are generally said to be part of the endomembrane system. The endomembrane system: A system of compartments that generally includes all of the membrane-bou ...
... eukaryotes. In addition, there are many other membrane-bound organelles of the cytoplasm that carry out specific functions, and these components are generally said to be part of the endomembrane system. The endomembrane system: A system of compartments that generally includes all of the membrane-bou ...
AP Biology Quiz Name Date The tendency of an organism to
... constantly changing environment is a process known as (a) digestion (b) regulation (c) synthesis (d) respiration 9. Which life function provides substances that may be used by an organism for its growth and for the repair of its tissues? (a)excretion (b)reproduction (c)nutrition (d) regulation 10. A ...
... constantly changing environment is a process known as (a) digestion (b) regulation (c) synthesis (d) respiration 9. Which life function provides substances that may be used by an organism for its growth and for the repair of its tissues? (a)excretion (b)reproduction (c)nutrition (d) regulation 10. A ...
File
... Specialised Cells Animals and plants are made up of lots of different types of cell Cells can become specialised to do a particular job The structure of the cells are suited to their function Examples of specialised cells include nerve cells, muscle cells, sperm cells, red blood cells, palis ...
... Specialised Cells Animals and plants are made up of lots of different types of cell Cells can become specialised to do a particular job The structure of the cells are suited to their function Examples of specialised cells include nerve cells, muscle cells, sperm cells, red blood cells, palis ...
Passive Transport
... diffusion of specific particles through transport proteins found in the PM ...
... diffusion of specific particles through transport proteins found in the PM ...
Chapter 3 Cells - McCarter Anatomy & Physiology
... • can divide to form a stem cell and a progenitor cell • totipotent – can give rise to every cell type • pluripotent – can give rise to a restricted number of cell types Progenitor cell • committed cell • can divide to become any of a restricted number of cells ...
... • can divide to form a stem cell and a progenitor cell • totipotent – can give rise to every cell type • pluripotent – can give rise to a restricted number of cell types Progenitor cell • committed cell • can divide to become any of a restricted number of cells ...
Outline - Membranes Membranes Membrane Phospholipids
... 1. Proteins allow transport 2. Mechanisms of movement through proteins 1. Passive Transport – “down” concentration gradient ¾ Channels, carriers & pores ¾ Diffusion ...
... 1. Proteins allow transport 2. Mechanisms of movement through proteins 1. Passive Transport – “down” concentration gradient ¾ Channels, carriers & pores ¾ Diffusion ...
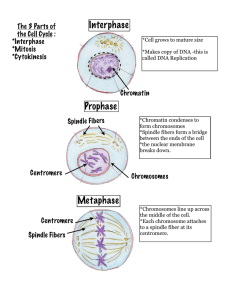
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
Apple Anatomy - Agriculture in the Classroom
... when looking through their microscope. The cell membrane forms a barrier between the inside of the apple and the outside. The cell membrane allows waste to exit the cell. The cell wall is used to provide structural support and control the amount of water entering the cell. The golgi body stores and ...
... when looking through their microscope. The cell membrane forms a barrier between the inside of the apple and the outside. The cell membrane allows waste to exit the cell. The cell wall is used to provide structural support and control the amount of water entering the cell. The golgi body stores and ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.