Cells - Ms. V Biology
... 27. ______________________ like glucose are burned in the mitochondria to release cellular energy known as ______________________ 28. What surrounds the outside of all cells? 29. In plant cells, a cell surrounds the cell membrane for extra support. 30. What 2 things make up all cell membranes? 31. C ...
... 27. ______________________ like glucose are burned in the mitochondria to release cellular energy known as ______________________ 28. What surrounds the outside of all cells? 29. In plant cells, a cell surrounds the cell membrane for extra support. 30. What 2 things make up all cell membranes? 31. C ...
What are cells? - Duplin County Schools
... • A vacuole is the storage area of the cell. • Most plant cells have only one very big vacuole. • Vacuoles store food, waste products, and other materials for the cell. • When the vacuole is full of water the plants are plumped up and sturdy, but when the vacuoles are running low on water it causes ...
... • A vacuole is the storage area of the cell. • Most plant cells have only one very big vacuole. • Vacuoles store food, waste products, and other materials for the cell. • When the vacuole is full of water the plants are plumped up and sturdy, but when the vacuoles are running low on water it causes ...
Cells St. Francis Xavier University
... Multicellular animals are organized in a complex manner which starts with small single cells and builds into a large living entity. ...
... Multicellular animals are organized in a complex manner which starts with small single cells and builds into a large living entity. ...
Document
... http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/mitochondria/mitochondria.html Write a sentence that specifically describes the function of mitochondria ...
... http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/mitochondria/mitochondria.html Write a sentence that specifically describes the function of mitochondria ...
Chapter 4
... • Proposes that some of today’s eukaryotic organelles evolved by a symbiosis arising between two cells that were each freeliving • One cell, a prokaryote, was engulfed by and became part of another cell, which was the precursor of modern eukaryotes • Mitochondria and chloroplasts ...
... • Proposes that some of today’s eukaryotic organelles evolved by a symbiosis arising between two cells that were each freeliving • One cell, a prokaryote, was engulfed by and became part of another cell, which was the precursor of modern eukaryotes • Mitochondria and chloroplasts ...
Chapter 3 The Cell
... Membrane Transport (Interstitial Fluid): soup of nutrients that surrounds cells. Selectively permeable membrane around cell. Ability to select is lost with damage to cell, as in burns. ...
... Membrane Transport (Interstitial Fluid): soup of nutrients that surrounds cells. Selectively permeable membrane around cell. Ability to select is lost with damage to cell, as in burns. ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... the chemical bonds of carbohydrate, fat, and protein molecules is converted into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP—the energy source for all cellular functions and activities. ...
... the chemical bonds of carbohydrate, fat, and protein molecules is converted into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP—the energy source for all cellular functions and activities. ...
Developmental Biology, 9e
... develop what are called germ cells. These cells will provide the material and instructions for the next generation of that organism. In most of the organisms we have studied, there is a clear separation of germ cells from body (somatic) cells, but in some organisms the demarcation is not so obvious ...
... develop what are called germ cells. These cells will provide the material and instructions for the next generation of that organism. In most of the organisms we have studied, there is a clear separation of germ cells from body (somatic) cells, but in some organisms the demarcation is not so obvious ...
Cell Organelles
... Cells are made up of organelles o Organelles: “little organs” Two main parts of eukaryotic cells: o 1. Nucleus o 2. Cytoplasm ...
... Cells are made up of organelles o Organelles: “little organs” Two main parts of eukaryotic cells: o 1. Nucleus o 2. Cytoplasm ...
Cell Organelles and Functions
... surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in humans and animals. ...
... surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in humans and animals. ...
Cells
... membrane, lets things in/out of nucleus contain enzymes to break down large food particles, and old cell parts; membrane ...
... membrane, lets things in/out of nucleus contain enzymes to break down large food particles, and old cell parts; membrane ...
File
... make proteins for the cell; found in BOTH cells n. rough ER: transport system of membranes (directly off the nucleus with ribosomes attached to the surface) that move proteins to other parts of the cell; found in BOTH cells o. smooth ER: transport system of membranes (directly off the nucleus with N ...
... make proteins for the cell; found in BOTH cells n. rough ER: transport system of membranes (directly off the nucleus with ribosomes attached to the surface) that move proteins to other parts of the cell; found in BOTH cells o. smooth ER: transport system of membranes (directly off the nucleus with N ...
Motor-clutch model for substrate stiffness sensing by living cells
... these vital decisions is not clear. We recently showed that a simple “motor-clutch” model exhibits stiffness sensitivity (Chan and Odde, Science, 2008). In particular, the F-actin retrograde flow rate and traction force exhibit a biphasic response to substrate Young’s modulus, an effect that we conf ...
... these vital decisions is not clear. We recently showed that a simple “motor-clutch” model exhibits stiffness sensitivity (Chan and Odde, Science, 2008). In particular, the F-actin retrograde flow rate and traction force exhibit a biphasic response to substrate Young’s modulus, an effect that we conf ...
Multiple Choice – Chapter 1
... 7. The information in ____ underlies all of the properties that distinguish life from nonlife. a. carbon b. DNA c. proteins d. populations e. nutrients 8. There are many interdependencies in an ecosystem. Prokaryotes and fungi play an important role in the ecosystem primarily because they a. cause d ...
... 7. The information in ____ underlies all of the properties that distinguish life from nonlife. a. carbon b. DNA c. proteins d. populations e. nutrients 8. There are many interdependencies in an ecosystem. Prokaryotes and fungi play an important role in the ecosystem primarily because they a. cause d ...
Cell Parts and Function Analogy
... Animal cells…try to spot them by the end of the show Plant cells ...
... Animal cells…try to spot them by the end of the show Plant cells ...
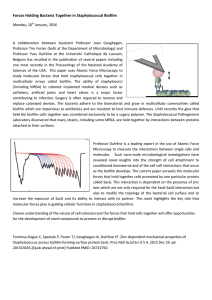
Forces Holding Bacteria Together in Staphylococcal Biofilm
... A collaboration between Assistant Professor Joan Geoghegan, Professor Tim Foster (both at the Department of Microbiology) and Professor Yves Dufrêne at the Université Catholique de Louvain, Belgium has resulted in the publication of several papers including one most recently in the Proceedings of th ...
... A collaboration between Assistant Professor Joan Geoghegan, Professor Tim Foster (both at the Department of Microbiology) and Professor Yves Dufrêne at the Université Catholique de Louvain, Belgium has resulted in the publication of several papers including one most recently in the Proceedings of th ...
Cells Notes
... Cell Specialization: Multicellular organisms are able to___________ which allows the cells to ___________ _____________ ________________. For example, a cell can become a nerve cell or muscle Groups of these cells then combine to form systems: _________ ___ _________________ ________Tissu ...
... Cell Specialization: Multicellular organisms are able to___________ which allows the cells to ___________ _____________ ________________. For example, a cell can become a nerve cell or muscle Groups of these cells then combine to form systems: _________ ___ _________________ ________Tissu ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Schleiden who said that cells make up every part of a plant Schwann who claimed that animals are also made of cells Virchow who determined that cells come from other cells. ...
... Schleiden who said that cells make up every part of a plant Schwann who claimed that animals are also made of cells Virchow who determined that cells come from other cells. ...
Lindenmayer Systems (L
... Control theory can be applied to other areas such as the growth process in organisms and populations In general, several choices of controls to steer a system from an initial state to a goal state. A selection among those succesful controls can be made to minimize some quantity (cost) Examples of co ...
... Control theory can be applied to other areas such as the growth process in organisms and populations In general, several choices of controls to steer a system from an initial state to a goal state. A selection among those succesful controls can be made to minimize some quantity (cost) Examples of co ...
Organ Systems Organs Tissues Cells
... solution in which the salt concentration is much higher than the salt concentration in the red blood cells? a. The red blood cells will absorb water and increase in size. b. The red blood cells will lose water and decrease in size. c. The red blood cells will first absorb water, then lose water and ...
... solution in which the salt concentration is much higher than the salt concentration in the red blood cells? a. The red blood cells will absorb water and increase in size. b. The red blood cells will lose water and decrease in size. c. The red blood cells will first absorb water, then lose water and ...
The Cell : Notes/W.S.-30
... All cells contain ribosomes. The ribosomes are organelles that make proteins. All cells also contain mitochondria. These organelles produce energy for the cell. The nucleolus contains most of the DNA in the nucleus. The vacuole contains mostly water and some food and waste products. All plant cells ...
... All cells contain ribosomes. The ribosomes are organelles that make proteins. All cells also contain mitochondria. These organelles produce energy for the cell. The nucleolus contains most of the DNA in the nucleus. The vacuole contains mostly water and some food and waste products. All plant cells ...
PGS: 124 – 138 - Lincoln County Schools
... i. These function in the transport of molecules and foundation. (Help to maintain the integrity of the structure.) b. Peripheral – These are located on one side of the membrane. (They do not extend into the bi-layer of the membrane. i.These act as sites for attachment of the Cytoskeleton on the insi ...
... i. These function in the transport of molecules and foundation. (Help to maintain the integrity of the structure.) b. Peripheral – These are located on one side of the membrane. (They do not extend into the bi-layer of the membrane. i.These act as sites for attachment of the Cytoskeleton on the insi ...
THE CELL
... After years of research, scientists summarized their findings into three statements. Together, they make up the cell theory: 1. All living things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all ...
... After years of research, scientists summarized their findings into three statements. Together, they make up the cell theory: 1. All living things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all ...
Types of Blood Cells All our blood cells have jobs to do. Red cells
... Platelets are fragments of cells. Each one is about a fifth of the size of a red blood cell. Crush three red sweets into smaller pieces. ...
... Platelets are fragments of cells. Each one is about a fifth of the size of a red blood cell. Crush three red sweets into smaller pieces. ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.