Grade 8 Nov EXAM Review Sheet - Nelson Heights Middle School
... 18)What is special about alveoli? Why is this characteristic important? 19)What process is used to move gases from the lungs into the blood and vice versa? 20)Describe the path that blood follows from when it first enters the right atrium until it returns to the right atrium. 21)What are the 2 adapt ...
... 18)What is special about alveoli? Why is this characteristic important? 19)What process is used to move gases from the lungs into the blood and vice versa? 20)Describe the path that blood follows from when it first enters the right atrium until it returns to the right atrium. 21)What are the 2 adapt ...
Chapter 8 - McGraw-Hill Education Canada
... 4. Use the illustration on the web page to help label your diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. Part B: Animal Cells 1. From the index, click on Animal Cell. 2. Draw a diagram of an animal cell. 3. Use the illustration on the web page to help label your ...
... 4. Use the illustration on the web page to help label your diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. Part B: Animal Cells 1. From the index, click on Animal Cell. 2. Draw a diagram of an animal cell. 3. Use the illustration on the web page to help label your ...
Slide ()
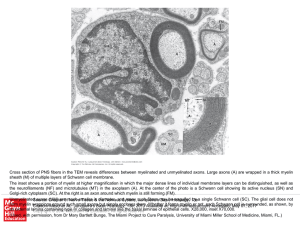
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
Cells and cell process
... Mitosis can take place in animal tissue at any stage in its development. Even though plants have the ability to grow new parts throughout their life cycle, on the whole animals are unable to do this. ...
... Mitosis can take place in animal tissue at any stage in its development. Even though plants have the ability to grow new parts throughout their life cycle, on the whole animals are unable to do this. ...
Intro to Cell - learningcanbefun
... • all living things are made up of cells • cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism • new cells are produced from existing cells ...
... • all living things are made up of cells • cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism • new cells are produced from existing cells ...
SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS- - Uplift Summit International
... Scanning Tunneling microscope Uses needle like probe to measure differences in voltage caused by electrons that leak, or tunnel from the surface of an object Micrographs Types of micrographs ...
... Scanning Tunneling microscope Uses needle like probe to measure differences in voltage caused by electrons that leak, or tunnel from the surface of an object Micrographs Types of micrographs ...
Cells: Its Alive!
... c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms. d. Explain that tissues, organs, and organ systems serve the needs cells have for oxygen, food, and waste removal. ...
... c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms. d. Explain that tissues, organs, and organ systems serve the needs cells have for oxygen, food, and waste removal. ...
Dr Colin Watts, Cambridge University
... AuNP-Pt + RT can decrease the growth of GBM cells significantly. ...
... AuNP-Pt + RT can decrease the growth of GBM cells significantly. ...
Eukaryotic Cell Substructure
... Cytoskeletal structures Cells contain elaborate arrays of protein fibers that serve such functions as: • Establishing cell shape • Providing mechanical strength • Locomotion (cilia, flagella) • Chromosome separation in mitosis and meiosis • Intracellular transport of organelles ...
... Cytoskeletal structures Cells contain elaborate arrays of protein fibers that serve such functions as: • Establishing cell shape • Providing mechanical strength • Locomotion (cilia, flagella) • Chromosome separation in mitosis and meiosis • Intracellular transport of organelles ...
What Battery is Better? Hess 1 Batteries come in many shapes and
... length overall but one might maintain higher voltage over more of its lifetime, in a sense providing better quality. A high powered device such as a motorized toy running constantly takes more current than a less power hungry device such as a personal stereo that alternately runs and rests. Batterie ...
... length overall but one might maintain higher voltage over more of its lifetime, in a sense providing better quality. A high powered device such as a motorized toy running constantly takes more current than a less power hungry device such as a personal stereo that alternately runs and rests. Batterie ...
CYTOSKELETON
... animal cells and just 20 sec. in dividing animal cells. Functions: 1. They maintain cell shape. 2. They are the structural components of centrioles, basal bodies, spindle apparatus, chromosomal fibers, cilia and flagella. 3. In term of Chromosomal fibers, they bring about anaphasic movement of Chrom ...
... animal cells and just 20 sec. in dividing animal cells. Functions: 1. They maintain cell shape. 2. They are the structural components of centrioles, basal bodies, spindle apparatus, chromosomal fibers, cilia and flagella. 3. In term of Chromosomal fibers, they bring about anaphasic movement of Chrom ...
What should I know for the TEST
... WHICH CELL PARTS HAVE A DOUBLE MEMBRANE AND THEIR OWN DNA? NUCLEUS, MITOCHONDRIA, CHLOROPLASTS WHAT ARE CELLS CALLED THAT HAVE NO NUCLEUS and NO ORGANELLES WITH MEMBRANES? PROKARYOTES WHICH ARE CELLS CALLED THAT HAVE A NUCLEUS and ORGANELLES WITH MEMBRANES? EUKARYOTES WHICH KINDS OF CELLS ARE EUKARY ...
... WHICH CELL PARTS HAVE A DOUBLE MEMBRANE AND THEIR OWN DNA? NUCLEUS, MITOCHONDRIA, CHLOROPLASTS WHAT ARE CELLS CALLED THAT HAVE NO NUCLEUS and NO ORGANELLES WITH MEMBRANES? PROKARYOTES WHICH ARE CELLS CALLED THAT HAVE A NUCLEUS and ORGANELLES WITH MEMBRANES? EUKARYOTES WHICH KINDS OF CELLS ARE EUKARY ...
McDougal Notes 1.2 Cell Structure for 8th period
... Press the F5 button at the top of your keyboard to start the presentation. ...
... Press the F5 button at the top of your keyboard to start the presentation. ...
Cell Structure and Function Part 1: Eukaryotic Cells
... Cell Structure and Function Although the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms, cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exc ...
... Cell Structure and Function Although the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms, cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exc ...
Implication of mitochondrial dysfunction in tumor malignancy
... Mitochondria play essential and various roles including production of cellular energy, participation of numerous metabolic reactions and apoptosis. Recently, it has been reported that mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with various pathological condition, especially cancer. However, the underly ...
... Mitochondria play essential and various roles including production of cellular energy, participation of numerous metabolic reactions and apoptosis. Recently, it has been reported that mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with various pathological condition, especially cancer. However, the underly ...
CHAPTER 7 STUDY GUIDE
... study the fine details of cell structures. Uses stains with heavy metals (ex: gold) which kills cells. Images are 3-dimensional. 3. Phase contract microscopes: used to examine unstained living cells and cell growth in tissue culture. b. Other tools for studying cells: i. Cell fractionation: taking c ...
... study the fine details of cell structures. Uses stains with heavy metals (ex: gold) which kills cells. Images are 3-dimensional. 3. Phase contract microscopes: used to examine unstained living cells and cell growth in tissue culture. b. Other tools for studying cells: i. Cell fractionation: taking c ...
Lesson Overview
... Cancer: Uncontrolled Cell Growth Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells. As a result, the cells divide uncontrollably. Cancer is a disorder in which body cells lose the ability to control cell growth. Cancer cells divide uncontrollably to form a mass of cel ...
... Cancer: Uncontrolled Cell Growth Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells. As a result, the cells divide uncontrollably. Cancer is a disorder in which body cells lose the ability to control cell growth. Cancer cells divide uncontrollably to form a mass of cel ...
Cell Structure, Function, and Transport Review Power point
... 31. How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different a. Eukaryotic cells have DNA b. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus c. Eukaryotic cells have ribosomes d. Prokayotic cells have a cell wall. ...
... 31. How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different a. Eukaryotic cells have DNA b. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus c. Eukaryotic cells have ribosomes d. Prokayotic cells have a cell wall. ...
Cells - TeacherWeb
... • All organisms are made up of one or more cells. • Cells are the fundamental and structural unit of life. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... • All organisms are made up of one or more cells. • Cells are the fundamental and structural unit of life. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Immunology Lab
... _________________________, the body’s own antigens. This process is known as _________________________ selection. Immature T cells that do not recognize the body’s own antigens are called _________________________ and allowed to mature. ...
... _________________________, the body’s own antigens. This process is known as _________________________ selection. Immature T cells that do not recognize the body’s own antigens are called _________________________ and allowed to mature. ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 13. The membrane surrounding the cell 14. Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells 15. Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell 16. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer 17. Storage for nutrients and water in plant cells ...
... 13. The membrane surrounding the cell 14. Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells 15. Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell 16. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer 17. Storage for nutrients and water in plant cells ...
Unit 1 - Lonoke School District
... MC.1.B.3 Investigate the properties and importance of water and its significance for life. MC.1.B.5 Explain the role of energy in chemical reactions of living systems. MC.2.B.1 Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. MC.2.B.2 Compare and contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotes. MC.2.B.4 ...
... MC.1.B.3 Investigate the properties and importance of water and its significance for life. MC.1.B.5 Explain the role of energy in chemical reactions of living systems. MC.2.B.1 Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. MC.2.B.2 Compare and contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotes. MC.2.B.4 ...
The Cell - davis.k12.ut.us
... Organelles (not notes) • In order to perform these functions, cells have parts called “organelles” • Basically you can think of them like the cell’s organs • And just like your organs, they have functions that keep it running ...
... Organelles (not notes) • In order to perform these functions, cells have parts called “organelles” • Basically you can think of them like the cell’s organs • And just like your organs, they have functions that keep it running ...
Watch thy neighbor: cancer is a communal affair
... analyses are needed to clarify just how malignant these lesions really are, including an assessment of their nuclear morphology and an assay of their metastatic potential. Moreover, given that loss of tissue architecture could predispose cells to genomic instability (Sternlicht et al., 1999), it wil ...
... analyses are needed to clarify just how malignant these lesions really are, including an assessment of their nuclear morphology and an assay of their metastatic potential. Moreover, given that loss of tissue architecture could predispose cells to genomic instability (Sternlicht et al., 1999), it wil ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.