Aim: How do the organelles work together to maintain homeostasis?
... and cows inhale oxygen through the nasal passages into their lungs. This statement demonstrates that living things 1. rely on similar or the same processes, but accomplish them in different ways 2. rely on different processes, but perform them in the same or related ways 3. rely on different process ...
... and cows inhale oxygen through the nasal passages into their lungs. This statement demonstrates that living things 1. rely on similar or the same processes, but accomplish them in different ways 2. rely on different processes, but perform them in the same or related ways 3. rely on different process ...
Chp3-Cells_TEST REVIEW
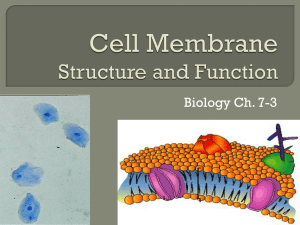
... 2. The Plasma(cell) Membrane: What is the fluid mosaic model?, What are the functions of the following structures: Channel and marker proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids(phosphates and lipids), phospholipid Bilayer, Selectively Permeable. 3. Be able to identify/draw/label diagram of plasma (cell) m ...
... 2. The Plasma(cell) Membrane: What is the fluid mosaic model?, What are the functions of the following structures: Channel and marker proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids(phosphates and lipids), phospholipid Bilayer, Selectively Permeable. 3. Be able to identify/draw/label diagram of plasma (cell) m ...
Cell - WordPress.com
... -The Golgi body further packages/stores proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export". - Flattened, layered, sac-like organelle. ...
... -The Golgi body further packages/stores proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export". - Flattened, layered, sac-like organelle. ...
Question Report - Blue Valley Schools
... A cell has 24 chromosomes during the "G1" phase of interphase. After this cell goes through the process of mitosis, there are two daughter cells. Each of these daughter cells has A B C D ...
... A cell has 24 chromosomes during the "G1" phase of interphase. After this cell goes through the process of mitosis, there are two daughter cells. Each of these daughter cells has A B C D ...
Name: Per. _____ UNIT 4 – CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... 1. Reviewing your notes & worksheets based on the material listed here. 2. By doing this study sheet and then by studying from it. How did the microscope lead to the study of microbiology and ultimately, to the discovery of cells? ...
... 1. Reviewing your notes & worksheets based on the material listed here. 2. By doing this study sheet and then by studying from it. How did the microscope lead to the study of microbiology and ultimately, to the discovery of cells? ...
Name______ -HOME Test Period______ Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... D. An internal membrane system in which components of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed E. Sac-like structure that stores materials ...
... D. An internal membrane system in which components of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed E. Sac-like structure that stores materials ...
Name - Hartland High School
... I. Using the blank Venn diagram on the back side of this page, compare and contrast plant and animal cells. II. How does a bacteria cell compare to a plant cell? How does it compare to an animal cell? ...
... I. Using the blank Venn diagram on the back side of this page, compare and contrast plant and animal cells. II. How does a bacteria cell compare to a plant cell? How does it compare to an animal cell? ...
Cells - Crossword Labs
... plant cell a regular, box-likes shape, also protects the cell membrane 5. traps the energy from the sun and changes it into chemical energy 7. are the type of cell whose organelles are not surrounded by membranes 8. is the network of membranes-covered channels 11. is the chemical reaction that takes ...
... plant cell a regular, box-likes shape, also protects the cell membrane 5. traps the energy from the sun and changes it into chemical energy 7. are the type of cell whose organelles are not surrounded by membranes 8. is the network of membranes-covered channels 11. is the chemical reaction that takes ...
Organelles in Plant and Animal Cells
... SIZE: range from .2m – 0.2um (most are 10-50um) -not all are microscopic (most are) ex: giraffe’s nerve cells extend 6.5 ft. down it’s leg!! ...
... SIZE: range from .2m – 0.2um (most are 10-50um) -not all are microscopic (most are) ex: giraffe’s nerve cells extend 6.5 ft. down it’s leg!! ...
cells
... storage because each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information. Cell division solves the problem of surfacearea-to-volume-ratio by increasing surface area and decreasing volume. ...
... storage because each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information. Cell division solves the problem of surfacearea-to-volume-ratio by increasing surface area and decreasing volume. ...
Cells - Kent
... that captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food during photosynthesis *only in plants, algae and some bacteria cells ...
... that captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food during photosynthesis *only in plants, algae and some bacteria cells ...
Cell growth - Singapore Math
... Cells grow and divide themselves regularly. Organisms are able to grow and recover from wounds because their cells go through cell division. When a cell divides, its nucleus and cytoplasm divide and create two identical cells. The original cell is called the mother cell and the resulting two cells a ...
... Cells grow and divide themselves regularly. Organisms are able to grow and recover from wounds because their cells go through cell division. When a cell divides, its nucleus and cytoplasm divide and create two identical cells. The original cell is called the mother cell and the resulting two cells a ...
12/10/09
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
Pathways of Communication
... 1. Cell specific 2. Dynamic – overstimulation = adaptation 3. Potential blockage ...
... 1. Cell specific 2. Dynamic – overstimulation = adaptation 3. Potential blockage ...
Name Period ______ Section 3: Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story
... Name ________________________________ Period __________ Section 3: Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story (p. 68) 1. What two things helped scientists see more details in cells? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ Holding It All Tog ...
... Name ________________________________ Period __________ Section 3: Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story (p. 68) 1. What two things helped scientists see more details in cells? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ Holding It All Tog ...
Cellular Structure
... Separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Controls what enters or leaves the nucleus. Has tiny openings called pores. ...
... Separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Controls what enters or leaves the nucleus. Has tiny openings called pores. ...
Chapter 8: Cell Reproduction
... faces as it increases in size • Be able to compare and contrast sexual & asexual reproduction • Be able to describe the structure of a chromosome • Be able to identify the differences in structure between prokaryotic chromosomes and eukaryotic chromosomes • Be able to explain the differences between ...
... faces as it increases in size • Be able to compare and contrast sexual & asexual reproduction • Be able to describe the structure of a chromosome • Be able to identify the differences in structure between prokaryotic chromosomes and eukaryotic chromosomes • Be able to explain the differences between ...
Notes for Cell Packet, p. 16-17 (PPT
... 2 kinds of E.R. • Smooth E.R.- Does not have ribosomes. • Rough E.R.-Has ribosomes studded on it and produces proteins. ...
... 2 kinds of E.R. • Smooth E.R.- Does not have ribosomes. • Rough E.R.-Has ribosomes studded on it and produces proteins. ...
Abstract
... *e-mail:[email protected] Received April 28, 2006; revision accepted August 5, 2006 The development of the suspensor in Sedum acre L. and S. hispanicum L. was investigated using cytochemical methods and light microscopy. After the first division of the zygote, two cells of unequal size ar ...
... *e-mail:[email protected] Received April 28, 2006; revision accepted August 5, 2006 The development of the suspensor in Sedum acre L. and S. hispanicum L. was investigated using cytochemical methods and light microscopy. After the first division of the zygote, two cells of unequal size ar ...