Video Worksheet: Bill Nye~Cells
... _______ 5. _________________ are the road map for cells and tell the cells what to do _______ 6. ___________ is our body’s fastest growing organ because we shed millions of these cells every day _______ 7. Genes are made of _______________ _______ 8. Humans have ______ pairs of chromosomes (46 total ...
... _______ 5. _________________ are the road map for cells and tell the cells what to do _______ 6. ___________ is our body’s fastest growing organ because we shed millions of these cells every day _______ 7. Genes are made of _______________ _______ 8. Humans have ______ pairs of chromosomes (46 total ...
The Cell
... in a discussion with Dr. Miller and expand on learned biological concepts by connecting ideas and asking questions. Summarize the main components of Dr. Miller’s presentation. ...
... in a discussion with Dr. Miller and expand on learned biological concepts by connecting ideas and asking questions. Summarize the main components of Dr. Miller’s presentation. ...
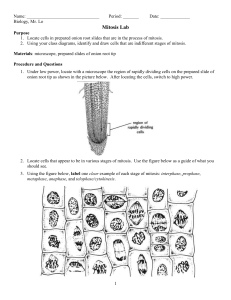
Lab 24 – Mitosis Wheel
... Cells form new cells by a process called cell division or mitosis. During mitosis, one cell divides in half to form two new cells. Suppose you could watch a cell divide. You could see that the cell parts called chromosomes move around the cell during mitosis. Because chromosomes move in particular w ...
... Cells form new cells by a process called cell division or mitosis. During mitosis, one cell divides in half to form two new cells. Suppose you could watch a cell divide. You could see that the cell parts called chromosomes move around the cell during mitosis. Because chromosomes move in particular w ...
Experiment 26 Bishop Voltaic and Electrolytic Cells Objective
... cathode Electrode enters the cell Negative in the electrolytic cell. ...
... cathode Electrode enters the cell Negative in the electrolytic cell. ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Mitosis
... Mitosis starts and ends with diploid cells. That means they have two sets of chromosomes (both parents each contribute a set). In humans, how many chromosomes should be in each of these diploid cells after mitosis? ...
... Mitosis starts and ends with diploid cells. That means they have two sets of chromosomes (both parents each contribute a set). In humans, how many chromosomes should be in each of these diploid cells after mitosis? ...
Cells Last minute sheet
... A cell cycles between periods of cell division, growth, normal activity (interphase) and back to division. DNA replication occurs - DNA makes exact copy of itself prior to cell division so there is a full set of genetic information available in each cell after division - then preparation for mitos ...
... A cell cycles between periods of cell division, growth, normal activity (interphase) and back to division. DNA replication occurs - DNA makes exact copy of itself prior to cell division so there is a full set of genetic information available in each cell after division - then preparation for mitos ...
Warm Up: Introduction to Cells Warm Up: Introduction to Cells
... Name _______________________________________________ Period ___________ Date ______________ ...
... Name _______________________________________________ Period ___________ Date ______________ ...
Cells
... All living things are composed of one or more cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living organisms Cells come from other cells ...
... All living things are composed of one or more cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living organisms Cells come from other cells ...
Micro Unit Test
... light and uses it to make food • Cellular Respiration- the process by which cells obtain energy from glucose ...
... light and uses it to make food • Cellular Respiration- the process by which cells obtain energy from glucose ...
Plant Cells - New Brigden School
... Cytoplasm is the fluid that fills a cell. Scientists used to call the fluid protoplasm. Early on, they didn't know about the many different types of fluids in the cell. There is special fluid in the mitochondria, ...
... Cytoplasm is the fluid that fills a cell. Scientists used to call the fluid protoplasm. Early on, they didn't know about the many different types of fluids in the cell. There is special fluid in the mitochondria, ...
Chapter 5 Cell Membrane
... Hydrophobic interactions force the "tails" to face inward Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid • Cholesterol embedded in the membrane makes it stronger and less fluid ...
... Hydrophobic interactions force the "tails" to face inward Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid • Cholesterol embedded in the membrane makes it stronger and less fluid ...
Phagocytosis - mrswalmsley
... using a carrier protein. ATP activates the protein to move glucose into the cell even though the concentration outside the cell is ...
... using a carrier protein. ATP activates the protein to move glucose into the cell even though the concentration outside the cell is ...
Plant and Animal Cells Study Guide
... 1. cells: c (all living things are made of these) 2. microscope: e (tool used to magnify objects) 3. cell wall: g (thick, rigid membrane surrounding plant cells) 4. cell membrane: h (surrounds all cells) 5. nucleus: b (controls cells, where DNA is stored) 6. vacuole: d (stores material and waste 7. ...
... 1. cells: c (all living things are made of these) 2. microscope: e (tool used to magnify objects) 3. cell wall: g (thick, rigid membrane surrounding plant cells) 4. cell membrane: h (surrounds all cells) 5. nucleus: b (controls cells, where DNA is stored) 6. vacuole: d (stores material and waste 7. ...
CHROMOSOMES - Bishop Montgomery High School
... Bacteria reproduce using __________________________________ ...
... Bacteria reproduce using __________________________________ ...
3 - Riverside City College
... Constantly changing Dynamic role in cellular activity Separates intracellular fluid (ICF) from extracellular fluid (ECF) ...
... Constantly changing Dynamic role in cellular activity Separates intracellular fluid (ICF) from extracellular fluid (ECF) ...
Cell Jeopardy
... around all cells, it controls interactions between the cell and its environment. It allows materials to enter and exit the cell. ...
... around all cells, it controls interactions between the cell and its environment. It allows materials to enter and exit the cell. ...
Unit1-KA1-Revision
... How do we improve the reliability of Repeat the experiment the results of an experiment? Why do we repeat experiments? To improve the reliability of the results How do we improve the validity of an By improving its design. For example, having experiment? all the reagents at the same temperature to s ...
... How do we improve the reliability of Repeat the experiment the results of an experiment? Why do we repeat experiments? To improve the reliability of the results How do we improve the validity of an By improving its design. For example, having experiment? all the reagents at the same temperature to s ...
Cell Structure Practice: Vacuole
... Explain how the cell wall is different from the cell membrane in terms of their functions. Cell membrane: controls what enters/leaves Cell wall: provides structure A ...
... Explain how the cell wall is different from the cell membrane in terms of their functions. Cell membrane: controls what enters/leaves Cell wall: provides structure A ...
Studies on BI-010
... an E3 ligase binds to the RXXL motif leading to ubiquitination of the lysine residue in the KEN box and ultimately degradation of the protein. This allows expression of proteins such as BI-010 to be highly regulated during the cell cycle so that cell division is controlled. In patients with a range ...
... an E3 ligase binds to the RXXL motif leading to ubiquitination of the lysine residue in the KEN box and ultimately degradation of the protein. This allows expression of proteins such as BI-010 to be highly regulated during the cell cycle so that cell division is controlled. In patients with a range ...
Animal Cell
... Membrane is a structure that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell ...
... Membrane is a structure that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell ...
cell notes organizer answers1
... 2. has many pores 3. regulates what goes in and out of nucleus Direct cell activity; pass on genetic traits Protects and supports the cell ...
... 2. has many pores 3. regulates what goes in and out of nucleus Direct cell activity; pass on genetic traits Protects and supports the cell ...
1. Organelle: A structure within a cell. 2. Chromosome: A threadlike
... • Before a cell can divide it needs to grow and increase the number of sub-cellular structures such as ribosomes and mitochondria. The DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome. • In mitosis one set of chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides. • Finally the cy ...
... • Before a cell can divide it needs to grow and increase the number of sub-cellular structures such as ribosomes and mitochondria. The DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome. • In mitosis one set of chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides. • Finally the cy ...
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function in the Bacteria and Archaea
... Cell Structure and Function in the Bacteria and Archaea Chapter Summary and Essay Questions Chapter 4 deals with the diversity of the two prokaryotic domains, the Bacteria and the Archaea. This is followed by a discussion of the diversity of their cell shape and arrangement. The remaining parts of t ...
... Cell Structure and Function in the Bacteria and Archaea Chapter Summary and Essay Questions Chapter 4 deals with the diversity of the two prokaryotic domains, the Bacteria and the Archaea. This is followed by a discussion of the diversity of their cell shape and arrangement. The remaining parts of t ...