1. Most viruses consist of genetic material and which of the following
... 6. Which cycle is demonstrated by a virus that has infected a host cell but is not being replicated? a) lysogenic cycle b) lytic cycle c) citric acid cycle d) cell cycle 7. Which illness is not caused by a virus? a) cholera b) flu c) HIV d) common cold 8. Which term applies to the specific type of v ...
... 6. Which cycle is demonstrated by a virus that has infected a host cell but is not being replicated? a) lysogenic cycle b) lytic cycle c) citric acid cycle d) cell cycle 7. Which illness is not caused by a virus? a) cholera b) flu c) HIV d) common cold 8. Which term applies to the specific type of v ...
What could have caused this?
... masses of cancerous cells) will result because of this uncontrolled cell division. • Tumors can be either malignant (spread dangerous) or benign (can’t spread – safe) ...
... masses of cancerous cells) will result because of this uncontrolled cell division. • Tumors can be either malignant (spread dangerous) or benign (can’t spread – safe) ...
Ch.4 Notes - Green Local Schools
... • Cell: smallest unit that can carry on the processes of life • Hooke (1665): looked at plants under microscope & saw “little boxes” – Named them “cells” ...
... • Cell: smallest unit that can carry on the processes of life • Hooke (1665): looked at plants under microscope & saw “little boxes” – Named them “cells” ...
Exchange with the Environment
... Mitosis: • If a cell wants to make a duplicate of itself, it first must copy its DNA (part of a chromosome). • The copies then must be separated & sorted into two sides of the cell. • The cell then splits in two. Part of each parent is carried to the two new cells. • Results in cells such as intern ...
... Mitosis: • If a cell wants to make a duplicate of itself, it first must copy its DNA (part of a chromosome). • The copies then must be separated & sorted into two sides of the cell. • The cell then splits in two. Part of each parent is carried to the two new cells. • Results in cells such as intern ...
Plasma Membrane
... Fluid Mosaic Model • The phospholipids flow like water (fluid) • The proteins move throughout the phospholipids like boats. – They make up the “Mosaic” ...
... Fluid Mosaic Model • The phospholipids flow like water (fluid) • The proteins move throughout the phospholipids like boats. – They make up the “Mosaic” ...
NoB1ch02QUICKcheck-ed
... Consider a cell with cilia beating on its surface. Identify one other organelle that would be expected to assist in the action of these cilia. Because the beating of cilia is an energy-requiring process of a cell, it is reasonable to suggest that mitochondria would be present to assist the action of ...
... Consider a cell with cilia beating on its surface. Identify one other organelle that would be expected to assist in the action of these cilia. Because the beating of cilia is an energy-requiring process of a cell, it is reasonable to suggest that mitochondria would be present to assist the action of ...
Apple Cells
... Identify 3 functions of plastids. Perform photosynthesis, gravity perception, storage of molecules. ...
... Identify 3 functions of plastids. Perform photosynthesis, gravity perception, storage of molecules. ...
Cell division and mitosis
... A kinetochore is formed at the centromere, the point where the sister chromatids are attached Microtubules attach at the kinetochores Metaphase Shortest phase of mitosis Centrioles are at poles Chromosomes line up in the middle along equator Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes on the centromere Ana ...
... A kinetochore is formed at the centromere, the point where the sister chromatids are attached Microtubules attach at the kinetochores Metaphase Shortest phase of mitosis Centrioles are at poles Chromosomes line up in the middle along equator Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes on the centromere Ana ...
Name: Date:______ Period
... Many cells grow until they reach a certain size and then divide. Why don’t cells grow indefinitely until they become the size of basketballs? What problems arise when a cell grows larger? Why does a cell divide into two smaller cells when it reaches a certain size? These are all questions that scien ...
... Many cells grow until they reach a certain size and then divide. Why don’t cells grow indefinitely until they become the size of basketballs? What problems arise when a cell grows larger? Why does a cell divide into two smaller cells when it reaches a certain size? These are all questions that scien ...
Microscope and Cells
... Cytoskeleton (including cilia, flagella, and centrioles in animal cells) ◦ Maintenance of cell shape; anchorage for organelles; movement of organelles within cells; cell movement; mechanical transmission of signals from exterior of cell to interior. Cilia and flagella move the cell or move substance ...
... Cytoskeleton (including cilia, flagella, and centrioles in animal cells) ◦ Maintenance of cell shape; anchorage for organelles; movement of organelles within cells; cell movement; mechanical transmission of signals from exterior of cell to interior. Cilia and flagella move the cell or move substance ...
Radiobiology Lec:3 Stage:2 3.Cell death after irradiation
... Cellular senescence is the term given to the observation that over time normal cells permanently lose their ability to divide. These cells remain present, metabolically intact and may or may not display functional changes. In addition to this replicative form of senescence, ‘premature’ senescence ca ...
... Cellular senescence is the term given to the observation that over time normal cells permanently lose their ability to divide. These cells remain present, metabolically intact and may or may not display functional changes. In addition to this replicative form of senescence, ‘premature’ senescence ca ...
Commercial uses of cells: FUNGUS
... Fungus live on dead and rotting matter, as do BACTERIA Fungus use ANTIBIOTICS to protect themselves from Bacterial infections ...
... Fungus live on dead and rotting matter, as do BACTERIA Fungus use ANTIBIOTICS to protect themselves from Bacterial infections ...
THE CELL THEORY 1. All living things are composed of cells and
... ♦ Various substances move into Golgi Bodies from vesicles formed from ER. Other vesicles pinch off from Golgi Bodies and carry their contents to other parts of the cell. 3 Types of Vacuoles ♦ Mostly found in plant cells and protozoans ♦ Plant vacuoles may contain dissolved starch ♦ Food vacuoles in ...
... ♦ Various substances move into Golgi Bodies from vesicles formed from ER. Other vesicles pinch off from Golgi Bodies and carry their contents to other parts of the cell. 3 Types of Vacuoles ♦ Mostly found in plant cells and protozoans ♦ Plant vacuoles may contain dissolved starch ♦ Food vacuoles in ...
7 Structural components of eucaryote cells
... Make tracks along which transport proteins drag various organelles, such as secretory granules or mitochondria They form the spindle which aligns the chromosomes during mitosis They are constantly being dynamically rearranged; gamma-tubulin is involved in this process DRUGS TARGET MICROTUBULES: COLC ...
... Make tracks along which transport proteins drag various organelles, such as secretory granules or mitochondria They form the spindle which aligns the chromosomes during mitosis They are constantly being dynamically rearranged; gamma-tubulin is involved in this process DRUGS TARGET MICROTUBULES: COLC ...
Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic Cells
... • Monotrichous: a single flagellum at one end • Amphitrichous: a single flagellum at both ends of the cell • Lophotrichous: two or more flagella at one or both ends of the cell. • Peritrichous: flagella all over the cell. ...
... • Monotrichous: a single flagellum at one end • Amphitrichous: a single flagellum at both ends of the cell • Lophotrichous: two or more flagella at one or both ends of the cell. • Peritrichous: flagella all over the cell. ...
Answers to exam questions on Chloroplasts and
... Discuss why the plants did not grow in the sealed bottle but did after the lid was removed. Sealed bottle is a closed envt – water, nutrients, oxygen and carbon dioxide are only available in constant amounts. Plant uses carbon dioxide in p/s (p/s releases oxygen) Oxygen is used in respiration, ...
... Discuss why the plants did not grow in the sealed bottle but did after the lid was removed. Sealed bottle is a closed envt – water, nutrients, oxygen and carbon dioxide are only available in constant amounts. Plant uses carbon dioxide in p/s (p/s releases oxygen) Oxygen is used in respiration, ...
Rev. 1/06 1 LECTURE 3 Cell Structure and Cell Division I. The cell
... a. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is the site of ribosomes. This is where many proteins are made. b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is the site of synthesis for some hormones. It is also the site for detoxification (such as in liver cells). 5. Golgi apparatus –Proteins and other molecules made in the ...
... a. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is the site of ribosomes. This is where many proteins are made. b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is the site of synthesis for some hormones. It is also the site for detoxification (such as in liver cells). 5. Golgi apparatus –Proteins and other molecules made in the ...
Split Notes Cells and Life October 28, 2013
... b. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell. It passes genetic information to offspring from parents. It includes instructions for cell growth, cell reproduction, and cell processes that allow a cell to respond to its environment. DNA is used to make RNA. RNA is used to make prot ...
... b. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell. It passes genetic information to offspring from parents. It includes instructions for cell growth, cell reproduction, and cell processes that allow a cell to respond to its environment. DNA is used to make RNA. RNA is used to make prot ...
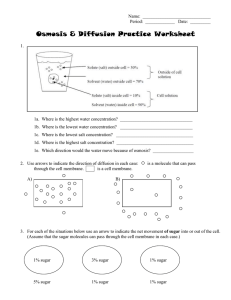
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 3. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
... 3. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
Ch. 4: Plant and Animal Cells
... The thick, gel like liquid inside a cell. Mostly made of water. Keeps the cell thick and puffy. Protects the other organelles inside the cell from bumping into each other and things in the ...
... The thick, gel like liquid inside a cell. Mostly made of water. Keeps the cell thick and puffy. Protects the other organelles inside the cell from bumping into each other and things in the ...
Cellular level of organization
... Nucleus and related structures Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi apparatus Ribosome ...
... Nucleus and related structures Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi apparatus Ribosome ...
Notes 5.1 Osmosis in Action
... Review the Objectives 1.Compare different models to explain the movement of materials into and out of the cell and the role of the solution the cells exist within. ...
... Review the Objectives 1.Compare different models to explain the movement of materials into and out of the cell and the role of the solution the cells exist within. ...
Cell Structure
... 3. Fill in: Name the organelle or organelles that perform each of the following functions. ...
... 3. Fill in: Name the organelle or organelles that perform each of the following functions. ...