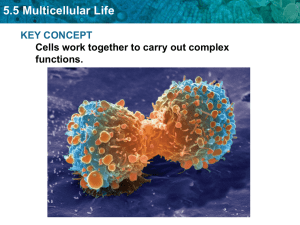
5.5 Multicellular Life KEY CONCEPT Cells work together to carry out complex functions.
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
Cell Quiz/Test
... 7. An organic molecule used for energy (includes sugars and starches) 8. When molecules spread out to reach a balance (equilibrium) 9. The pigment in plant cells (inside the choloroplast) that traps the energy in sunlight 10. In the ribosomes of a cell chemical reactions join amino acids to form thi ...
... 7. An organic molecule used for energy (includes sugars and starches) 8. When molecules spread out to reach a balance (equilibrium) 9. The pigment in plant cells (inside the choloroplast) that traps the energy in sunlight 10. In the ribosomes of a cell chemical reactions join amino acids to form thi ...
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
... - The scanning electron microscope (SEM) provides for detailed study of the surface of a specimen. - The transmission electron microscope (TEM) provides for detailed study of the internal ultrastructure of cells. B. Isolating Organelles by Cell Fractionation - Cell fractionation takes cells apart an ...
... - The scanning electron microscope (SEM) provides for detailed study of the surface of a specimen. - The transmission electron microscope (TEM) provides for detailed study of the internal ultrastructure of cells. B. Isolating Organelles by Cell Fractionation - Cell fractionation takes cells apart an ...
Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells
... By not digesting them completely, but removing the cell wall, the archaeon has gained two gigantic biochemical pathways: respiration and photosynthesis By moving critical genes from each endosymbiont, using its transposon feature, the archaeon has trapped both endosymbionts as permanent organelles T ...
... By not digesting them completely, but removing the cell wall, the archaeon has gained two gigantic biochemical pathways: respiration and photosynthesis By moving critical genes from each endosymbiont, using its transposon feature, the archaeon has trapped both endosymbionts as permanent organelles T ...
Brief Introduction to Animal and Plant Cells NAME: ANIMAL CELLS
... more cells. Cells are filled with a jellylike fluid called cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is like a thick soup filled with small structures that have specific jobs to do in the cell. These structures are called organelles, and they work together to keep alive molecules used by the cell. Plant cells also h ...
... more cells. Cells are filled with a jellylike fluid called cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is like a thick soup filled with small structures that have specific jobs to do in the cell. These structures are called organelles, and they work together to keep alive molecules used by the cell. Plant cells also h ...
Introduction to Cell Biology Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
... Basic building blocks Matthias Jakob Schleiden, a German botanist, proposes that all plant tissues are composed of cells, and that cells are the basic building blocks of all plants. This statement was the first generalized statement about cells. Cell theory Theodor Schwann, a German botanist reached ...
... Basic building blocks Matthias Jakob Schleiden, a German botanist, proposes that all plant tissues are composed of cells, and that cells are the basic building blocks of all plants. This statement was the first generalized statement about cells. Cell theory Theodor Schwann, a German botanist reached ...
Vocabulary Assignment Unit 03
... n. Small organelle found in all cells that makes protein; not wrapped in membrane o. Sacks of membranes that move material around the cell; the cell’s ‘highway’ p. One part of this says all cells came from other cells q. Diffusion in which the material is helped in or out of the cell by protein chan ...
... n. Small organelle found in all cells that makes protein; not wrapped in membrane o. Sacks of membranes that move material around the cell; the cell’s ‘highway’ p. One part of this says all cells came from other cells q. Diffusion in which the material is helped in or out of the cell by protein chan ...
Microviewer Slides
... Cells of Plants and Animals (Microslides 102) Name: ___________________________ In this lab, you will view a variety of plant and animal cells. For each slide, you will draw and picture and answer the questions related to each cell. Some of the answers will be found in the reading booklet, while oth ...
... Cells of Plants and Animals (Microslides 102) Name: ___________________________ In this lab, you will view a variety of plant and animal cells. For each slide, you will draw and picture and answer the questions related to each cell. Some of the answers will be found in the reading booklet, while oth ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins into sacs called vesicles Vesicles can than fuse with the cell’s plasma membrane to release proteins to the environment outside the cell or they can be used internally ...
... Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins into sacs called vesicles Vesicles can than fuse with the cell’s plasma membrane to release proteins to the environment outside the cell or they can be used internally ...
Cells
... 1. Using a scalpel and forceps, remove a small piece of ONE LAYER of onion skin off of an onion and place it on a microscope slide. Avoid wrinkling the specimen. 2. View the onion cells on low power. Center the group of onion cells in field of vision. 3. View the onion cells on medium power. Only us ...
... 1. Using a scalpel and forceps, remove a small piece of ONE LAYER of onion skin off of an onion and place it on a microscope slide. Avoid wrinkling the specimen. 2. View the onion cells on low power. Center the group of onion cells in field of vision. 3. View the onion cells on medium power. Only us ...
Hedgehog Learning. Copying permitted for purchasing campus only
... Bacteria and viruses reproduce using genetic coding found in nucleic acids. ...
... Bacteria and viruses reproduce using genetic coding found in nucleic acids. ...
Cell PP
... the nucleus in which ________(s) are made. 3. Ribosomes are important since they are the sites for ___________ synthesis. 4. Ribosomes leave the __________ and attach to the ____ ____, or the highway of the cell. 5. The mitochondria contains its own ________ and turns the energy from ________ molecu ...
... the nucleus in which ________(s) are made. 3. Ribosomes are important since they are the sites for ___________ synthesis. 4. Ribosomes leave the __________ and attach to the ____ ____, or the highway of the cell. 5. The mitochondria contains its own ________ and turns the energy from ________ molecu ...
This question is about cells. A and B
... Give the letters of two parts of the leaf cell which would not be found in a sperm cell. ...
... Give the letters of two parts of the leaf cell which would not be found in a sperm cell. ...
Cell Structure
... animal cell drawing with labels…what kind of drawing do you want to have for your catalog. (1 point) • Label the drawing (1 point) • Think of a name for your catalog of organelles (What analogy will you use for this catalog) (1 point) • Put your name, date and period on this page (1 point) • Finish ...
... animal cell drawing with labels…what kind of drawing do you want to have for your catalog. (1 point) • Label the drawing (1 point) • Think of a name for your catalog of organelles (What analogy will you use for this catalog) (1 point) • Put your name, date and period on this page (1 point) • Finish ...
What is a cell Cell is the basic living, structural and
... Concentration gradient: one area ions are highly concentrated than the other & the difference in the concentration is known as the gradient. One two such areas are connected they cause movement of ions/molecules from area of high conc to low conc called net diffusion. Point of even distribution is c ...
... Concentration gradient: one area ions are highly concentrated than the other & the difference in the concentration is known as the gradient. One two such areas are connected they cause movement of ions/molecules from area of high conc to low conc called net diffusion. Point of even distribution is c ...
Biology - Central Lyon CSD
... 4. Using the internet, books, and other resources, implement the following structures into your cell: Golgi body, plasma membrane, lysosome, vacuole, nucleolus, nucleus, centriole, microfilaments, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, free ribosomes, microtubules, nuclear membrane, chromatin, and cyt ...
... 4. Using the internet, books, and other resources, implement the following structures into your cell: Golgi body, plasma membrane, lysosome, vacuole, nucleolus, nucleus, centriole, microfilaments, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, free ribosomes, microtubules, nuclear membrane, chromatin, and cyt ...
Bringing Classical Embryology to C. elegans Gastrulation
... rolling of MSxx provides the driving force for cell rearrangement in C. elegans. It should now be possible to address these traditionally difficult questions by generating mosaic explants where individual cells are selectively modified by genetic or pharmacological techniques. It will also be import ...
... rolling of MSxx provides the driving force for cell rearrangement in C. elegans. It should now be possible to address these traditionally difficult questions by generating mosaic explants where individual cells are selectively modified by genetic or pharmacological techniques. It will also be import ...
Cells: A Busy Factory Adapted
... cell's "factory floor." The term "cytoplasm" refers to everything between the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane. It consists mostly of water, salts, some proteins, and many small structures called organelles (or little organs). These structures perform ...
... cell's "factory floor." The term "cytoplasm" refers to everything between the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane. It consists mostly of water, salts, some proteins, and many small structures called organelles (or little organs). These structures perform ...
15. Cell Structure Gizmo CellStructureTG
... their cells. Each group will need to bring in a container for the Jell-O and edible items to represent the organelles. Examples could be jawbreakers for a nucleus, licorice for the Golgi apparatus, orange slices for mitochondria, etc. Be creative! On the second day, students bring in their materials ...
... their cells. Each group will need to bring in a container for the Jell-O and edible items to represent the organelles. Examples could be jawbreakers for a nucleus, licorice for the Golgi apparatus, orange slices for mitochondria, etc. Be creative! On the second day, students bring in their materials ...
5.1 The Cell Cycle
... ~ could not contain necessary organelles & molecules – cannot be too large ~ if ratio of surface area to volume is too small, oxygen, nutrients, and waste cannot move in and out of the cell ...
... ~ could not contain necessary organelles & molecules – cannot be too large ~ if ratio of surface area to volume is too small, oxygen, nutrients, and waste cannot move in and out of the cell ...























