Name Date Block ______ Cell Theory Equation Directions: Write in
... Name _________________________ Date _______________ Block __________ ...
... Name _________________________ Date _______________ Block __________ ...
7.3 From Cell To Organism
... a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood throughout the body ...
... a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood throughout the body ...
Slide 1
... 4. In the cell membrane model shown below, the molecules which move large molecules into and out of the cell are known as — A cholesterol B proteins C lipids D carbohydrates ...
... 4. In the cell membrane model shown below, the molecules which move large molecules into and out of the cell are known as — A cholesterol B proteins C lipids D carbohydrates ...
WHAT AM I?
... the resting potential?, What triggers the action potential? Compare the central nervous system and the Peripheral nervous system? 4. WHITE BLOOD CELLS, FUNCTION: This cell functions in defending the body against infections and cancer cells. The white blood cells have a variety of ways by which they ...
... the resting potential?, What triggers the action potential? Compare the central nervous system and the Peripheral nervous system? 4. WHITE BLOOD CELLS, FUNCTION: This cell functions in defending the body against infections and cancer cells. The white blood cells have a variety of ways by which they ...
STAAR Review, Friday, Jan 20
... b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c. Contain ribosomes d. DNA B. Major differences a. Eukaryotes are more complex and larger in size ...
... b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c. Contain ribosomes d. DNA B. Major differences a. Eukaryotes are more complex and larger in size ...
The cell is the smallest unit of life
... The _________ is the smallest unit of life. Anything smaller is not alive. ___________ living things are made of cells. There are three basic types of cells. ________________,________________, &_______________. Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________ ...
... The _________ is the smallest unit of life. Anything smaller is not alive. ___________ living things are made of cells. There are three basic types of cells. ________________,________________, &_______________. Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________ ...
Assessment
... _____ 7. Which of these includes the main parts of an organ system? a. leaves on a tree c. heart and blood vessels b. stem of a flower d. large mass of amoebas _____ 8. In which of these does true multicellularity occur? a. eukaryotes c. colonial organisms b. prokaryotes d. All of the above _____ 9. ...
... _____ 7. Which of these includes the main parts of an organ system? a. leaves on a tree c. heart and blood vessels b. stem of a flower d. large mass of amoebas _____ 8. In which of these does true multicellularity occur? a. eukaryotes c. colonial organisms b. prokaryotes d. All of the above _____ 9. ...
Cell Features
... cell interior is called the Cytoplasm Cytosol: fluid in the cytoplasm Microscopic fibers called the cytoskeleton in the cytoplasm help suspend structures Ribosomes: cellular structure on which proteins are made ...
... cell interior is called the Cytoplasm Cytosol: fluid in the cytoplasm Microscopic fibers called the cytoskeleton in the cytoplasm help suspend structures Ribosomes: cellular structure on which proteins are made ...
Structure and Function of Cells
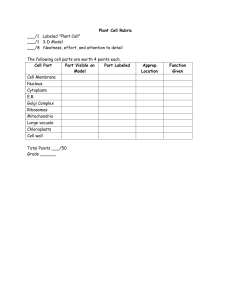
... Complete the table below. You do not need to write in full sentences. Cell Part ...
... Complete the table below. You do not need to write in full sentences. Cell Part ...
Ch.1 Notes - Green Local Schools
... cell specialization elaboration of one function and reduction of others ...
... cell specialization elaboration of one function and reduction of others ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure Crossword Puzzle
... 7 This type of cell has a membrane-bound nucleus. 8 The scientific name for fat, this forms two layers in the cell membrane. 11This provides energy to the cell. 14This is made up of microfilaments and microtubules and help to maintain the shape of the cell. 15This structure is only found in animal c ...
... 7 This type of cell has a membrane-bound nucleus. 8 The scientific name for fat, this forms two layers in the cell membrane. 11This provides energy to the cell. 14This is made up of microfilaments and microtubules and help to maintain the shape of the cell. 15This structure is only found in animal c ...
Cells and Batteries
... to obtain a larger amount of energy and a higher electric potential (voltage). Batteries are made of a serious of cells. A 9 volt, has 6 cells that produced 1.5V each (1.5V x 6 cells = 9V). ...
... to obtain a larger amount of energy and a higher electric potential (voltage). Batteries are made of a serious of cells. A 9 volt, has 6 cells that produced 1.5V each (1.5V x 6 cells = 9V). ...
Biology- ch. 7
... • Used a microscope to study nature in 1600’s in Holland • He was the first person to see living organisms in a drop of water ...
... • Used a microscope to study nature in 1600’s in Holland • He was the first person to see living organisms in a drop of water ...
Review Test 2 Life , Cells, Cell Processes
... chloroplasts in which animal cells do not. Otherwise they contain the same organelles, are alive, and are the building blocks of living things ...
... chloroplasts in which animal cells do not. Otherwise they contain the same organelles, are alive, and are the building blocks of living things ...
The Cell and Cell Division Exercises
... 12. A species has a chromosome number of 8 in a root cell. How many would you expect to find in pollen grains and why? ...
... 12. A species has a chromosome number of 8 in a root cell. How many would you expect to find in pollen grains and why? ...
Cell: Smallest Unit of Life
... compartments Endomembrane system- internal system of membrane bound compartments ...
... compartments Endomembrane system- internal system of membrane bound compartments ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.