The Cell
... Mitochondrion produces ATP through respiration, and regulates cellular metabolism. A stomach digests food and produces waste. ...
... Mitochondrion produces ATP through respiration, and regulates cellular metabolism. A stomach digests food and produces waste. ...
Unit 5 SCA Review Sheet
... 4. I am a group of cells who work together to perform a particular function. __________________________________________________ 5. I am one of the four different types of tissue. I add support and structure to the body, I fill spaces and I also store fat. ___________________________________________ ...
... 4. I am a group of cells who work together to perform a particular function. __________________________________________________ 5. I am one of the four different types of tissue. I add support and structure to the body, I fill spaces and I also store fat. ___________________________________________ ...
The Cell Cycle
... What do we know so far? • Still working out all the chemical and physical signals. • Over 50 growth factors have been identified • Different cell types respond differently to different growth factors ...
... What do we know so far? • Still working out all the chemical and physical signals. • Over 50 growth factors have been identified • Different cell types respond differently to different growth factors ...
Cells
... All living things are composed of 1 or more cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function. Cells come only from existing cells. ...
... All living things are composed of 1 or more cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function. Cells come only from existing cells. ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... microscope? Explain your answer. With a light microscope you could easily distinguish the prokaryotic bacteria from the other cell types. The prokaryotic bacteria would not have a nucleus, the other cell types would. The yeast cell wall would distinguish yeast cells from human and insect cells. Dist ...
... microscope? Explain your answer. With a light microscope you could easily distinguish the prokaryotic bacteria from the other cell types. The prokaryotic bacteria would not have a nucleus, the other cell types would. The yeast cell wall would distinguish yeast cells from human and insect cells. Dist ...
Lecture 11: Cell proliferation, differentiation, and death
... It is a normal physiological form of cell death with a distinct process known as apoptosis. It plays a key role both in the maintenance of adult tissues and in embryonic development. Renewal of 5 × 1011 blood cells a day elimination of nerve cells with faulty connection Elimination of damaged and po ...
... It is a normal physiological form of cell death with a distinct process known as apoptosis. It plays a key role both in the maintenance of adult tissues and in embryonic development. Renewal of 5 × 1011 blood cells a day elimination of nerve cells with faulty connection Elimination of damaged and po ...
Study Guide for Microscope and Cell Test
... 6. A compound microscope is the most common type of microscope use in the classroom. 7. 2 differences between a plant and an animal cell are plant cells contain a cell wall and chloroplasts. 8. Ro ...
... 6. A compound microscope is the most common type of microscope use in the classroom. 7. 2 differences between a plant and an animal cell are plant cells contain a cell wall and chloroplasts. 8. Ro ...
Student printout - The Cell Big Picture
... So again we are learning about the very small, but… Looking at it like this ...
... So again we are learning about the very small, but… Looking at it like this ...
Organelle Notes
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
New Treatments Methods for TBI
... What in the world is a human neural progenitor cell?! • “A progenitor cell is a biological cell that, like a stem cell, has a tendency to change into a specific type of cell, but is already more specific than a stem cell and is pushed to change into its "target" cell. • The most important differenc ...
... What in the world is a human neural progenitor cell?! • “A progenitor cell is a biological cell that, like a stem cell, has a tendency to change into a specific type of cell, but is already more specific than a stem cell and is pushed to change into its "target" cell. • The most important differenc ...
Notes Outline: How Cells Divide (4
... Notes Outline: Mitosis and Cell Division (6.2) “ As cells busily carry out the functions of life, they grow and develop. When most cells reach a certain size, they either stop growing or divide into two cells. Cell division is essential for the growth and development or an organism.” I. ...
... Notes Outline: Mitosis and Cell Division (6.2) “ As cells busily carry out the functions of life, they grow and develop. When most cells reach a certain size, they either stop growing or divide into two cells. Cell division is essential for the growth and development or an organism.” I. ...
First Six Weeks Test Corrections The cell membrane controls what
... 8. Carbon is considered to be an element and carbon dioxide is considered a compound. Carbon dioxide has two different elements. 9. Organic means made from living material. 10. Carbon is found in all organic compounds. 11. Na, Fe, K and C are elements ...
... 8. Carbon is considered to be an element and carbon dioxide is considered a compound. Carbon dioxide has two different elements. 9. Organic means made from living material. 10. Carbon is found in all organic compounds. 11. Na, Fe, K and C are elements ...
Unit 1 Lesson 1 Notes - Belle Vernon Area School District
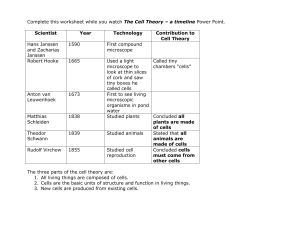
... The three basic characteristics of all organisms 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. (Schleiden) 2. The cell is the basic unit of life (Schwann) 3. All cells come from existing cells (Virchow) Things found in all Cells ...
... The three basic characteristics of all organisms 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. (Schleiden) 2. The cell is the basic unit of life (Schwann) 3. All cells come from existing cells (Virchow) Things found in all Cells ...
Slide 1
... The process by which water molecules defuse across a cell membrane from a area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. ...
... The process by which water molecules defuse across a cell membrane from a area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. ...
No Slide Title
... obtains nourishment mostly by eating small fish. Its cells do not have a cell wall and it moves by pushing water outward. What type of organism is a jellyfish? a. plant b. animal c. fungi d. protist ...
... obtains nourishment mostly by eating small fish. Its cells do not have a cell wall and it moves by pushing water outward. What type of organism is a jellyfish? a. plant b. animal c. fungi d. protist ...
Microbiology Slides - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
File
... d Living cells are able to detect changes in their environment and to make appropriate responses. For example, hormones interact with receptors on their target cells, bringing about specific changes in the target cells. This is an example of cell signalling. The hormone secretin attaches to the cell ...
... d Living cells are able to detect changes in their environment and to make appropriate responses. For example, hormones interact with receptors on their target cells, bringing about specific changes in the target cells. This is an example of cell signalling. The hormone secretin attaches to the cell ...
THE CELL HANDOUTS
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
THE CELL HANDOUTS - Wildcat Chemistry
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.