Plant cells - Sackville School
... Cell structure and function • Cells are the ‘building blocks’ of living organisms. • Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. • All cells have the same overall structure (cell membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus) that allow them to carry out the basic life processes - but some are c ...
... Cell structure and function • Cells are the ‘building blocks’ of living organisms. • Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. • All cells have the same overall structure (cell membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus) that allow them to carry out the basic life processes - but some are c ...
4. Cells Alive Internet Lesson 71KB Dec 07 2010 11:05:12 AM
... From here, you will access the links: "How Big is a..", the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell model. Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, mi ...
... From here, you will access the links: "How Big is a..", the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell model. Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, mi ...
Cell Organelle Notes - Beachwood City Schools
... Prokaryotic cells (cells without a nucleus) are very simple. The majority of cell jobs occur in the center of the cell with no organization. There are a few areas, but not many that have specific jobs. Prokaryotic cells are bacteria. Eukaryotic cells (cells with a nucleus) have compartments called o ...
... Prokaryotic cells (cells without a nucleus) are very simple. The majority of cell jobs occur in the center of the cell with no organization. There are a few areas, but not many that have specific jobs. Prokaryotic cells are bacteria. Eukaryotic cells (cells with a nucleus) have compartments called o ...
Investigating the Influence of Probiotics on Cell Proliferation
... Cancer is a group of diseases that is characteristic of unregulated and uncontrollable cell growth. We focused on the cell proliferation of IM-9 cells which are a multiple myeloma cancer cell line (blood cancer) and identify the pathways leading to inhibition of cell proliferation. A cell is induced ...
... Cancer is a group of diseases that is characteristic of unregulated and uncontrollable cell growth. We focused on the cell proliferation of IM-9 cells which are a multiple myeloma cancer cell line (blood cancer) and identify the pathways leading to inhibition of cell proliferation. A cell is induced ...
GAMETE FORMATION IN ANIMALS
... 1. Before birth, the oogonium (diploid cell) reproduces by mitosis then begin meiosis but stop at prophase I. 2. Meiosis I will continue for one cell each month beginning at puberty. 3. Oogenesis involves the unequal division of the cytoplasm. The cell that receives the most cytoplasm after the firs ...
... 1. Before birth, the oogonium (diploid cell) reproduces by mitosis then begin meiosis but stop at prophase I. 2. Meiosis I will continue for one cell each month beginning at puberty. 3. Oogenesis involves the unequal division of the cytoplasm. The cell that receives the most cytoplasm after the firs ...
The Cell Content Vocabulary Clues
... Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word terms. ...
... Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word terms. ...
Cell Structure (Organelles)
... (Simplest) Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism (Most Complex) Endosymbiosis: theory of how organelles may have at one time been cells that developed a mutual symbiotic relationship within another cell. (This may be why mitochondria have DNA) Molecules to know! Water ...
... (Simplest) Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism (Most Complex) Endosymbiosis: theory of how organelles may have at one time been cells that developed a mutual symbiotic relationship within another cell. (This may be why mitochondria have DNA) Molecules to know! Water ...
Sections 3
... 3. The structure that regulates what enters and leaves the cell is called the ____________ _____________. ...
... 3. The structure that regulates what enters and leaves the cell is called the ____________ _____________. ...
Name
... 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, etc. 31. _____________________: outside cell membrane; only in plant cells 32. _____________________: mak ...
... 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, etc. 31. _____________________: outside cell membrane; only in plant cells 32. _____________________: mak ...
Research into human body cell behaviour reveals
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
TheHumanCheekCellANSWERKEY
... The Human Cheek Cell : KEY 1. List the 3 parts of the Cell Theory: All living things are made of cells Cells can only come from other cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 2. Describe or define each of the following: Cell membrane: Outer boundary of the cell Cytoplasm: Fluid withi ...
... The Human Cheek Cell : KEY 1. List the 3 parts of the Cell Theory: All living things are made of cells Cells can only come from other cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 2. Describe or define each of the following: Cell membrane: Outer boundary of the cell Cytoplasm: Fluid withi ...
Looking Inside Cells (a tiny tour)
... 12. Compare plant and animal cells • Plant cells have 2 structures that animal cells do not: cell wall, which gives them a boxy shape chloroplasts, which allow them to capture sunlight energy. ...
... 12. Compare plant and animal cells • Plant cells have 2 structures that animal cells do not: cell wall, which gives them a boxy shape chloroplasts, which allow them to capture sunlight energy. ...
8 Levels of Organization
... Living organisms are divided into eight levels of organization in order for scientists to study problems on several different levels ...
... Living organisms are divided into eight levels of organization in order for scientists to study problems on several different levels ...
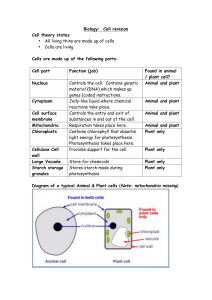
Biology Cell revision
... 2. Place layer of cells on to slide. 3. Add drops of stain onto the cell in order to colour the cell (in particularly, the nucleus). • Use iodine solution for plant cells (e.g. onion cells) • Use methylene blue for animal cells (e.g. human cheek cells) 4. Lower a cover slip carefully over the cells ...
... 2. Place layer of cells on to slide. 3. Add drops of stain onto the cell in order to colour the cell (in particularly, the nucleus). • Use iodine solution for plant cells (e.g. onion cells) • Use methylene blue for animal cells (e.g. human cheek cells) 4. Lower a cover slip carefully over the cells ...
Book Review
... immunology and cancer research, in each of which molecular biology provides the tools for elucidating the biology of the cell. At a higher level, cell–cell interactions are of critical importance for the understanding of how organisms function, whether they be plant or animal. These days we take the ...
... immunology and cancer research, in each of which molecular biology provides the tools for elucidating the biology of the cell. At a higher level, cell–cell interactions are of critical importance for the understanding of how organisms function, whether they be plant or animal. These days we take the ...
Programmed Cell Death(Apoptosis)
... 2- limiting spread of virus through the host organism. DNA damage, programmed cell death may eliminate cells carrying potentially harmful mutations, including cells with mutations that might lead to the development of cancer. During development, programmed cell death plays a key role by eliminating ...
... 2- limiting spread of virus through the host organism. DNA damage, programmed cell death may eliminate cells carrying potentially harmful mutations, including cells with mutations that might lead to the development of cancer. During development, programmed cell death plays a key role by eliminating ...
Notes 11 The Cell Cycle
... Cells must be able to produce new _______________; Why? All organisms grow and ______________, and must be maintained; the cells of a multicellular organism’s body are called _____________ cells Most organisms can produce new _______________ (or can play a role in doing so); to do this most or ...
... Cells must be able to produce new _______________; Why? All organisms grow and ______________, and must be maintained; the cells of a multicellular organism’s body are called _____________ cells Most organisms can produce new _______________ (or can play a role in doing so); to do this most or ...
Standard
... describe and investigate natural systems in a communicate how natural life science context. (cell parts) systems work and interact. 2. Tissue, organs and organ systems are composed of cells and function to serve the needs of all cells for food, air and waste removal. ...
... describe and investigate natural systems in a communicate how natural life science context. (cell parts) systems work and interact. 2. Tissue, organs and organ systems are composed of cells and function to serve the needs of all cells for food, air and waste removal. ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.