Cellular Organelle
... • Not found in animal cells • In plants, the cell wall provides support for the cell (no skeleton) – Is made of cellulose, a tough, stringy macromolecule ...
... • Not found in animal cells • In plants, the cell wall provides support for the cell (no skeleton) – Is made of cellulose, a tough, stringy macromolecule ...
Notes Chapter 10 Lesson 1 The Basics of a Cell
... Single Celled Organism- Living things that are made up of only ONE Cell Multi-celled Organism- Describes organisms that are composed of different kinds of specialized cells ...
... Single Celled Organism- Living things that are made up of only ONE Cell Multi-celled Organism- Describes organisms that are composed of different kinds of specialized cells ...
9 Weeks Assessment Review (You can use your notebook, green
... 2. How big are cells? And how does using a model help us understand cells? 3. What is the difference between the plant cell and the animal cell? 4. What does the nucleus do? 5. What does a vacuole do? 6. What does the cell membrane do? 7. What part releases waste from the cell? (think of the mall an ...
... 2. How big are cells? And how does using a model help us understand cells? 3. What is the difference between the plant cell and the animal cell? 4. What does the nucleus do? 5. What does a vacuole do? 6. What does the cell membrane do? 7. What part releases waste from the cell? (think of the mall an ...
Cells - Biology Junction
... 2. surrounds the outside of all cells 3. organisms made of more than one cell working together 5. cells like bacteria without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles 8. cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 10. domain containing ancient bacterial forms 11. this determines the f ...
... 2. surrounds the outside of all cells 3. organisms made of more than one cell working together 5. cells like bacteria without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles 8. cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 10. domain containing ancient bacterial forms 11. this determines the f ...
organs inside the cell Golgi complex
... Lipids – the fats in a cell – lipids are hydrophobic (they hate water) they also store energy – cell membranes are made of these Carbohydrates – the energy in a cell (cellulose in plants – Chitin in animals) Nucleic Acids – hold all the instructions for the cell (DNA & RNA) The Cell Theory: All li ...
... Lipids – the fats in a cell – lipids are hydrophobic (they hate water) they also store energy – cell membranes are made of these Carbohydrates – the energy in a cell (cellulose in plants – Chitin in animals) Nucleic Acids – hold all the instructions for the cell (DNA & RNA) The Cell Theory: All li ...
Review Guide Ch. 7 CP
... These are topics and vocabulary terms covered in this chapter which may appear on the chapter test. See chapter guide, warm-ups, quick reviews, and text chapter 7 parts 1 and 2 ...
... These are topics and vocabulary terms covered in this chapter which may appear on the chapter test. See chapter guide, warm-ups, quick reviews, and text chapter 7 parts 1 and 2 ...
CHAPTER 4: Cell Structure and Function Review
... 5. The _C_ _ __ __ _W_ __ __ __ is found outside the cell membrane in plants and bacteria and provides support and protection. 6. An organism like a green plant that can make its own food = _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 7. These sausage shaped organelles burn glucose and store the energy as ATP = _M_ ...
... 5. The _C_ _ __ __ _W_ __ __ __ is found outside the cell membrane in plants and bacteria and provides support and protection. 6. An organism like a green plant that can make its own food = _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 7. These sausage shaped organelles burn glucose and store the energy as ATP = _M_ ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems - Blair Community Schools
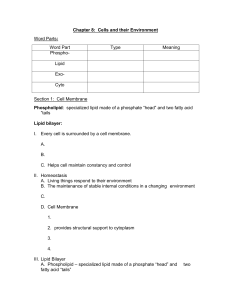
... Phospholipid: specialized lipid made of a phosphate “head” and two fatty acid “tails Lipid bilayer: I. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane. A. B. C. Helps cell maintain constancy and control ...
... Phospholipid: specialized lipid made of a phosphate “head” and two fatty acid “tails Lipid bilayer: I. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane. A. B. C. Helps cell maintain constancy and control ...
I. Introduction to the Cell
... I. Introduction to the Cell “With the cell, biology discovered its atom.” –Jacob A. The cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all processes of life. 1. make energy 2. produce waste 3. reproduce 4. respond to stimulus 5. evolve B. Unicellular: one celled organisms…Protists and Bacteria C. Multi ...
... I. Introduction to the Cell “With the cell, biology discovered its atom.” –Jacob A. The cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all processes of life. 1. make energy 2. produce waste 3. reproduce 4. respond to stimulus 5. evolve B. Unicellular: one celled organisms…Protists and Bacteria C. Multi ...
Mitosis When Cells Divide
... During Cell division a parent cell gives rise to two identical daughter cells Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus so they undergo a simple division called binary fission Eukaryotes undergo a more complex process where the nucleus needs to split in a process called mitosis ...
... During Cell division a parent cell gives rise to two identical daughter cells Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus so they undergo a simple division called binary fission Eukaryotes undergo a more complex process where the nucleus needs to split in a process called mitosis ...
Anchorage, cell density, and chemical growth factors affect cell
... -Cells do not divide unless they are signaled by other cells to do so. Growth factors are the main signal. -The events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system (it is a set of molecules in the cell that both trigger and coordinate key events in the cycle). Ex. Within th ...
... -Cells do not divide unless they are signaled by other cells to do so. Growth factors are the main signal. -The events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system (it is a set of molecules in the cell that both trigger and coordinate key events in the cycle). Ex. Within th ...
Outcome 7.5 Assessment Study Guide ANSWER
... Items you will need to complete this study guide… 1. “7.1: Cell Structure and Function” reading packet 2. Types of Cells Graphic Organizer 3. Investigating Cells Lab 4. “7.2: Cells, a Look Inside” reading packet 5. Plant and animal cell foldable 6. “Cells, Tissues and Organs” reading 7. “Building a ...
... Items you will need to complete this study guide… 1. “7.1: Cell Structure and Function” reading packet 2. Types of Cells Graphic Organizer 3. Investigating Cells Lab 4. “7.2: Cells, a Look Inside” reading packet 5. Plant and animal cell foldable 6. “Cells, Tissues and Organs” reading 7. “Building a ...
Looking Inside Cells
... A. The cytoplasm, the region ____________________________________________ between the cell membrane and the nucleus gel-like fluid B. Made up of a clear, thick, _____________________________________________ C. The fluid in the cytoplasm is __________________________________________ constantly moving ...
... A. The cytoplasm, the region ____________________________________________ between the cell membrane and the nucleus gel-like fluid B. Made up of a clear, thick, _____________________________________________ C. The fluid in the cytoplasm is __________________________________________ constantly moving ...
Anton von Leeuwenhoek
... Definitions and plant cell parts. Cytoplasm-gel like substance found in a cell Chloroplasts-a green structure in a plant Cell Wall-a stiff covering that protects plant cells Nucleus-control center of the cell Chromosomes-provides direction for cell to follow Endoplasmic Reticulum-transportation net ...
... Definitions and plant cell parts. Cytoplasm-gel like substance found in a cell Chloroplasts-a green structure in a plant Cell Wall-a stiff covering that protects plant cells Nucleus-control center of the cell Chromosomes-provides direction for cell to follow Endoplasmic Reticulum-transportation net ...
Cell and Human Body Systems Unit Test- Cardoza
... the form of ATP. Mitochondria require oxygen to carry out cellular respiration to make ATP from glucose. Describe how the circulatory and respiratory systems interact to transport a molecule of oxygen from the air to a mitochondrion. Be sure to discuss both systems IN DETAIL in your response. (10 po ...
... the form of ATP. Mitochondria require oxygen to carry out cellular respiration to make ATP from glucose. Describe how the circulatory and respiratory systems interact to transport a molecule of oxygen from the air to a mitochondrion. Be sure to discuss both systems IN DETAIL in your response. (10 po ...
bio12_sm_07_4
... 1. (a) An operon is a cluster of genes that codes for the proteins involved in one cellular process. For example, the lac operon codes for the proteins that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. An operon consists of an operator, a promoter, and the coding region. (b) An operator is the region ...
... 1. (a) An operon is a cluster of genes that codes for the proteins involved in one cellular process. For example, the lac operon codes for the proteins that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. An operon consists of an operator, a promoter, and the coding region. (b) An operator is the region ...
Cells Powerpoint
... • contains enzymes that catalyze oxidation reactions producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a by-product • additional enzymes break down the H2O2 which is toxic to the cell ...
... • contains enzymes that catalyze oxidation reactions producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a by-product • additional enzymes break down the H2O2 which is toxic to the cell ...
221_exam_3_2008
... Two proteins controlling a gene means there are two chances to activate a gene. Two proteins delay the response time so the cell can be sure the change is permanent. One of the two proteins can be exposed to the external environment to receive a signal. Phosphorylation is a permanent change so genes ...
... Two proteins controlling a gene means there are two chances to activate a gene. Two proteins delay the response time so the cell can be sure the change is permanent. One of the two proteins can be exposed to the external environment to receive a signal. Phosphorylation is a permanent change so genes ...