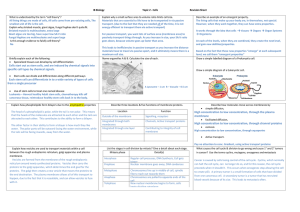
Chapter 4: Cellular Organization
... 4.2.7 Golgi apparatus (dictyosome) - similar to smooth ER but is more compact vesicles: small membranous sacs pinching off from the cisterna - normally only one Golgi apparatus in animal cells but a large number of stacks known as dictyosomes in plant cells - well developed in secretory cells and n ...
... 4.2.7 Golgi apparatus (dictyosome) - similar to smooth ER but is more compact vesicles: small membranous sacs pinching off from the cisterna - normally only one Golgi apparatus in animal cells but a large number of stacks known as dictyosomes in plant cells - well developed in secretory cells and n ...
Cells Alive Activity
... 23. Every cell is enclosed in a membrane, a double layer of _________________________. 24. The heads of the bilayer are known as __________________________________. 25. The tails of the phospholipids are _____________________________________. 26. The cell membrane acts as a _________________________ ...
... 23. Every cell is enclosed in a membrane, a double layer of _________________________. 24. The heads of the bilayer are known as __________________________________. 25. The tails of the phospholipids are _____________________________________. 26. The cell membrane acts as a _________________________ ...
The Cell Membrane
... • What is the difference between the two? • Where might the phosphate group come from? • Where do the fatty acids come from? ...
... • What is the difference between the two? • Where might the phosphate group come from? • Where do the fatty acids come from? ...
Functions of Cellular Organelles and Structures
... The job of each organelle is to help in the production of protein. ...
... The job of each organelle is to help in the production of protein. ...
Keyword/concepts: Definition: Darwin Charles Darwin theorised
... Interior of the cell. The cytosol and organelles of eukaryotic cells, excluding the nucleus. ...
... Interior of the cell. The cytosol and organelles of eukaryotic cells, excluding the nucleus. ...
C) Interactive Organelle Breakdown 9.28 REG
... homeostasis by regulating what goes in and out of the cell ...
... homeostasis by regulating what goes in and out of the cell ...
Cell structure
... between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. It consists of primarily of water. It also contains various organelles as well as salts, dissolved gasses and nutrients. There are 3 groups of organelles in the cytoplasm: Protein producers, Energy Producers and ...
... between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. It consists of primarily of water. It also contains various organelles as well as salts, dissolved gasses and nutrients. There are 3 groups of organelles in the cytoplasm: Protein producers, Energy Producers and ...
IB Biology Topic 2 - Cells Revision Sheet What is understood by the
... Vesicles are formed from the membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum around newly synthesized proteins. Vesicles then carry the proteins to the golgi apparatus, which determines the end goal for the proteins. The golgi then creates a new vesicle that moves the proteins to the end destination. Th ...
... Vesicles are formed from the membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum around newly synthesized proteins. Vesicles then carry the proteins to the golgi apparatus, which determines the end goal for the proteins. The golgi then creates a new vesicle that moves the proteins to the end destination. Th ...
Chp_7
... Chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes (endosymbiotic theory) and make their own proteins. They develop from an undifferentiated organelle called a Protoplast. Depending on location in the plant and or the presence or absence of light, the protoplast may develop into one of three organelles: ...
... Chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes (endosymbiotic theory) and make their own proteins. They develop from an undifferentiated organelle called a Protoplast. Depending on location in the plant and or the presence or absence of light, the protoplast may develop into one of three organelles: ...
Question Correct answer Complex network that transports materials
... Contains digestive enzymes, helps the cell to commit suicide and break down materials Storage sacks for water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates, food or waste Modifies or packages proteins for export from th ...
... Contains digestive enzymes, helps the cell to commit suicide and break down materials Storage sacks for water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates, food or waste Modifies or packages proteins for export from th ...
Eukaroytic Cells
... Plant cells share all the common features of animal cells, but also contain some additional organelles. Plants gain all their energy from sunlight; cells in their leaves contain many chloroplasts to convert this into a useful form. chloroplast vacuole Every plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall, a ...
... Plant cells share all the common features of animal cells, but also contain some additional organelles. Plants gain all their energy from sunlight; cells in their leaves contain many chloroplasts to convert this into a useful form. chloroplast vacuole Every plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall, a ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Review Questions
... _____ Endoplasmic reticulum b. Stack of membranes in which enzymes attach _____ Golgi apparatus carbohydrates and lipids to proteins _____ Lysosome c. Uses energy from food to make high-energy _____ Vacuole compounds _____ Chloroplast d. An internal membrane system in which components _____ Mitochon ...
... _____ Endoplasmic reticulum b. Stack of membranes in which enzymes attach _____ Golgi apparatus carbohydrates and lipids to proteins _____ Lysosome c. Uses energy from food to make high-energy _____ Vacuole compounds _____ Chloroplast d. An internal membrane system in which components _____ Mitochon ...
The Cell Membrane - Needham.K12.ma.us
... • What is the difference between the two? • Where might the phosphate group come from? • Where do the fatty acids come from? ...
... • What is the difference between the two? • Where might the phosphate group come from? • Where do the fatty acids come from? ...
CELL SNAP - YourGenome.org
... of the cell and is involved in the production, folding and transport of proteins produced by the ribosomes on its surface. Rod- or sausage-shaped organelles found inside cells. They are the power stations of the cell providing chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Thread-like ...
... of the cell and is involved in the production, folding and transport of proteins produced by the ribosomes on its surface. Rod- or sausage-shaped organelles found inside cells. They are the power stations of the cell providing chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Thread-like ...
Cells Gizmo
... Enroll in Class: Click “Enroll in Class” – this is a blue button located in the upper right corner Enter the CLASS CODE: ZZEU6ABS3F Choose “I need to create an Explore Learning Account. Register Now” Fill in your info Under CreateYour Account Login Info Username: FirstName_LastName (use your ...
... Enroll in Class: Click “Enroll in Class” – this is a blue button located in the upper right corner Enter the CLASS CODE: ZZEU6ABS3F Choose “I need to create an Explore Learning Account. Register Now” Fill in your info Under CreateYour Account Login Info Username: FirstName_LastName (use your ...
Question Report
... 1. Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing ______________ ...
... 1. Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing ______________ ...
St. Bonaventure College and High School Form 4 Biology
... The structures of animal cells and plant cells • Cell is the basic unit of life. • There are more than 200 types of cells in our body. • The shape and size of cells vary, but some features are common to all. ...
... The structures of animal cells and plant cells • Cell is the basic unit of life. • There are more than 200 types of cells in our body. • The shape and size of cells vary, but some features are common to all. ...
Cell Organelle Notes A. Cell Wall
... 1. Found in plants and other organisms— not in animal or fungal cells 2. Has double membrane 3. **Where photosynthesis occurs 4. Contain green pigment called chlorophyll 5. Have stacks of photosynthetic membranes ...
... 1. Found in plants and other organisms— not in animal or fungal cells 2. Has double membrane 3. **Where photosynthesis occurs 4. Contain green pigment called chlorophyll 5. Have stacks of photosynthetic membranes ...
Common Parts of the Cell Practice
... A. Research challenge: Name the “tail-like cell structures that function in movement/locomotion in ...
... A. Research challenge: Name the “tail-like cell structures that function in movement/locomotion in ...
CLASS COPY Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice
... Type of Transport (active or passive) ...
... Type of Transport (active or passive) ...
Cell Study Guide
... Chloroplasts – Where photosynthesis takes place; contains chlorophyll Cytoplasm – Where organelles are located; jelly-like material Endoplasmic Reticulum – Transports materials through the cell Rough ER – Transports materials through the cell; covered with ribosomes Golgi Bodies – The packaging hous ...
... Chloroplasts – Where photosynthesis takes place; contains chlorophyll Cytoplasm – Where organelles are located; jelly-like material Endoplasmic Reticulum – Transports materials through the cell Rough ER – Transports materials through the cell; covered with ribosomes Golgi Bodies – The packaging hous ...