Unit 3 Biology - moleculesoflife2
... Atoms are the basic unit of all matter. Substances consisting of only one kind of atom are called elements. Molecules are two or more of the same (or different kind) of atoms held together by chemical bonds. ...
... Atoms are the basic unit of all matter. Substances consisting of only one kind of atom are called elements. Molecules are two or more of the same (or different kind) of atoms held together by chemical bonds. ...
Cells questions
... A. Z, Y, W, X B. Y, X, Z, W C. W, Z, X, Y D. Z, W, X, Y 34. Which of the following is true for SER, but NOT for RER? A. Produce vesicles. B. Intracellular transport. C. Detoxify substances for the cell. D. Associated with the synthesis of hormones. 35. Which of the following organelles most likely h ...
... A. Z, Y, W, X B. Y, X, Z, W C. W, Z, X, Y D. Z, W, X, Y 34. Which of the following is true for SER, but NOT for RER? A. Produce vesicles. B. Intracellular transport. C. Detoxify substances for the cell. D. Associated with the synthesis of hormones. 35. Which of the following organelles most likely h ...
Cell Structure - AVC Distance Education: Learn anywhere
... The Nucleus: The Cell’s Control Center ...
... The Nucleus: The Cell’s Control Center ...
The Cell
... Rough ER: has ribosomes on its surface; proteins are made directly into ER where they can then be modified. Smooth ER: Lipids are produced (steroids, phospholipids) ...
... Rough ER: has ribosomes on its surface; proteins are made directly into ER where they can then be modified. Smooth ER: Lipids are produced (steroids, phospholipids) ...
HW#1: Grey cell green
... 1. Which part of the cell did Robert Hooke see when he saw the “little boxes”? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. Why can’t a single-c ...
... 1. Which part of the cell did Robert Hooke see when he saw the “little boxes”? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. Why can’t a single-c ...
The Basic ideas of Cells The Methods to observe Cells
... others are bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough-ER) ...
... others are bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough-ER) ...
Define Cell Parts
... mitochondrion provides energy for the cell vacuole contains the waste golgi apparatus packs protein nucleus controls the cell rhibosomes synthesizes (transforms) protein cytoplasm holds the cell’s organelles in place cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside microvilli involved ...
... mitochondrion provides energy for the cell vacuole contains the waste golgi apparatus packs protein nucleus controls the cell rhibosomes synthesizes (transforms) protein cytoplasm holds the cell’s organelles in place cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside microvilli involved ...
Document
... III. Moving Materials In and Out: Diffusion and Gradients A. Random Movement and Diffusion: 1. Diffusion = movement of molecules from region of higher to lower concentration 2. Concentration gradient = difference between the highest and lowest concentration of a solute; like bike coasting downhill, ...
... III. Moving Materials In and Out: Diffusion and Gradients A. Random Movement and Diffusion: 1. Diffusion = movement of molecules from region of higher to lower concentration 2. Concentration gradient = difference between the highest and lowest concentration of a solute; like bike coasting downhill, ...
THE CELL
... 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2) Cells are the basic living units within organisms. 3) All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
... 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2) Cells are the basic living units within organisms. 3) All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
animal cells
... Cells are the smallest units that can carry out the activities of life All cells must obtain energy, remove waste products, and reproduce in order to stay alive The development of the microscope helped create the cell theory. Know the function of each organelle: lysosomes, vacuole, cell memb ...
... Cells are the smallest units that can carry out the activities of life All cells must obtain energy, remove waste products, and reproduce in order to stay alive The development of the microscope helped create the cell theory. Know the function of each organelle: lysosomes, vacuole, cell memb ...
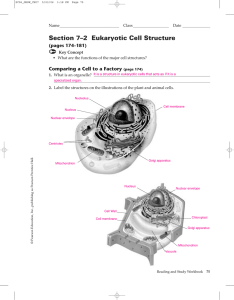
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... 15. Using the cell as a factory analogy, describe the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell. The Golgi apparatus is like a customization shop, where the finishing touches are put on proteins before they are ready to leave the cell “factory.” ...
... 15. Using the cell as a factory analogy, describe the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell. The Golgi apparatus is like a customization shop, where the finishing touches are put on proteins before they are ready to leave the cell “factory.” ...
Cell membrane ppt notes File
... 3. Carbohydrate molecules (attached to proteins or lipids) have antenna to help cells identify or recognize other cells 4. Cholesterol (lipid) that is found in the fatty acid tails helps the cell membrane maintain it’s flexible shape. ...
... 3. Carbohydrate molecules (attached to proteins or lipids) have antenna to help cells identify or recognize other cells 4. Cholesterol (lipid) that is found in the fatty acid tails helps the cell membrane maintain it’s flexible shape. ...
Cytology ch. 7 Study
... b. What process in cells creates ATP? c. What organelle produces ATP? d. What types of cells utilize ATP? ...
... b. What process in cells creates ATP? c. What organelle produces ATP? d. What types of cells utilize ATP? ...
Chap 4 sec 2c Fact Review Sheet
... Ribosomes are the smallest organelles. There are more ribosomes than any other organelle in a cell. Some ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm. Other ribosomes attach to the membranes of other organelles or to the cytoskeleton. Unlike other organelles, ribosomes are not covered with a membrane. Th ...
... Ribosomes are the smallest organelles. There are more ribosomes than any other organelle in a cell. Some ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm. Other ribosomes attach to the membranes of other organelles or to the cytoskeleton. Unlike other organelles, ribosomes are not covered with a membrane. Th ...
2.4 Membranes - Rufus King Biology
... *People that are more lean have more water than people who have more fat because muscle cells hold more water than fat cells. ...
... *People that are more lean have more water than people who have more fat because muscle cells hold more water than fat cells. ...
Chapter 7 ppt
... cell by fusion of vesicles with the macromolecules into cell by plasma membrane forming vesicles derived from the plasma membrane Vesicle usually budded from ER Vesicle forms from a localized or Golgi then migrates to PM region of the PM; is pinched off into the cytoplasm Used by secretory cells to ...
... cell by fusion of vesicles with the macromolecules into cell by plasma membrane forming vesicles derived from the plasma membrane Vesicle usually budded from ER Vesicle forms from a localized or Golgi then migrates to PM region of the PM; is pinched off into the cytoplasm Used by secretory cells to ...
Passive Transport – No energy required for these processes to
... Active Transport - The cell must use energy to either remove the substance from the cell or to bring more of it into the cell. For molecules that are too large to actively transport through the cell membrane, endocytosis and exocytosis are used. Endocytosis: the cell membrane surrounds and encloses ...
... Active Transport - The cell must use energy to either remove the substance from the cell or to bring more of it into the cell. For molecules that are too large to actively transport through the cell membrane, endocytosis and exocytosis are used. Endocytosis: the cell membrane surrounds and encloses ...
Cells 1.3
... Chlorophyll uses the sun’s energy to make sugar. This is photosynthesis The mitochondria then use this sugar to make ATP ...
... Chlorophyll uses the sun’s energy to make sugar. This is photosynthesis The mitochondria then use this sugar to make ATP ...
Basic information on cell
... surface is studded with ribosomes. This is the place where proteins are synthesized by translation of the mRNA. 2) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) do not contain ribosomes and do not function in protein synthesis. SER contains phospholipids, neutral fats, sterols and other lipids that it is ...
... surface is studded with ribosomes. This is the place where proteins are synthesized by translation of the mRNA. 2) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) do not contain ribosomes and do not function in protein synthesis. SER contains phospholipids, neutral fats, sterols and other lipids that it is ...
Cell Structure
... and called chromosomes when the cell is dividing. • Function: Passes DNA to new cells ...
... and called chromosomes when the cell is dividing. • Function: Passes DNA to new cells ...
Active Transport
... Thus, far we have talked about small the movement of ________ particles traveling across the membrane. ...
... Thus, far we have talked about small the movement of ________ particles traveling across the membrane. ...
The Cell
... Cytoplasm: cytosol and organelles; “egg white”; high in proteins including enzymes cytoskeleton: proteins called microtubules that hold the organelles loosely in place ...
... Cytoplasm: cytosol and organelles; “egg white”; high in proteins including enzymes cytoskeleton: proteins called microtubules that hold the organelles loosely in place ...