Cell Organelles
... with ribosomes; it collects proteins made by ribosmes Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids – detoxifies alcohol ...
... with ribosomes; it collects proteins made by ribosmes Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids – detoxifies alcohol ...
Concept Covered: Cell Internal Organiza8on
... 1. Basic eukaryotic cell structure consists of an outer membrane, cytoplasm filled with organelles and a nucleus. Describe and give the function of each of the following: ...
... 1. Basic eukaryotic cell structure consists of an outer membrane, cytoplasm filled with organelles and a nucleus. Describe and give the function of each of the following: ...
Looking Inside Cells
... VACUOLE • This sac stores water, food, waste products, and other materials. ...
... VACUOLE • This sac stores water, food, waste products, and other materials. ...
Spring 2012 Lecture 1 - Department of Chemistry -
... * Smooth ER = site of lipid synthesis * Rough ER = site of protein synthesis via ribosomes - Ribosomes are made up of RNA and proteins not bound by a membrane 5. Lysosomes - Internal sacs bound by a single membrane - Responsible for degrading cell components that have become obsolete for the cell or ...
... * Smooth ER = site of lipid synthesis * Rough ER = site of protein synthesis via ribosomes - Ribosomes are made up of RNA and proteins not bound by a membrane 5. Lysosomes - Internal sacs bound by a single membrane - Responsible for degrading cell components that have become obsolete for the cell or ...
CHAPTER 4: Cell Structure and Function Review Crossword
... 1. Small structure in a cell that performs a specific function = _O_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 2. Dark spot in the nucleus where ribosomal RNA & proteins are made =_N_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 3. Sac of digestive enzymes involved in apoptosis = _L_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 4. _R_ __ __ __ __ ER is covered ...
... 1. Small structure in a cell that performs a specific function = _O_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 2. Dark spot in the nucleus where ribosomal RNA & proteins are made =_N_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 3. Sac of digestive enzymes involved in apoptosis = _L_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 4. _R_ __ __ __ __ ER is covered ...
Cell Organelles
... are ready to leave the “factory” From here, proteins are then “shipped” to their final destinations throughout the cell or outside of the cell. ...
... are ready to leave the “factory” From here, proteins are then “shipped” to their final destinations throughout the cell or outside of the cell. ...
CellsJeopardyaclinton
... What is the correct order of the following words from smallest to largest?: ...
... What is the correct order of the following words from smallest to largest?: ...
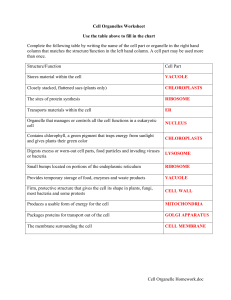
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only) ...
... Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only) ...
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
CELL PROJECT: Due
... Directions: Create either a 3-D model or poster that shows the following plant cell organelles AND their functions. You MAY cut out the organelle description and function to use as labels. ...
... Directions: Create either a 3-D model or poster that shows the following plant cell organelles AND their functions. You MAY cut out the organelle description and function to use as labels. ...
Blank flipbook
... Membranes are ________________________________________ (=Semi-permeable) Allow certain molecules to pass through; but keep others out _________________ what enters and leaves cell Helps with ____________________________ ___________________= gel-like material + organelles between nucleus and cell mem ...
... Membranes are ________________________________________ (=Semi-permeable) Allow certain molecules to pass through; but keep others out _________________ what enters and leaves cell Helps with ____________________________ ___________________= gel-like material + organelles between nucleus and cell mem ...
EOC Review Part 3
... Cellular Basis of Life What does the term “membrane-bound organelles mean?” What cell type are they found in? Cell parts that have unique functions (e.g., nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, ER), surrounded by a lipid bilayer. They are found in eukaryotic cells only. What are the three parts of cel ...
... Cellular Basis of Life What does the term “membrane-bound organelles mean?” What cell type are they found in? Cell parts that have unique functions (e.g., nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, ER), surrounded by a lipid bilayer. They are found in eukaryotic cells only. What are the three parts of cel ...
L3 I Have, Who Has? Cards
... Who has the basic unit of structure and function in all living things? ...
... Who has the basic unit of structure and function in all living things? ...
CELL THEORY
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID BILAYER with POLAR heads facing OUTWARD and NON-POLAR tails facing INWARD ...
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID BILAYER with POLAR heads facing OUTWARD and NON-POLAR tails facing INWARD ...
Flipbook with answers filled in
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID BILAYER with POLAR heads facing OUTWARD and NON-POLAR tails facing INWARD ...
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID BILAYER with POLAR heads facing OUTWARD and NON-POLAR tails facing INWARD ...
Chapter 3: Principles of Plant Growth
... The control center of the cell. The nucleus contains chromosomal DNA that regulates the production and structure of proteins within the cell. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane, a porous membrane that allows materials to pass in and out of the nucleus. ...
... The control center of the cell. The nucleus contains chromosomal DNA that regulates the production and structure of proteins within the cell. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane, a porous membrane that allows materials to pass in and out of the nucleus. ...
Cell Structure and theory
... Prokaryotes are simple but they come in many varieties Eukaryotes are more complex: o Eukaryotes can be multicellular or unicellular. o Eukaryotes contain many organelles Regulates what materials enter and leave the cell. Controls most cell processes and contains nearly all of the cell’s DNA a ...
... Prokaryotes are simple but they come in many varieties Eukaryotes are more complex: o Eukaryotes can be multicellular or unicellular. o Eukaryotes contain many organelles Regulates what materials enter and leave the cell. Controls most cell processes and contains nearly all of the cell’s DNA a ...
Reproduction
... • vesicles - membranecovered sacs formed by the endoplasmic reticulum. Vesicles transport new proteins to the Golgi body. • Golgi body - sorts and packages proteins for transport ...
... • vesicles - membranecovered sacs formed by the endoplasmic reticulum. Vesicles transport new proteins to the Golgi body. • Golgi body - sorts and packages proteins for transport ...
Organic Molecules - Riverdale Middle School
... • Short term energy storage – body uses first • Makes up cell wall and cell membrane • Fruits, breads, pasta, rice, potatoes, candy, and cookies • Examples: – starches - large sugar molecules that store excess energy – glucose (sugar) – body breaks down starches into glucose when eaten; cells use to ...
... • Short term energy storage – body uses first • Makes up cell wall and cell membrane • Fruits, breads, pasta, rice, potatoes, candy, and cookies • Examples: – starches - large sugar molecules that store excess energy – glucose (sugar) – body breaks down starches into glucose when eaten; cells use to ...
The Cell in Action
... For the cells that make up your body and the body of every other living thing to survive they must be constantly at work. Never a dull moment in a cell. For everything to run smoothly, some important processes must be in place. If they don’t work, you don’t work!!! How do materials move into & ou ...
... For the cells that make up your body and the body of every other living thing to survive they must be constantly at work. Never a dull moment in a cell. For everything to run smoothly, some important processes must be in place. If they don’t work, you don’t work!!! How do materials move into & ou ...