Phase separation in the cell cytoplasm
... Cells exhibit a complex spatial organization, often involving organelles that are surrounded by a membrane. However, there exist many structures that are not membrane bounded. Examples are the centrosome, meiotic and mitotoc spindles as well as germ granules. An interesting question is how such stru ...
... Cells exhibit a complex spatial organization, often involving organelles that are surrounded by a membrane. However, there exist many structures that are not membrane bounded. Examples are the centrosome, meiotic and mitotoc spindles as well as germ granules. An interesting question is how such stru ...
CELL STRUCTURE chart97
... Double membrane with inner membrane modified into sacs called thylakoids Stacks of thylakoids called grana & interconnected Gel like innermost substance called stroma ...
... Double membrane with inner membrane modified into sacs called thylakoids Stacks of thylakoids called grana & interconnected Gel like innermost substance called stroma ...
Cell Membrane and Organelle Webquest
... 3. What is one of the cell membrane’s jobs? 4. What is the location of the cell membrane? 5. The heads of phospholipids (lipids) are so they like to be with water. 6. The tails of phospholipids are ...
... 3. What is one of the cell membrane’s jobs? 4. What is the location of the cell membrane? 5. The heads of phospholipids (lipids) are so they like to be with water. 6. The tails of phospholipids are ...
Cells are the basic units of life
... Closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs (pancakes) Newly made proteins and lipids from the ER are sent here Sent to the Golgi Apparatus in small, membrane- bound packages called vesicles that were pinched off in the ER Vesicles are distributed to the cell membrane and other cell organelles, sent ou ...
... Closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs (pancakes) Newly made proteins and lipids from the ER are sent here Sent to the Golgi Apparatus in small, membrane- bound packages called vesicles that were pinched off in the ER Vesicles are distributed to the cell membrane and other cell organelles, sent ou ...
cells
... Other Cell Structures • Microbodies – Peroxisomes: enzymes that help neutralize peroxide and other acids and bases (ex. Catalase) Found mostly in liver, spleen, and kidney – Glyoxysomes – help produce the seed coat ...
... Other Cell Structures • Microbodies – Peroxisomes: enzymes that help neutralize peroxide and other acids and bases (ex. Catalase) Found mostly in liver, spleen, and kidney – Glyoxysomes – help produce the seed coat ...
9/7
... Photosynthetic prokaryotes Often have extensive infoldings of the plasma membrane In the form of flattened or spherical vesicles or tubules May serve to provide larger surface area for metabolic processes ...
... Photosynthetic prokaryotes Often have extensive infoldings of the plasma membrane In the form of flattened or spherical vesicles or tubules May serve to provide larger surface area for metabolic processes ...
Signal Transduction
... • Glial cells supply neurons with cholesterol • Improves rate of nerve signal transmission • Allows neuronal connections ...
... • Glial cells supply neurons with cholesterol • Improves rate of nerve signal transmission • Allows neuronal connections ...
Cells, Tissues, & Organs
... • Lysosomes - Vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. Break down old cell parts • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
... • Lysosomes - Vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. Break down old cell parts • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
Horticulture
... • Control Center: regulates activities – Nuclear Membrane: controls materials in and out – Chromosomes: thin, rod-shaped, carry on traits – Nucleolus: makes ribosomes ...
... • Control Center: regulates activities – Nuclear Membrane: controls materials in and out – Chromosomes: thin, rod-shaped, carry on traits – Nucleolus: makes ribosomes ...
Chapter 7 - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... what the external conditions are. • Waste and other products also leave the cell through the PM ...
... what the external conditions are. • Waste and other products also leave the cell through the PM ...
Skills Worksheet
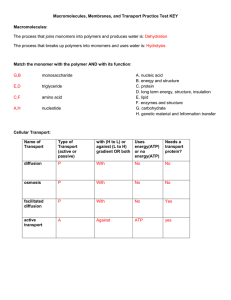
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
Enzymes
... 3. Nucleus, nucleoid: It contains the genom. It can be found in every living organism. Practically it is the packed DNA. Bacterial nucleoid: it is unbounded, embedded into the cytoplasm ...
... 3. Nucleus, nucleoid: It contains the genom. It can be found in every living organism. Practically it is the packed DNA. Bacterial nucleoid: it is unbounded, embedded into the cytoplasm ...
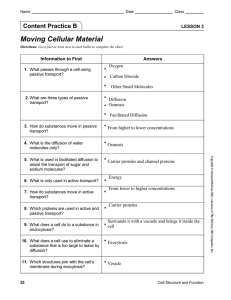
Moving Cellular Material
... Directions: List a fact or term next to each bullet to complete the chart. ...
... Directions: List a fact or term next to each bullet to complete the chart. ...
The Cell
... with the cell membrane. Function as channels within the cell. Two types: Smooth and Rough. Smooth are for fat and membrane protein production. Rough have ribosomes on its surface and synthesize other proteins ...
... with the cell membrane. Function as channels within the cell. Two types: Smooth and Rough. Smooth are for fat and membrane protein production. Rough have ribosomes on its surface and synthesize other proteins ...
Study Guide - Southington Public Schools
... Study Guide for Honors Biology Unit test: Chapter 4 & 5 This test will consist of two sections. Some will be multiple choice and you will have to write some short answers. There will also be diagrams to interpret and label. ...
... Study Guide for Honors Biology Unit test: Chapter 4 & 5 This test will consist of two sections. Some will be multiple choice and you will have to write some short answers. There will also be diagrams to interpret and label. ...
Cell Structure
... in Eukaryotic cells It is an internal membrane structure. The ER assembles components of the cell membrane and modifies some proteins. Rough ER is involved in the synthesis of proteins. Smooth ER does not have ribosomes on its surface. ...
... in Eukaryotic cells It is an internal membrane structure. The ER assembles components of the cell membrane and modifies some proteins. Rough ER is involved in the synthesis of proteins. Smooth ER does not have ribosomes on its surface. ...
Cell Organelles and Their Functions
... membrane; includes fluid, cytoskeleton, and all organelles (except nucleus) ...
... membrane; includes fluid, cytoskeleton, and all organelles (except nucleus) ...
The Cell - Angelfire
... • The first name is always the Genus name • The second name is always the species name • The first letter of the first name is always in upper case & the first letter of the species name is always in the lower case • The name is written in italics or alternatively underlined • e.g. Amoeba proteus OR ...
... • The first name is always the Genus name • The second name is always the species name • The first letter of the first name is always in upper case & the first letter of the species name is always in the lower case • The name is written in italics or alternatively underlined • e.g. Amoeba proteus OR ...