A cell structure - CIE Alevel notes!
... proteins. They are found free in the cytoplasm, and attached to rough ER. Proteins are made on the ribosomes, by linking them together amino acid. ...
... proteins. They are found free in the cytoplasm, and attached to rough ER. Proteins are made on the ribosomes, by linking them together amino acid. ...
sept-9-cells-bread-on
... the differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the missing blanks below with either the word “plant” or “animal” then fully describe (using complete sentences) why you paired each character with each type of cell. Your description should include the three major differences between plant and ...
... the differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the missing blanks below with either the word “plant” or “animal” then fully describe (using complete sentences) why you paired each character with each type of cell. Your description should include the three major differences between plant and ...
Six Kingdoms of Life
... What are the raw materials and products of photosynthesis and respiration? How do active transport and passive transport differ? Describe the events that occur during the cell cycle. Describe the events that occur during meiosis. Why is the cell cycle necessary? Why is meiosis necessary? ...
... What are the raw materials and products of photosynthesis and respiration? How do active transport and passive transport differ? Describe the events that occur during the cell cycle. Describe the events that occur during meiosis. Why is the cell cycle necessary? Why is meiosis necessary? ...
Cell Structure and Function - Tri
... Looks like a stack of pancakes usually near the ER packages cellular secretions for export from the cell In some cells, hormones are produced in the ER and the Golgi Apparatus packages these for export. ...
... Looks like a stack of pancakes usually near the ER packages cellular secretions for export from the cell In some cells, hormones are produced in the ER and the Golgi Apparatus packages these for export. ...
Cells are the basic
... • Made of a lipid bi-layer with proteins floating in it and carbohydrate chains stuck on the outside of it ...
... • Made of a lipid bi-layer with proteins floating in it and carbohydrate chains stuck on the outside of it ...
The Cell Membrane
... membrane without assistance if they are moving from high to low areas of concentration. All other types of particles need some sort of assistance, such as a protein channel in order to pass across the cell membrane. ...
... membrane without assistance if they are moving from high to low areas of concentration. All other types of particles need some sort of assistance, such as a protein channel in order to pass across the cell membrane. ...
Cellular Transport WebQuest
... 4. Animal cell membranes contain _______________linking the fatty acids together and so stabilizing and strengthening the membrane. 1. Proteins ______________ proteins usually span from one side of the phospholipid bilayer to the other (integral proteins) 2. ______________ proteins sit on one the su ...
... 4. Animal cell membranes contain _______________linking the fatty acids together and so stabilizing and strengthening the membrane. 1. Proteins ______________ proteins usually span from one side of the phospholipid bilayer to the other (integral proteins) 2. ______________ proteins sit on one the su ...
Slide () - AccessEmergency Medicine
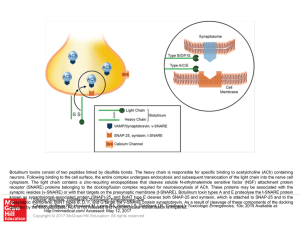
... Botulinum toxins consist of two peptides linked by disulfide bonds. The heavy chain is responsible for specific binding to acetylcholine (ACh) containing neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the ...
... Botulinum toxins consist of two peptides linked by disulfide bonds. The heavy chain is responsible for specific binding to acetylcholine (ACh) containing neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the ...
Insights into the inner side: new facettes of endocytosis
... plasma membrane that does this job. Here is the site where a cell is confronted with its environment and here cluster numerous receptors, channels, carriers, but also nonproteinaceous molecules that are involved in signalling. One would presume that such a complex structure is strictly preserved onc ...
... plasma membrane that does this job. Here is the site where a cell is confronted with its environment and here cluster numerous receptors, channels, carriers, but also nonproteinaceous molecules that are involved in signalling. One would presume that such a complex structure is strictly preserved onc ...
The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments A. The Cell: The
... F. The Endomembrane System • The Golgi apparatus is the cellular post office; storing, modifying and packaging proteins. • It receives materials from the rough ER via vesicles that fuse with the cis region of the Golgi. • It adds signal molecules to proteins, directing them to various destinations. ...
... F. The Endomembrane System • The Golgi apparatus is the cellular post office; storing, modifying and packaging proteins. • It receives materials from the rough ER via vesicles that fuse with the cis region of the Golgi. • It adds signal molecules to proteins, directing them to various destinations. ...
Diffusion with Eggs Lab
... Learning Targets “I Can. . .” -Define “selective permeability.” -Model a living cell by using eggs with a dissolved shell. -Predict the results of an experiment that involves the movement of water through a membrane. -Recognize cells that are in a hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solution. ...
... Learning Targets “I Can. . .” -Define “selective permeability.” -Model a living cell by using eggs with a dissolved shell. -Predict the results of an experiment that involves the movement of water through a membrane. -Recognize cells that are in a hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solution. ...
9 Week Benchmark Study Guide Fill-In
... 20. What are the three types of passive transport? a. Osmosis: the movement of water from high to low concentration b. Facilitated Diffusion: moves large molecules in (only) via the help of a channel protein c. Simple Diffusion: moves small, nonpolar molecules from high to low concentration 21. Wha ...
... 20. What are the three types of passive transport? a. Osmosis: the movement of water from high to low concentration b. Facilitated Diffusion: moves large molecules in (only) via the help of a channel protein c. Simple Diffusion: moves small, nonpolar molecules from high to low concentration 21. Wha ...
1. The substance inside the cell membrane that consists of the
... 6. Science is based on ____; this requires careful observation and testing ideas, not just accepting them 7. The name given to the cell membrane because it is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules 8. Science generally starts by making ____; the act of noticing and describing events or process ...
... 6. Science is based on ____; this requires careful observation and testing ideas, not just accepting them 7. The name given to the cell membrane because it is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules 8. Science generally starts by making ____; the act of noticing and describing events or process ...
File
... Learning Target (7.12DEF) Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole ...
... Learning Target (7.12DEF) Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole ...
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
... • Active transport plays a very important role in homeostasis. Many molecules needed by the cell cannot enter the cell through passive transport because they are too large. • The cell must use energy to move these molecules across the plasma membrane. • There are two types of active transport; endoc ...
... • Active transport plays a very important role in homeostasis. Many molecules needed by the cell cannot enter the cell through passive transport because they are too large. • The cell must use energy to move these molecules across the plasma membrane. • There are two types of active transport; endoc ...
Chapter 6 - MrsAllisonMagee
... Smooth ER: has no ribosomes on it; makes lipids, carbs, enzymes, and detoxifies drugs and poisons. ...
... Smooth ER: has no ribosomes on it; makes lipids, carbs, enzymes, and detoxifies drugs and poisons. ...
H. Bio Cell Membrane
... 3. Two K ions outside bind to the pump 4. Two K ions are transported are released inside the cell. ...
... 3. Two K ions outside bind to the pump 4. Two K ions are transported are released inside the cell. ...
Cell Review
... important in cells that are responsible for ridding the body of toxic substances (ex: liver) Cytoplasm a semi-fluid substance in which all of the cell’s organelles are suspended located between the nucleus and the cell membrane Golgi apparatus also called the Golgi body or the Golgi complex ...
... important in cells that are responsible for ridding the body of toxic substances (ex: liver) Cytoplasm a semi-fluid substance in which all of the cell’s organelles are suspended located between the nucleus and the cell membrane Golgi apparatus also called the Golgi body or the Golgi complex ...
Cells and Cell Organelles
... • Protects and supports cell • Regulates what enters and leaves • Phospholipid bilayer- to layers of lipids ...
... • Protects and supports cell • Regulates what enters and leaves • Phospholipid bilayer- to layers of lipids ...
Cells - Warren County Schools
... • Makes lipids and other materials for use inside and outside the cell • Breaks down chemicals that can damage the cell • It is the internal delivery system for the cell ...
... • Makes lipids and other materials for use inside and outside the cell • Breaks down chemicals that can damage the cell • It is the internal delivery system for the cell ...
Cell Pats and Movement Across Memebranes
... Rough ER: has ribosomes, makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes, makes lipids Ribosomes: attached to ER or free Composed of protein and RNA molecules Structure for RNA molecule and protein synthesis ...
... Rough ER: has ribosomes, makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes, makes lipids Ribosomes: attached to ER or free Composed of protein and RNA molecules Structure for RNA molecule and protein synthesis ...