Extraction and Purification
... – Exploits the different density of organelles – Density gradients are formed by using sucrose as solute – Can be step gradient or continuous – Centrifuge for set time at a know force and determine where your compound is or run it until it reaches equilibrium. Sample will stop moving once its densit ...
... – Exploits the different density of organelles – Density gradients are formed by using sucrose as solute – Can be step gradient or continuous – Centrifuge for set time at a know force and determine where your compound is or run it until it reaches equilibrium. Sample will stop moving once its densit ...
cells
... • The storage tank of the cell. • Contains mostly water. • May contain food and waste. ...
... • The storage tank of the cell. • Contains mostly water. • May contain food and waste. ...
Life’s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon 8/25/2011 1
... immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
... immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
Chapter Outline
... a. Motile bacteria usually have flagella; the filament, hook, and basal body work to rotate the flagellum like a propeller to move through fluid medium. b. Fimbriae are small, bristle-like fibers that attach bacteria to an appropriate surface. c. Conjugation pili are tubes used by bacteria to pass D ...
... a. Motile bacteria usually have flagella; the filament, hook, and basal body work to rotate the flagellum like a propeller to move through fluid medium. b. Fimbriae are small, bristle-like fibers that attach bacteria to an appropriate surface. c. Conjugation pili are tubes used by bacteria to pass D ...
Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria
... Eukaryotes contain multiple chromosomes surrounded by a membrane (nucleus) and membrane-bound organelles. Some organelles such as the nucleus and mitochondrion have two membranes. Animal Cell ...
... Eukaryotes contain multiple chromosomes surrounded by a membrane (nucleus) and membrane-bound organelles. Some organelles such as the nucleus and mitochondrion have two membranes. Animal Cell ...
THIS IS OUR THEME SLIDE
... • Stats view (default) will list percent incorrect, correct, and total complete. • Race view will animate student avatars as they move towards the finish line. A student will cross the finish line when they get 70% correct. ...
... • Stats view (default) will list percent incorrect, correct, and total complete. • Race view will animate student avatars as they move towards the finish line. A student will cross the finish line when they get 70% correct. ...
Layout
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
cell theory
... 4.6 The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic information Nucleus contains chromatin, a network of strands that condenses to form chromosomes Chromosomes contain DNA which carries genes, the units of heredity Nucleolus - dark region of chromatin with ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Nuclear envelope sepa ...
... 4.6 The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic information Nucleus contains chromatin, a network of strands that condenses to form chromosomes Chromosomes contain DNA which carries genes, the units of heredity Nucleolus - dark region of chromatin with ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Nuclear envelope sepa ...
Living Systems Test Study Guide
... Students should know the definitions for the following words: Cell, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, classification, kingdoms, vascular, nonvascular, vertebrates and invertebrates They will need to be able to look at the pictures of a plant and animal cell and label the parts. They should also be ...
... Students should know the definitions for the following words: Cell, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, classification, kingdoms, vascular, nonvascular, vertebrates and invertebrates They will need to be able to look at the pictures of a plant and animal cell and label the parts. They should also be ...
Name__________________________________
... 2. Which structure is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? ...
... 2. Which structure is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? ...
Lec.8 Lysosomes
... are enclosed in the lysosomal membrane and second, even if the enzymes were to leak out of the lysosome, they would not be active at the neutral pH of the cytosol. ...
... are enclosed in the lysosomal membrane and second, even if the enzymes were to leak out of the lysosome, they would not be active at the neutral pH of the cytosol. ...
A Tour of the Cell
... in plants, neighboring cells joined to form interconnected and coordinated group cell ...
... in plants, neighboring cells joined to form interconnected and coordinated group cell ...
Cells Chapter 7-2 Cell Organelle Notes
... • Found only in __________________ cells • Many are membrane-____________ (a membrane surrounds the organelle) o ___________: watery matrix that organelles float in o ______________: everything in a cell except the nucleus (cytosol + all organelles) ...
... • Found only in __________________ cells • Many are membrane-____________ (a membrane surrounds the organelle) o ___________: watery matrix that organelles float in o ______________: everything in a cell except the nucleus (cytosol + all organelles) ...
Anatomy Memorization: Chapter 1
... 7. Facilitated diffusion (type of carrier mediated transport) – needs a transport protein 8. Active transport – NEEDS energy to move a. ion pumps b. exchange pumps 9. Vesicular transport – transport in a vesicle) a. endocytosis (movement from outside to in…EN = in) b. exocytosis (movement form insid ...
... 7. Facilitated diffusion (type of carrier mediated transport) – needs a transport protein 8. Active transport – NEEDS energy to move a. ion pumps b. exchange pumps 9. Vesicular transport – transport in a vesicle) a. endocytosis (movement from outside to in…EN = in) b. exocytosis (movement form insid ...
Review_Cells_ANSWERS_MOD
... NOTE: Some of the answers below are written in short hand. They are not to be considered suitable as test answers, for example. 1. What are the three principles of Cell Theory? - All cells come from pre-existing cells, the cell is the smallest living organizational unit, and the organisms are made o ...
... NOTE: Some of the answers below are written in short hand. They are not to be considered suitable as test answers, for example. 1. What are the three principles of Cell Theory? - All cells come from pre-existing cells, the cell is the smallest living organizational unit, and the organisms are made o ...
The Cell
... • All cells contains organelles which are the equivalent to organs of an organism. – They provide a specific function within the cell. • produces different types of proteins (enzymes) – That carry out overall cell activity. • There are many different types of cells that contain different proportions ...
... • All cells contains organelles which are the equivalent to organs of an organism. – They provide a specific function within the cell. • produces different types of proteins (enzymes) – That carry out overall cell activity. • There are many different types of cells that contain different proportions ...
BIOL241StudyGuideExp1JUL2012
... simple sugars, double sugars, complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. State the basic function(s) of each of these classes of (bio) molecules/macromolecules. 11. Define an enzyme. Describe the role of enzymes in metabolism. 12. Describe the properties of cell me ...
... simple sugars, double sugars, complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. State the basic function(s) of each of these classes of (bio) molecules/macromolecules. 11. Define an enzyme. Describe the role of enzymes in metabolism. 12. Describe the properties of cell me ...
Cell Membrane Reading Guide
... 13. If a cell contains the same amount of solute as its environment, it is said to be _________________ 14. Plant, bacterial and fungal cells respond to hypotonic solutions differently than animal cells. Explain why this is so. _____________________________________________________________ 15. In a h ...
... 13. If a cell contains the same amount of solute as its environment, it is said to be _________________ 14. Plant, bacterial and fungal cells respond to hypotonic solutions differently than animal cells. Explain why this is so. _____________________________________________________________ 15. In a h ...
LIPIDS IN MEMBRANES –
... cellular function, i.e. the membrane proteins which float laterally within the membrane. However, a large variety of lipids of different structure were found to reside in plasma membranes, much more than one would expect for just performing the functions of frame giving / compartmentation. Biophysic ...
... cellular function, i.e. the membrane proteins which float laterally within the membrane. However, a large variety of lipids of different structure were found to reside in plasma membranes, much more than one would expect for just performing the functions of frame giving / compartmentation. Biophysic ...
cells internet activity answers
... 1. What do chloroplasts do for cells? Chloroplasts take in sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make oxygen and sugar (a form of food). This process is called photosynthesis. 2. Do animals have chloroplasts? No, animal cells do not have chloroplasts. 3. What pigment is stored inside the chloroplast ...
... 1. What do chloroplasts do for cells? Chloroplasts take in sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make oxygen and sugar (a form of food). This process is called photosynthesis. 2. Do animals have chloroplasts? No, animal cells do not have chloroplasts. 3. What pigment is stored inside the chloroplast ...
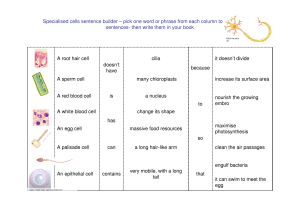
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...