Cells - SchoolRack
... • Assembly of Lipids • Assists with Protein Synthesis • Rough ER: contains ribosomes • Smooth ER: no ribosomes ...
... • Assembly of Lipids • Assists with Protein Synthesis • Rough ER: contains ribosomes • Smooth ER: no ribosomes ...
Randolph-Henry Biology Benchmark Test Six Weeks #1
... _____3. In the metric system which of the following is a smaller unit? a. 5 millimeters b. 5 meters c. 5 centimeter d. 5 kilometers _____4. A microscope is fitted with a 10x ocular lens and a 35x objective. What is the total magnification of the specimen studied? a. 35x b. 45x c. 100x d. 350x _____5 ...
... _____3. In the metric system which of the following is a smaller unit? a. 5 millimeters b. 5 meters c. 5 centimeter d. 5 kilometers _____4. A microscope is fitted with a 10x ocular lens and a 35x objective. What is the total magnification of the specimen studied? a. 35x b. 45x c. 100x d. 350x _____5 ...
Cell Continuity 2
... Cell A has twice as much DNA as cell B. Both cells are of the same type. A possible explanation for this is that cell A is … Photosynthesising ...
... Cell A has twice as much DNA as cell B. Both cells are of the same type. A possible explanation for this is that cell A is … Photosynthesising ...
CELL ORGANELLES
... Proteins need to be packaged up. Bent into their 3D structure. Who does that? ...
... Proteins need to be packaged up. Bent into their 3D structure. Who does that? ...
PROKARYOTES
... Types of Cells (Prokaryote and eukaryote) Are: • They both have DNA as their genetic material. • They are both membrane bound. • They both have ribosomes . • They have similar basic metabolism . • They are both amazingly diverse in forms. ...
... Types of Cells (Prokaryote and eukaryote) Are: • They both have DNA as their genetic material. • They are both membrane bound. • They both have ribosomes . • They have similar basic metabolism . • They are both amazingly diverse in forms. ...
CELL ORGANELLE ANALOGY PROJECT RUBERIC
... Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your analogy relates to the organel ...
... Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your analogy relates to the organel ...
An Interactive Lecture Guide to help you understand THE
... • Sodium ions bind to the protein on the inside of the cell membrane; • ATP is hydrolyzed and the phosphate produced is linked to the protein • The shape of the protein is changed in such a way that the sodium ion can be expelled out of the cell • Potassium ions bind to the protein • Phosphate grou ...
... • Sodium ions bind to the protein on the inside of the cell membrane; • ATP is hydrolyzed and the phosphate produced is linked to the protein • The shape of the protein is changed in such a way that the sodium ion can be expelled out of the cell • Potassium ions bind to the protein • Phosphate grou ...
Week 3 Agenda and Notes
... Nucleoplasm: (like cytoplasm but for nucleus) Chromatin – contains genetic material (DNA); later condense to form the chromosomes ...
... Nucleoplasm: (like cytoplasm but for nucleus) Chromatin – contains genetic material (DNA); later condense to form the chromosomes ...
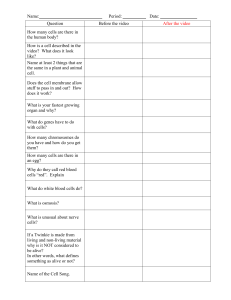
Question Before the video After the video How many cells are there
... video? What does it look like? Name at least 2 things that are the same in a plant and animal cell. Does the cell membrane allow stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do yo ...
... video? What does it look like? Name at least 2 things that are the same in a plant and animal cell. Does the cell membrane allow stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do yo ...
Lecture 04 Notes
... • Nuclear envelope – a double membrane with pores that control flow of material into and out of nucleus • Nucleolus – ribosomes made here – “little nucleus” • Ribosomes – sites of protein synthesis – ...
... • Nuclear envelope – a double membrane with pores that control flow of material into and out of nucleus • Nucleolus – ribosomes made here – “little nucleus” • Ribosomes – sites of protein synthesis – ...
Visual PPT Quiz # 5
... constant temperatures for twenty-four hours every day. They did the same for the corn and cucumber plants. The graph shows the growth rates that they recorded for the different groups of plants. ...
... constant temperatures for twenty-four hours every day. They did the same for the corn and cucumber plants. The graph shows the growth rates that they recorded for the different groups of plants. ...
Chapter 7 Cells
... Plasma Membrane or Cell Membrane: surrounds the entire cell and regulates the movement of materials or signals into and out of the cell. Cytoplasm: fluid environment between the nucleus and plasma membrane in which other organelles are suspended. This is where biochemical processes occur. ...
... Plasma Membrane or Cell Membrane: surrounds the entire cell and regulates the movement of materials or signals into and out of the cell. Cytoplasm: fluid environment between the nucleus and plasma membrane in which other organelles are suspended. This is where biochemical processes occur. ...
cell structures powerpoint
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells. ...
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells. ...
Cell Wall - Cloudfront.net
... permeable due to their structure • 2B2: Growth and dynamic homeostasis are maintained by the constant movement of molecules across membranes • 2B3: Eukaryotic cells maintain internal membranes that partition the cell into specialized regions ...
... permeable due to their structure • 2B2: Growth and dynamic homeostasis are maintained by the constant movement of molecules across membranes • 2B3: Eukaryotic cells maintain internal membranes that partition the cell into specialized regions ...
FIGURE 18.1
... – Most 1-10 μm; seen in fossil record by 3.5 bya; lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (DNA free in cell, in nucleoid ...
... – Most 1-10 μm; seen in fossil record by 3.5 bya; lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (DNA free in cell, in nucleoid ...
File
... Animal cells split into two separate identical cells during division while plant cells stay connected and grow a ________ to divide. ...
... Animal cells split into two separate identical cells during division while plant cells stay connected and grow a ________ to divide. ...
Cells- the smallest unit that can perform all of life
... nuclei. 29. Multicellular organisms- are organisms consisting of more than one cell. 30. Nuclear Membranes- is a double lipid bilayer (thin membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules) that encloses the genetic material in eukaryotic cells….layer around the nucleus 31. Nucleolus- non-membrane bou ...
... nuclei. 29. Multicellular organisms- are organisms consisting of more than one cell. 30. Nuclear Membranes- is a double lipid bilayer (thin membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules) that encloses the genetic material in eukaryotic cells….layer around the nucleus 31. Nucleolus- non-membrane bou ...
Cells 2 Quail
... Rough and Smooth Rough has ribosomes- makes/transports proteins Smooth makes/transports lipids ...
... Rough and Smooth Rough has ribosomes- makes/transports proteins Smooth makes/transports lipids ...
Cell Structure
... The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is one of the main manufacturing facilities in a cell. The ER produces an enormous variety of molecules Is composed of smooth and rough ER Rough ER The “rough” in the rough ER is due to ribosomes that stud the outside of the ER membrane. These ribosomes produce membran ...
... The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is one of the main manufacturing facilities in a cell. The ER produces an enormous variety of molecules Is composed of smooth and rough ER Rough ER The “rough” in the rough ER is due to ribosomes that stud the outside of the ER membrane. These ribosomes produce membran ...
Cell Structures
... Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function Stores material within the cell Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only ...
... Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function Stores material within the cell Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only ...
Active & Passive Transport Illlustrations
... Endocytosis • Take in external fluid, macromolecules and other large particles. • Forms “vesicle” some fuse with lysosomes (digestion) others fuse with membrane of other organelles. • 2 Types: a) pinocytosis – cell drinking fluid ...
... Endocytosis • Take in external fluid, macromolecules and other large particles. • Forms “vesicle” some fuse with lysosomes (digestion) others fuse with membrane of other organelles. • 2 Types: a) pinocytosis – cell drinking fluid ...
Biology: Cell Test
... What are the threadlike structures that contain genetic information called? Ribosomes Lysosomes Chromosomes None of the above What do the endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and mitochondria have in common? They are all organelles They are all found in the nucleus They are all ribosomes What are ...
... What are the threadlike structures that contain genetic information called? Ribosomes Lysosomes Chromosomes None of the above What do the endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and mitochondria have in common? They are all organelles They are all found in the nucleus They are all ribosomes What are ...