Cells - Barbados SDA Secondary
... • To see even smaller things inside a cell, an electron microscope is used. • This uses a beam of electrons instead of light, and can magnify up to 500 000 times. This means that a lot more detail can be seen inside a cell, as shown in Next ...
... • To see even smaller things inside a cell, an electron microscope is used. • This uses a beam of electrons instead of light, and can magnify up to 500 000 times. This means that a lot more detail can be seen inside a cell, as shown in Next ...
Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells
... By not digesting them completely, but removing the cell wall, the archaeon has gained two gigantic biochemical pathways: respiration and photosynthesis By moving critical genes from each endosymbiont, using its transposon feature, the archaeon has trapped both endosymbionts as permanent organelles T ...
... By not digesting them completely, but removing the cell wall, the archaeon has gained two gigantic biochemical pathways: respiration and photosynthesis By moving critical genes from each endosymbiont, using its transposon feature, the archaeon has trapped both endosymbionts as permanent organelles T ...
4. Cells Alive Internet Lesson 71KB Dec 07 2010 11:05:12 AM
... 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? ...
... 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? ...
AP Biology – Unit 1 Review Terms/Questions Use this to help you
... Saturated versus Unsaturated Fatty Acids – implication on structure? If an organism has a higher number of unsaturated fatty acids in its cell membrane compared to another organism, predict how the fluidity of the two organisms membranes would differ Building blocks of phospholipids – amphipathic mo ...
... Saturated versus Unsaturated Fatty Acids – implication on structure? If an organism has a higher number of unsaturated fatty acids in its cell membrane compared to another organism, predict how the fluidity of the two organisms membranes would differ Building blocks of phospholipids – amphipathic mo ...
Amazing Cells Build-A-Membrane
... graphics. • Tips for using Print-and-Go™ activities with online materials. and much more! ...
... graphics. • Tips for using Print-and-Go™ activities with online materials. and much more! ...
© 2010–2015 Edusmart 1 Plant vs Animal Cell Note
... ______________________. Since prokaryotic cells lack a ______________, their DNA floats freely in their cytoplasm. ...
... ______________________. Since prokaryotic cells lack a ______________, their DNA floats freely in their cytoplasm. ...
BY 123 SI Mock Exam #1 Chapters 1
... Rough ER nuclear envelope Golgi smooth ER lysosome Rough ER transport vesicle Golgi smooth ER plasma membrane Rough ER transport vesicle Golgi vesicle extracellular matrix ...
... Rough ER nuclear envelope Golgi smooth ER lysosome Rough ER transport vesicle Golgi smooth ER plasma membrane Rough ER transport vesicle Golgi vesicle extracellular matrix ...
Cells
... • Endoplasmic Reticulum: Serves as the protein transport system of the cell. – Smooth E.R.: Has no ribosomes. – Rough E.R.: Has ribosomes. (Highway) ...
... • Endoplasmic Reticulum: Serves as the protein transport system of the cell. – Smooth E.R.: Has no ribosomes. – Rough E.R.: Has ribosomes. (Highway) ...
Cell Structure
... Made in the nucleolus Found mostly on ER but also floating in cytoplasm Found in all types of cells “Protein factories” for cell • Join amino acids to make proteins (process called protein synthesis) ...
... Made in the nucleolus Found mostly on ER but also floating in cytoplasm Found in all types of cells “Protein factories” for cell • Join amino acids to make proteins (process called protein synthesis) ...
Chapter 7
... • Cells containing membrane-bound structures • Mostly multicellular with some exceptions such as algae and yeast • Ex: plants and animals ...
... • Cells containing membrane-bound structures • Mostly multicellular with some exceptions such as algae and yeast • Ex: plants and animals ...
LS1 PowerPoint Cells ls1.powerpoint.cells
... membrane and the nucleus. (organelles + cytosol) a. Cytosol = liquid portion/non-organelles. 2. Structure: made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus ...
... membrane and the nucleus. (organelles + cytosol) a. Cytosol = liquid portion/non-organelles. 2. Structure: made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus ...
Cell Organelle Pre Test - Gulf Coast State College
... _____1. Which organelle provides energy to the cell through the process of cellular respiration? A. Chloroplast B. Mitochondria C. Lysosome D. Nucleus _____ 2. A gel-like substance that holds the organelles in place and acts like a filler for the cell is known as the: A. Cytoplasm B. Cytoskeleton C. ...
... _____1. Which organelle provides energy to the cell through the process of cellular respiration? A. Chloroplast B. Mitochondria C. Lysosome D. Nucleus _____ 2. A gel-like substance that holds the organelles in place and acts like a filler for the cell is known as the: A. Cytoplasm B. Cytoskeleton C. ...
Year 12 Revision Quiz
... • Translocation requires energy/ goes up and down/ carried in the phloem ...
... • Translocation requires energy/ goes up and down/ carried in the phloem ...
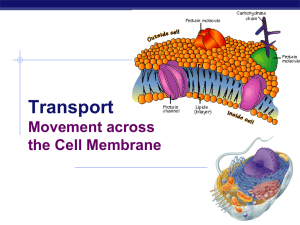
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... How about large molecules? Moving large molecules into & out of cell through vesicles & vacuoles Endocytosis (moving into cell) phagocytosis = “cellular eating” ...
... How about large molecules? Moving large molecules into & out of cell through vesicles & vacuoles Endocytosis (moving into cell) phagocytosis = “cellular eating” ...
chapter 9 homeostasis & the plasma membrane
... 2. Adhesion Proteins - composed of glycoproteins attached to oligosaccharides. Serve as the “glue” to hold cells together. ...
... 2. Adhesion Proteins - composed of glycoproteins attached to oligosaccharides. Serve as the “glue” to hold cells together. ...
cell structure and function
... must be done to overcome the influences of diffusion and osmosis. Since in the normal state of a cell, large concentration differences in K+, Na+ and Ca2+ are maintained, it is evident that active transport mechanisms are at work. ...
... must be done to overcome the influences of diffusion and osmosis. Since in the normal state of a cell, large concentration differences in K+, Na+ and Ca2+ are maintained, it is evident that active transport mechanisms are at work. ...
Osmosis in a Plant Cell
... hospital! A patient was given an I.V. bag with distilled water in it rather than saline solution. • Describe what would happen to their red blood cells and explain why this would occur. ...
... hospital! A patient was given an I.V. bag with distilled water in it rather than saline solution. • Describe what would happen to their red blood cells and explain why this would occur. ...
Cell Structures and Their Functions
... • Diffusion of water molecules through cell membranes. • Results in changes in osmotic pressure (water pressure). • Hypotonic: More water outside of cell so water moves in. • Isotonic: Same amount of water outside and in. • Hypertonic: Less water outside of cell so water moves out. ...
... • Diffusion of water molecules through cell membranes. • Results in changes in osmotic pressure (water pressure). • Hypotonic: More water outside of cell so water moves in. • Isotonic: Same amount of water outside and in. • Hypertonic: Less water outside of cell so water moves out. ...
Cell function notes
... Oval discs with green chlorophyll Found in plant cells Function is to use the energy from the sun (photosynthesis) to make food (glucose) & oxygen ...
... Oval discs with green chlorophyll Found in plant cells Function is to use the energy from the sun (photosynthesis) to make food (glucose) & oxygen ...
Cell membrane
... They are more important in plant cells. Most of the center of a plant cell is occupied by a central vacuole. The central vacuole gives support because pressure within the vacuole makes the cell rigid (turgid). The cell wall prevents the cell from bursting. ...
... They are more important in plant cells. Most of the center of a plant cell is occupied by a central vacuole. The central vacuole gives support because pressure within the vacuole makes the cell rigid (turgid). The cell wall prevents the cell from bursting. ...
Looking Inside Cells
... The Nucleus The nucleus is the cell’s control center, directing all of the cell’s activities. Instructions that guide the cell’s activities are contained in the DNA. DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell. ...
... The Nucleus The nucleus is the cell’s control center, directing all of the cell’s activities. Instructions that guide the cell’s activities are contained in the DNA. DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell. ...
transport proteins
... • Free (unbound) water molecules will move from the hypotonic solution where they are abundant to the hypertonic solution where they are rarer. • This diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is a special case of passive transport called osmosis. ...
... • Free (unbound) water molecules will move from the hypotonic solution where they are abundant to the hypertonic solution where they are rarer. • This diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is a special case of passive transport called osmosis. ...
Cells Structure and Functions
... the smallest unit of life that carries out all life functions Contain major structures inside that perform these life functions Vary in size, but contain many of the same structures ...
... the smallest unit of life that carries out all life functions Contain major structures inside that perform these life functions Vary in size, but contain many of the same structures ...
cell as a school powerpoint webquest
... because he provides shape and order for our school like a cell wall provides the shape of the cell. ...
... because he provides shape and order for our school like a cell wall provides the shape of the cell. ...
CHAPTER 3 OBJECTIVES: CELLS
... Describe what a nuclear pore is and explain its function. Nuclear envelope is a double membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm; At various points, these two membranes fuse = nuclear pore. ...
... Describe what a nuclear pore is and explain its function. Nuclear envelope is a double membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm; At various points, these two membranes fuse = nuclear pore. ...