Cellular Organization and Cell Theory Notes
... 2) The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things 3) All cells come from existing cells Exceptions to the Cell Theory – Where did the first cell come from? ...
... 2) The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things 3) All cells come from existing cells Exceptions to the Cell Theory – Where did the first cell come from? ...
RBC_memb
... BAND 3 One of the integral proteins Has two major functions within the red cell membrane: 1- Its primary function is to facilitate anion transport via the red cell membrane. 2- It is an important binding site for cytoskeletal and other red cell proteins. ...
... BAND 3 One of the integral proteins Has two major functions within the red cell membrane: 1- Its primary function is to facilitate anion transport via the red cell membrane. 2- It is an important binding site for cytoskeletal and other red cell proteins. ...
6th Grade
... 8. The sixth step is to place 3 skittles at random anywhere on the cell. The skittles represent lysosomes. Lysosomes are important to the cell because they ______________________________________________. 9. The seventh step is to place one ___ hot above the Golgi body to represent the centrosome. 10 ...
... 8. The sixth step is to place 3 skittles at random anywhere on the cell. The skittles represent lysosomes. Lysosomes are important to the cell because they ______________________________________________. 9. The seventh step is to place one ___ hot above the Golgi body to represent the centrosome. 10 ...
Cells The Working Units of Life Course: Environment & Biological Diversity
... the site of DNA replication. the site of genetic control of the cell's activities. A region within the nucleus, the nucleolus, begins the assembly of ribosomes from RNA and specific proteins. ...
... the site of DNA replication. the site of genetic control of the cell's activities. A region within the nucleus, the nucleolus, begins the assembly of ribosomes from RNA and specific proteins. ...
study guide for biology final 2008
... Know all the main events associated with each stage of the cell cycle; be able to identify each phase of mitosis. You will not draw it yourself. Know the main differences between mitosis in animals and plants Understand how cancer is related to cell division Know chromosome structure and the relatio ...
... Know all the main events associated with each stage of the cell cycle; be able to identify each phase of mitosis. You will not draw it yourself. Know the main differences between mitosis in animals and plants Understand how cancer is related to cell division Know chromosome structure and the relatio ...
Cell Project Choices
... Learning Target: I can d escribe the physical structure a nd function a nd of cell organelles. Organelles to research: ...
... Learning Target: I can d escribe the physical structure a nd function a nd of cell organelles. Organelles to research: ...
Membrane PPT
... cell uses no energy molecules move randomly Molecules spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. ...
... cell uses no energy molecules move randomly Molecules spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Diagram B shows their appearance after the addition of another liquid. ...
... Diagram B shows their appearance after the addition of another liquid. ...
File
... C) peroxisome. D) Golgi apparatus. 36) An immune system cell called the plasma cell produces thousands of antibodies per second for release into the body. What type of intracellular structure would you expect to be very prominent within the cell? A) nucleus B) endoplasmic reticulum C) peroxisome D) ...
... C) peroxisome. D) Golgi apparatus. 36) An immune system cell called the plasma cell produces thousands of antibodies per second for release into the body. What type of intracellular structure would you expect to be very prominent within the cell? A) nucleus B) endoplasmic reticulum C) peroxisome D) ...
Life Science Unit Test Review Key File
... They do not have a nucleus, and their DNA is scattered randomly throughout the cell. They don’t contain as many organelles as eukaryotic cells. They contain cytoplasm, a cell membrane, and ribosomes. They are less complicated and smaller that eukaryotes. All Bacteria and Achaea are prokaryot ...
... They do not have a nucleus, and their DNA is scattered randomly throughout the cell. They don’t contain as many organelles as eukaryotic cells. They contain cytoplasm, a cell membrane, and ribosomes. They are less complicated and smaller that eukaryotes. All Bacteria and Achaea are prokaryot ...
Domain 1
... 28. B) mitochondria 29. B) Proteins make up most of the cell and tissue structures in animals. 30. D) ribosome 31. B) Bonds in the hydrogen peroxide are weakened in catalase's active site, allowing the chemical reaction to occur. 32. D) clot protein 33. A) It would be unable to regulate water storag ...
... 28. B) mitochondria 29. B) Proteins make up most of the cell and tissue structures in animals. 30. D) ribosome 31. B) Bonds in the hydrogen peroxide are weakened in catalase's active site, allowing the chemical reaction to occur. 32. D) clot protein 33. A) It would be unable to regulate water storag ...
Skills Worksheet
... 9. Scientists first discovered cells by using a(n) ______________________. 10. A cell’s boundary is called the ______________________ ______________________. 11. ______________________ are cell structures common to both prokaryotes and eukaryotes on which proteins are made. 12. Eukaryotes differ fro ...
... 9. Scientists first discovered cells by using a(n) ______________________. 10. A cell’s boundary is called the ______________________ ______________________. 11. ______________________ are cell structures common to both prokaryotes and eukaryotes on which proteins are made. 12. Eukaryotes differ fro ...
AP ch6 cells - Foglia and Reidell
... Regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell Includes: Plasma membrane Nuclear membrane Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Vacuoles Lysosomes ...
... Regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell Includes: Plasma membrane Nuclear membrane Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Vacuoles Lysosomes ...
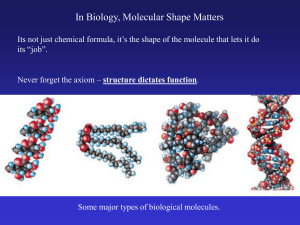
In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters
... In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
Cellular Transport Review
... __HYPER____tonic means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. __HYPO____ tonic means there is a LOWER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. __ISO_____tonic means there is the SAME concentration of solute molecules outside the cell ...
... __HYPER____tonic means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. __HYPO____ tonic means there is a LOWER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. __ISO_____tonic means there is the SAME concentration of solute molecules outside the cell ...
MITOSIS
... 1. is the first stage of mitosis 2. Chromatin (the bundled mass that our DNA stays as 99% of the time) will untangle to form 92 condensed, rod like structures called Chromatids 3. The chromatids find their matching (homologous) partner and make 46 chromosomes 4. One chromosome= 2 chromatids attached ...
... 1. is the first stage of mitosis 2. Chromatin (the bundled mass that our DNA stays as 99% of the time) will untangle to form 92 condensed, rod like structures called Chromatids 3. The chromatids find their matching (homologous) partner and make 46 chromosomes 4. One chromosome= 2 chromatids attached ...
Interactive Review CHAPTER REVIEW Reviewing
... have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that perform specialized tasks within the cell. Many of these organelles are involved in making proteins. Plant and animal cells share many of the same types of organelles, but both also have organelles that are specific to the cells’ unique functio ...
... have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that perform specialized tasks within the cell. Many of these organelles are involved in making proteins. Plant and animal cells share many of the same types of organelles, but both also have organelles that are specific to the cells’ unique functio ...
Cell Membranes
... 4 Parts of All Cells 1. Cytoplasm- watery substance inside all cells 2. Cell membrane (plasma membrane)- “door” to the factory that’s made of lipids and proteins ...
... 4 Parts of All Cells 1. Cytoplasm- watery substance inside all cells 2. Cell membrane (plasma membrane)- “door” to the factory that’s made of lipids and proteins ...
active transport
... The cytoplasm of plant cells is about 95% water, and of animal and bacterial cells is about 70% water. There are different concentrations of both water-soluble and -soluble substances in the cytoplasm that must pass into and out of the cell and organelle membranes. Membranes Fluid-Mosaic Model ...
... The cytoplasm of plant cells is about 95% water, and of animal and bacterial cells is about 70% water. There are different concentrations of both water-soluble and -soluble substances in the cytoplasm that must pass into and out of the cell and organelle membranes. Membranes Fluid-Mosaic Model ...
EE I Chapter 2 Cell Structures and Functions
... Function: Provides a route for cell products to move throughout the cell ...
... Function: Provides a route for cell products to move throughout the cell ...
Cells
... List A gives the names of different types of cells found in plants and animals. List B gives one special feature of each of these cells. Match each cell type with its feature by writing the relevant letter and number next to one another. List A ...
... List A gives the names of different types of cells found in plants and animals. List B gives one special feature of each of these cells. Match each cell type with its feature by writing the relevant letter and number next to one another. List A ...
Macromolecules of Life Macromolecules of Life
... g adult male human: 11kg g of p protein,, 9 kg g of fat,, 1 kg g of carbohydrate, 4 kg of minerals and 40 kg of water, but the weight of nucleic acids in an organism is much less than the corresponding weights of other macromolecules Macromolecules of different classes interact with each other by fo ...
... g adult male human: 11kg g of p protein,, 9 kg g of fat,, 1 kg g of carbohydrate, 4 kg of minerals and 40 kg of water, but the weight of nucleic acids in an organism is much less than the corresponding weights of other macromolecules Macromolecules of different classes interact with each other by fo ...