Chapter 27
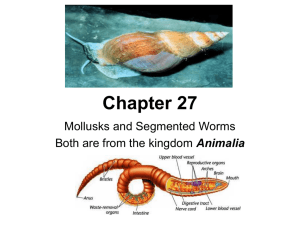
... Mouth-takes in food Crop-stores food until it can be broken down Gizzard-has stone-like structures that grind up soil/food until tiny pieces can be absorbed by the intestines Nephridia-structures that eliminate waste found on each segment Setae-tiny hairs that extend from each segment – Anchors worm ...
... Mouth-takes in food Crop-stores food until it can be broken down Gizzard-has stone-like structures that grind up soil/food until tiny pieces can be absorbed by the intestines Nephridia-structures that eliminate waste found on each segment Setae-tiny hairs that extend from each segment – Anchors worm ...
The Amazing Cell - Trisha Hanka`s VTI site
... • Prokaryotes- “before nucleus”, cells without nucleus were thought to have developed first. • Has DNA but not in a separate compartment • Eukaryotes- “true nucleus”, developed later and are found in all multicellular organisms. • Has distinct nucleus surrounded by protective nuclear envelope. ...
... • Prokaryotes- “before nucleus”, cells without nucleus were thought to have developed first. • Has DNA but not in a separate compartment • Eukaryotes- “true nucleus”, developed later and are found in all multicellular organisms. • Has distinct nucleus surrounded by protective nuclear envelope. ...
Animal Development, Organogenesis, and Animal Tissues
... embryo. The center of the plate sinks, giving rise to a neural groove, and the edges of the plate elevate to form neural folds. These folds move towards each other until they eventually fuse, producing the hollow neural tube. The anterior end of the tube develops into the brain, while the posterior ...
... embryo. The center of the plate sinks, giving rise to a neural groove, and the edges of the plate elevate to form neural folds. These folds move towards each other until they eventually fuse, producing the hollow neural tube. The anterior end of the tube develops into the brain, while the posterior ...
Clara Cell Differentiation in the Albino Rat Ultrastructural and
... was in the apical region of the cells. Labeling was increased by 7 DPN to the same intensity and distribution of adult. The Clara cell population was virtually restricted to the bronchioles. The lining epithelium was formed of single layer, at all studied ages, but showed gradual increase in height ...
... was in the apical region of the cells. Labeling was increased by 7 DPN to the same intensity and distribution of adult. The Clara cell population was virtually restricted to the bronchioles. The lining epithelium was formed of single layer, at all studied ages, but showed gradual increase in height ...
PDF file - School of Mathematics and Statistics
... around 9 million predicted to die in 2015, with the number rising to 11.5 million in 2030. Perhaps a major reason for these statistics is that cancer growth is a complicated complex phenomenon involving many inter-related processes across a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. New approaches a ...
... around 9 million predicted to die in 2015, with the number rising to 11.5 million in 2030. Perhaps a major reason for these statistics is that cancer growth is a complicated complex phenomenon involving many inter-related processes across a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. New approaches a ...
Unit 5.2 Plant Cells
... cells. Cells need energy to carry out their required functions, such as reproduction. They obtain this energy by ‘burning’ the glucose in a chemical reaction known as cellular respiration. Respiration requires glucose and a supply of oxygen gas. The glucose is formed by photosynthesis and the oxygen ...
... cells. Cells need energy to carry out their required functions, such as reproduction. They obtain this energy by ‘burning’ the glucose in a chemical reaction known as cellular respiration. Respiration requires glucose and a supply of oxygen gas. The glucose is formed by photosynthesis and the oxygen ...
What you absolutely must know to pass the regent`s test
... A great diversity of species increases the chance that at least some living things will survive when the environment changes. ...
... A great diversity of species increases the chance that at least some living things will survive when the environment changes. ...
7th_Unit 3_Part 3_Body Systems_SS
... in the abdomen that expands to hold all the food that is swallowed. Small Intestines- Organ where chemical digestion occurs. Liver- The largest and heaviest organ, breaks down substances and eliminates nitrogen from the body. Pancreas-Produces enzymes that flow into the small intestines. Large Intes ...
... in the abdomen that expands to hold all the food that is swallowed. Small Intestines- Organ where chemical digestion occurs. Liver- The largest and heaviest organ, breaks down substances and eliminates nitrogen from the body. Pancreas-Produces enzymes that flow into the small intestines. Large Intes ...
SHL_Paper1_v2_Stemcell
... access to unlimited stem cell cures? However, isn’t it unethical or even just plain mean to keep this panacea for solely research purposes? And even more so for those who can afford it? Then there would be further arguments in the religious world. Having the ability to cure all these diseases and si ...
... access to unlimited stem cell cures? However, isn’t it unethical or even just plain mean to keep this panacea for solely research purposes? And even more so for those who can afford it? Then there would be further arguments in the religious world. Having the ability to cure all these diseases and si ...
Transport Study Guide Key
... A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system has reached ____________ ...
... A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system has reached ____________ ...
Nervous System
... the cell and Na+ not able to enter the cell. Increase in negative charge since + ions are leaving axon with no + ions being able to enter the neuron. ...
... the cell and Na+ not able to enter the cell. Increase in negative charge since + ions are leaving axon with no + ions being able to enter the neuron. ...
Lab #2 – Skin Cells - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Human Biology 11 – Dalesandro Lab #2 – Skin Cells ...
... Human Biology 11 – Dalesandro Lab #2 – Skin Cells ...
Section 3 Workbook (Unit 8 ANSWERS) Urinary System
... When you are dehydrated, the kidneys reabsorb most of the water from the filtrate. This occurs because the blood passes through the hypothalamus. This allows the hypothalamus to detect a low concentration of water in the blood and cause the posterior pituitary gland to release ADH. ADH travels throu ...
... When you are dehydrated, the kidneys reabsorb most of the water from the filtrate. This occurs because the blood passes through the hypothalamus. This allows the hypothalamus to detect a low concentration of water in the blood and cause the posterior pituitary gland to release ADH. ADH travels throu ...
756. Synthesis of Poly(ester amide)
... determine no significant cell death from treatment with 2015, work from the Beier lab at UWO looked at the role the material. of PPARd in OA, and determined that PPARd inhibitors could be a significant new target therapeutic in the treatment of OA.3While these inhibitors exist they are extremely hyd ...
... determine no significant cell death from treatment with 2015, work from the Beier lab at UWO looked at the role the material. of PPARd in OA, and determined that PPARd inhibitors could be a significant new target therapeutic in the treatment of OA.3While these inhibitors exist they are extremely hyd ...
Tissue
... Permeability layers – prevent passage of materials Intestinal lining and most simple epithelia Desmosomes – anchor cells to one another Hemidesmosomes – anchor cells to basement membrane Epithelia subject to stress (skin stratified squamous) Gap Junctions – allow passage of molecules/ions be ...
... Permeability layers – prevent passage of materials Intestinal lining and most simple epithelia Desmosomes – anchor cells to one another Hemidesmosomes – anchor cells to basement membrane Epithelia subject to stress (skin stratified squamous) Gap Junctions – allow passage of molecules/ions be ...
Schoolnet
... 29. A student compares a plant cell to an animal cell. Which structure will the student find ONLY in the plant cell? A. ...
... 29. A student compares a plant cell to an animal cell. Which structure will the student find ONLY in the plant cell? A. ...
Journey into a Cell: Organizer Sheet
... ensure a quality story. This "Planning Page" will help your team outline your story, Journey into a Cell. Use the "Organizer Sheet" on the reverse side to help you add facts to your story. ...
... ensure a quality story. This "Planning Page" will help your team outline your story, Journey into a Cell. Use the "Organizer Sheet" on the reverse side to help you add facts to your story. ...
Living Cells Notes
... 4. Osmosis is a special case of water diffusion. Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration, down a water concentration gradient, and through a selectively permeable membrane. 5. Cell membranes are known as selectively permeable me ...
... 4. Osmosis is a special case of water diffusion. Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration, down a water concentration gradient, and through a selectively permeable membrane. 5. Cell membranes are known as selectively permeable me ...
A molecular mechanism involved in cellular proliferation
... optimise current oncological therapies specifically designed to fight against this framework, named by the scientific community as microtubules. Key molecules for cellular proliferation "During cell division, alterations in microtubule formation may bring about chromosome instability and aneuploidy. ...
... optimise current oncological therapies specifically designed to fight against this framework, named by the scientific community as microtubules. Key molecules for cellular proliferation "During cell division, alterations in microtubule formation may bring about chromosome instability and aneuploidy. ...
Lecture 6
... Some transport proteins have channels with gates. The gate opens to let the target molecule pass through when it receives an electrical or chemical signal. For example, neurotransmitter chemicals serve as signal molecules to open the gates for sodium to flow into the nerve cell. Facilitated diffusio ...
... Some transport proteins have channels with gates. The gate opens to let the target molecule pass through when it receives an electrical or chemical signal. For example, neurotransmitter chemicals serve as signal molecules to open the gates for sodium to flow into the nerve cell. Facilitated diffusio ...
INDEX OF AUTHORS
... Xenopus laevis, electron-microscope anacell-surface protein produced by, ability to lysis : HILL & MACGREGOR 87 modify tissue affinity behaviour of Differentiating macronuclei cardiac myocytes: ARMSTRONG 263 of Loxodes magnus, changes in DNA conof hamster, inhibition of fibronectintent Of: BOBYLEVA, ...
... Xenopus laevis, electron-microscope anacell-surface protein produced by, ability to lysis : HILL & MACGREGOR 87 modify tissue affinity behaviour of Differentiating macronuclei cardiac myocytes: ARMSTRONG 263 of Loxodes magnus, changes in DNA conof hamster, inhibition of fibronectintent Of: BOBYLEVA, ...
Jan 14
... • No germ line! Cells at apical meristem become flowers: allows Lamarckian evolution! • Different parts of the same 2000 year old tree have different DNA & form different gametes ...
... • No germ line! Cells at apical meristem become flowers: allows Lamarckian evolution! • Different parts of the same 2000 year old tree have different DNA & form different gametes ...
BIL 255 – CMB
... tonoplast membrane permeable to water influx, helps establish turgor pressure (5-20 ATM) Mallery ...
... tonoplast membrane permeable to water influx, helps establish turgor pressure (5-20 ATM) Mallery ...























