Test 1
... F. (pg 11) Describe and understand 2 examples of how chemical agents injure cells. Some chemicals act directly by combining with a critical molecular component or cellular component or cellular organelle. Ex: mercuric chloride poisoning, mercury binds to the sulfhydryl groups of various cell membran ...
... F. (pg 11) Describe and understand 2 examples of how chemical agents injure cells. Some chemicals act directly by combining with a critical molecular component or cellular component or cellular organelle. Ex: mercuric chloride poisoning, mercury binds to the sulfhydryl groups of various cell membran ...
Adaptations for Life on Land -fossils and other evidence indicate that
... arteries- carry blood away from the heart -carry oxygenated blood (which is bright red) -larger in diameter -thicker – more smooth muscle tissue that allows blood vessels to contract and move blood -able to constrict on their own -found deep (closer to the bone) -coronary arteries: carry blood to th ...
... arteries- carry blood away from the heart -carry oxygenated blood (which is bright red) -larger in diameter -thicker – more smooth muscle tissue that allows blood vessels to contract and move blood -able to constrict on their own -found deep (closer to the bone) -coronary arteries: carry blood to th ...
BOTANY FOLDABLES FOR CH 23
... OUTSIDE: Most plants have a method of development that involves an INSIDE: open or indeterminate, type of growth. They grow and produce new cells at the _________________________________________ for as long as they live. These cells are produced in _________________________. OUTSIDE: Meristem INSIDE ...
... OUTSIDE: Most plants have a method of development that involves an INSIDE: open or indeterminate, type of growth. They grow and produce new cells at the _________________________________________ for as long as they live. These cells are produced in _________________________. OUTSIDE: Meristem INSIDE ...
ch 7 test-transport systems
... -a healthy blood pressure is maintained through complex interactions involving hormones and the nervous, excretory, and circulatory systems -nerves connect pressure receptors in the aorta and the artery leading to the brain -other cardiac things respond to sensory input like emotions and chemical in ...
... -a healthy blood pressure is maintained through complex interactions involving hormones and the nervous, excretory, and circulatory systems -nerves connect pressure receptors in the aorta and the artery leading to the brain -other cardiac things respond to sensory input like emotions and chemical in ...
Lymphoid B cells induce NF-jB activation in high endothelial cells
... domains. In unstimulated cells, homo- or heterodimers of NF-jB are retained in the cytoplasm in an inactive form through interaction with the family of inhibitory proteins IjBs, which impede their nuclear translocation. In response to a variety of stimuli, IjB proteins undergo phosphorylation and ra ...
... domains. In unstimulated cells, homo- or heterodimers of NF-jB are retained in the cytoplasm in an inactive form through interaction with the family of inhibitory proteins IjBs, which impede their nuclear translocation. In response to a variety of stimuli, IjB proteins undergo phosphorylation and ra ...
Insulin-Resistance, Browning
... In humans, brown fat is abundant at birth but is rapidly replaced by white adipose tissue (WAT) and is relatively scarce in the adult as an identifiable tissue. Brown fat cells are interspersed within WAT of rodents and humans. Activation of BAT requires 3-adrenergic receptor agonism. ...
... In humans, brown fat is abundant at birth but is rapidly replaced by white adipose tissue (WAT) and is relatively scarce in the adult as an identifiable tissue. Brown fat cells are interspersed within WAT of rodents and humans. Activation of BAT requires 3-adrenergic receptor agonism. ...
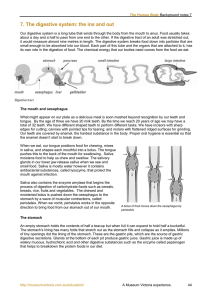
The Human Body - Background Notes 7-9
... digestive juices from our liver, gall bladder and pancreas are squirted and mixed into the food. The small intestine is where most digestion and absorption take place. Food usually spends about six hours being digested in the small intestine. The digested liquid slowly moves along by muscular contra ...
... digestive juices from our liver, gall bladder and pancreas are squirted and mixed into the food. The small intestine is where most digestion and absorption take place. Food usually spends about six hours being digested in the small intestine. The digested liquid slowly moves along by muscular contra ...
The cell biology of neural stem and progenitor cells - MPI
... have been linked to ciliary function: the sonic hedgehog (shh) and the wnt pathways [33,34]. Thus, shh signaling via the primary cilium has a crucial role for the expansion of neural progenitors during adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus [35] and during neurogenesis in the dev ...
... have been linked to ciliary function: the sonic hedgehog (shh) and the wnt pathways [33,34]. Thus, shh signaling via the primary cilium has a crucial role for the expansion of neural progenitors during adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus [35] and during neurogenesis in the dev ...
Phylum Platyhelminthes
... Nutritive cells in the gastrodermis then phagotize partially digested material that is distributed throughout the body. Because these worm lack a circulatory system, larger species have extensive anastomosing guts to aid in distribution. Since these worms have incomplete guts, all waste must p ...
... Nutritive cells in the gastrodermis then phagotize partially digested material that is distributed throughout the body. Because these worm lack a circulatory system, larger species have extensive anastomosing guts to aid in distribution. Since these worms have incomplete guts, all waste must p ...
Foreword
... Plant cell analysis by electron, scanning and confocal microscopy Plant Physiology (Plant growth regulators and polyphenolics) Pulp and Paper Science and Technology and Particle Science and Technology: ...
... Plant cell analysis by electron, scanning and confocal microscopy Plant Physiology (Plant growth regulators and polyphenolics) Pulp and Paper Science and Technology and Particle Science and Technology: ...
Chapter 44 Presentation-Osmoregulation and Excretion
... that produce urine and they all involve several steps: 1. Body fluid is collected 2. Filtration through a selectively permeable membrane. 3. Formation of filtrate. 4. Selective reabsorption of resources: sugars, amino acids. 5. Nonessential solutes are left in the fluid. travismulthaupt.com ...
... that produce urine and they all involve several steps: 1. Body fluid is collected 2. Filtration through a selectively permeable membrane. 3. Formation of filtrate. 4. Selective reabsorption of resources: sugars, amino acids. 5. Nonessential solutes are left in the fluid. travismulthaupt.com ...
Unit Three Respiratory System
... Human Respiratory System • Air first enters the respiratory system through the nostrils and mouth. • From the nostrils, air moves through hollow cavities, called nasal passages, to the throat. • The nasal passage is lined with mucous membranes and hair-like structures called cilia. • Air is filtere ...
... Human Respiratory System • Air first enters the respiratory system through the nostrils and mouth. • From the nostrils, air moves through hollow cavities, called nasal passages, to the throat. • The nasal passage is lined with mucous membranes and hair-like structures called cilia. • Air is filtere ...
A system for functional analysis of Ebola virus glycoprotein
... densely arrayed spikes on the envelopes of both VSVDG*ResGP and VSVDG*-G virions, but VSVDG* virions were spikeless (Fig. 2A). Immunogold staining showed that a monoclonal antibody to ResGP bound to partially disrupted VSVDG*-ResGP virions (Fig. 2B Middle, at the upper right) but not to intact parti ...
... densely arrayed spikes on the envelopes of both VSVDG*ResGP and VSVDG*-G virions, but VSVDG* virions were spikeless (Fig. 2A). Immunogold staining showed that a monoclonal antibody to ResGP bound to partially disrupted VSVDG*-ResGP virions (Fig. 2B Middle, at the upper right) but not to intact parti ...
Parathyroid hormone raises the Pi concentration in a cultured
... 7 days with a lactalbumin-based diet containing purified trypsin inhibitors ( 2 8 g/kg diet) resulted in a considerable increase in pancreatic dry weight ( + 82 f 14 mg) and polyamine content ( + 1345 f 350 nmol/pancreas) compared with that obtained for controls. The lectin ( 7 g/kg diet) had a simi ...
... 7 days with a lactalbumin-based diet containing purified trypsin inhibitors ( 2 8 g/kg diet) resulted in a considerable increase in pancreatic dry weight ( + 82 f 14 mg) and polyamine content ( + 1345 f 350 nmol/pancreas) compared with that obtained for controls. The lectin ( 7 g/kg diet) had a simi ...
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function
... Many molecules and ions that are normally impeded by the lipid bilayer of the membrane diffuse passively with the help of transport proteins that span the membrane. The passive movement of molecules down its concentration gradient via a transport protein is called facilitated diffusion. Transport pr ...
... Many molecules and ions that are normally impeded by the lipid bilayer of the membrane diffuse passively with the help of transport proteins that span the membrane. The passive movement of molecules down its concentration gradient via a transport protein is called facilitated diffusion. Transport pr ...
1 The Diversity of Cells
... (mah THEE uhs SHLIE duhn) studied plants. In 1838, he concluded that all plant parts were made of cells. Theodor Schwann (TAY oh dohr SHVAHN) studied animals. In 1839, Schwann concluded that all animal tissues were made of cells. Soon after that, Schwann wrote the first two parts of what is now know ...
... (mah THEE uhs SHLIE duhn) studied plants. In 1838, he concluded that all plant parts were made of cells. Theodor Schwann (TAY oh dohr SHVAHN) studied animals. In 1839, Schwann concluded that all animal tissues were made of cells. Soon after that, Schwann wrote the first two parts of what is now know ...
Chemotherapy introduction 1
... Mex A, Mex B & Opr F Pumps the antibiotic across the outer membrane Reduced intracellular concentration of active drug ...
... Mex A, Mex B & Opr F Pumps the antibiotic across the outer membrane Reduced intracellular concentration of active drug ...
Q1. The diagram shows an alveolus and a blood vessel in the lung
... If the air is dry, his body will not overheat. In humid conditions the same athlete can run the marathon in the same time. However, in humid conditions, if the outside temperature goes over 18 °C then his body will overheat. Suggest an explanation for the athlete overheating in humid conditions. ...
... If the air is dry, his body will not overheat. In humid conditions the same athlete can run the marathon in the same time. However, in humid conditions, if the outside temperature goes over 18 °C then his body will overheat. Suggest an explanation for the athlete overheating in humid conditions. ...
Collagen Type IV (H-234): sc
... The extensive collagen family is composed of several chain types, including fibril-forming interstitial collagens (types I, II, III and V) and basement membrane collagens (type IV), each type containing multiple isoforms. Collagens are fibrous, extracellular matrix proteins with high tensile strengt ...
... The extensive collagen family is composed of several chain types, including fibril-forming interstitial collagens (types I, II, III and V) and basement membrane collagens (type IV), each type containing multiple isoforms. Collagens are fibrous, extracellular matrix proteins with high tensile strengt ...
Chemotherapy Introduction
... Mex A, Mex B & Opr F Pumps the antibiotic across the outer membrane Reduced intracellular concentration of active drug ...
... Mex A, Mex B & Opr F Pumps the antibiotic across the outer membrane Reduced intracellular concentration of active drug ...
Microfilaments Intermediate filaments
... Intermediate filaments range in diameter from 8–12 nanometers, larger than microfilaments but smaller than microtubules They support cell shape and fix organelles in place Intermediate filaments are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes ...
... Intermediate filaments range in diameter from 8–12 nanometers, larger than microfilaments but smaller than microtubules They support cell shape and fix organelles in place Intermediate filaments are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes ...
THE DEVELOPMENT of the LIVING MATRIX CONCEPT AND IT`S
... During my career as a cell biologist and biophysicist, I continued to wonder about electrons and proteins and electronic biology. Eventually I had an opportunity to learn more about the subject, when I became a Staff Scientist at the MBL and occupied the laboratory across the hall from Szent-Györgyi ...
... During my career as a cell biologist and biophysicist, I continued to wonder about electrons and proteins and electronic biology. Eventually I had an opportunity to learn more about the subject, when I became a Staff Scientist at the MBL and occupied the laboratory across the hall from Szent-Györgyi ...
Investigations in Science 7 - Organelle poster tiered task
... organelles of a cell. For instance, think of something that you are familiar with, like a refrigerator. Your refrigerator has many parts, some that you see and some that you can not. Now, think of a cell. You have seen some organelles of a cell, and some have remained unseen. You also know that cert ...
... organelles of a cell. For instance, think of something that you are familiar with, like a refrigerator. Your refrigerator has many parts, some that you see and some that you can not. Now, think of a cell. You have seen some organelles of a cell, and some have remained unseen. You also know that cert ...
gas_exchange - biologypost
... • the thinness of the diffusion barrier (alveolar and capillary walls provide a total thickness of only 0.005 mm) ...
... • the thinness of the diffusion barrier (alveolar and capillary walls provide a total thickness of only 0.005 mm) ...