Unit 5 SCA Review Sheet
... 3. I hold in cytoplasm and protect all of the organelles. I am made up of a semi-permeable membrane, which allows some things to pass in and out of the cell. __________________________________________________ ...
... 3. I hold in cytoplasm and protect all of the organelles. I am made up of a semi-permeable membrane, which allows some things to pass in and out of the cell. __________________________________________________ ...
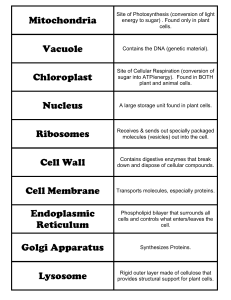
Mitochondria Site of Photosynthesis (conversion of light energy to
... Site of Photosynthesis (conversion of light energy to sugar) . Found only in plant cells. ...
... Site of Photosynthesis (conversion of light energy to sugar) . Found only in plant cells. ...
TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.5
... Organs: groups of tissues that work together to perform similar or related functions Tissues: groups of cells that work together to perform a similar function Cells: smallest, most basic structural unit of life; typically become specialized homeostasis: maintained by the interaction of different org ...
... Organs: groups of tissues that work together to perform similar or related functions Tissues: groups of cells that work together to perform a similar function Cells: smallest, most basic structural unit of life; typically become specialized homeostasis: maintained by the interaction of different org ...
Cell and Human Body Systems Unit Test- Cardoza
... 1. When a person exercises, the rate of cellular respiration increases to supply the body with more energy in the form of ATP. Mitochondria require oxygen to carry out cellular respiration to make ATP from glucose. Describe how the circulatory and respiratory systems interact to transport a molecule ...
... 1. When a person exercises, the rate of cellular respiration increases to supply the body with more energy in the form of ATP. Mitochondria require oxygen to carry out cellular respiration to make ATP from glucose. Describe how the circulatory and respiratory systems interact to transport a molecule ...
Homework: Respiration - Fall River Public Schools
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
cells-study-guide
... Be able to explain how surface area/volume ratio limits the size of cells. (textbook) Understand that in order for organisms (and individual cells) to survive, nutrients need to come in and wastes need to go out. ...
... Be able to explain how surface area/volume ratio limits the size of cells. (textbook) Understand that in order for organisms (and individual cells) to survive, nutrients need to come in and wastes need to go out. ...
answers - Biology Resources
... 6 If a cell develops in such a way that it does one particular job very efficiently, it is said to be specialised. Such a cell is also said to be adapted to its function. A nerve cell is specialised for conducting impulses. It can do this efficiently because of its shape and the chemical reactions i ...
... 6 If a cell develops in such a way that it does one particular job very efficiently, it is said to be specialised. Such a cell is also said to be adapted to its function. A nerve cell is specialised for conducting impulses. It can do this efficiently because of its shape and the chemical reactions i ...
Vocabulary for Chapter 4 Skeletal and Muscular Systems
... Vocabulary for Chapter 4 Skeletal and Muscular Systems - Part 1 Levels of Organization: ...
... Vocabulary for Chapter 4 Skeletal and Muscular Systems - Part 1 Levels of Organization: ...
Document
... The Cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. Cell contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
... The Cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. Cell contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
Study Guide for Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems
... o Connective tissue – bones, cartilage, blood o Nervous tissue – helps you think, talk, walk, and see. It is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Multi-celled organisms are made up of trillions of cells. Each cell carries out its own specific job. They work together to make tissues, organs, ...
... o Connective tissue – bones, cartilage, blood o Nervous tissue – helps you think, talk, walk, and see. It is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Multi-celled organisms are made up of trillions of cells. Each cell carries out its own specific job. They work together to make tissues, organs, ...
Cyclically stretched 3D bioprinted bioartificial alveolar sacs
... organs-on-chip is a new technology that is expected to revolutionize the way drug discovery process is carried out. The human lung parenchyma with its complex and dynamic (respiration) architecture is unique and particularly challenging to mimic. Available in-vitro models of the lung only poorly mim ...
... organs-on-chip is a new technology that is expected to revolutionize the way drug discovery process is carried out. The human lung parenchyma with its complex and dynamic (respiration) architecture is unique and particularly challenging to mimic. Available in-vitro models of the lung only poorly mim ...
Study Guide – Body Systems - Fifth Grade: Ocean Knoll Read!
... 7. A group of related organs that work together to perform a specific function is an organ system. 8. A cell is the basic unit that makes up living things. 9. A group of similar specialized cells is a tissue. 10. An organ is a group of related tissue that performs a specific function. ...
... 7. A group of related organs that work together to perform a specific function is an organ system. 8. A cell is the basic unit that makes up living things. 9. A group of similar specialized cells is a tissue. 10. An organ is a group of related tissue that performs a specific function. ...
Chapter 7 test review 2015
... 6. Know the structure and function of the organelles we discussed in class (we talked about 15) ...
... 6. Know the structure and function of the organelles we discussed in class (we talked about 15) ...
cell theory
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
1 Cells and simple cell transport AO1
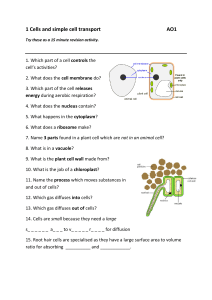
... 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell which are not in an animal cell? 8. What is in a vacuole? 9. What is the plant cell wall made from? 10. What is the job of a chloroplast? 11. Name the process which moves substances in and out of cells? 12. Which gas diffuses into c ...
... 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell which are not in an animal cell? 8. What is in a vacuole? 9. What is the plant cell wall made from? 10. What is the job of a chloroplast? 11. Name the process which moves substances in and out of cells? 12. Which gas diffuses into c ...
Cells Test What do I need to know???? Know the parts of a plant
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
BIO508: Cell Biology, Trimester III, 2016 Assignment Topics for
... Assignment Topics for Students 1. The 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Prof. Yoshinori Ohsumi for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy. 2. Different types of cancer in Fiji: Factors concerning for emerging cancer in Fiji. 3. Principles of Electron Microscopy: Contribution in Cell ...
... Assignment Topics for Students 1. The 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Prof. Yoshinori Ohsumi for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy. 2. Different types of cancer in Fiji: Factors concerning for emerging cancer in Fiji. 3. Principles of Electron Microscopy: Contribution in Cell ...
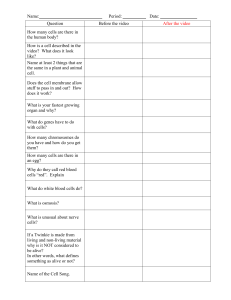
Question Before the video After the video How many cells are there
... stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? Wha ...
... stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? Wha ...
Cell Specialization
... • Tissue: A group of similar cells that perform a particular function • Organ: similar tissues of body which carry out 1+ similar functions • Organ system: work together to perform a specific function. ...
... • Tissue: A group of similar cells that perform a particular function • Organ: similar tissues of body which carry out 1+ similar functions • Organ system: work together to perform a specific function. ...
cells_can_you
... Describe the structure of each of these organelles and relate this to their function in the cell. Recognise the organelles in electron micrographs. List the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the ultrastructure of a typical bacterial cell, showing its cell wall, cell ...
... Describe the structure of each of these organelles and relate this to their function in the cell. Recognise the organelles in electron micrographs. List the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the ultrastructure of a typical bacterial cell, showing its cell wall, cell ...
science chapter 1 questions
... 1A. the cell wall helps to protect and support the cell. The cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes them ...
... 1A. the cell wall helps to protect and support the cell. The cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes them ...
Cellular Organization and Human Body Mapping
... Describe characteristics common to living things, including growth and development, reproduction, cellular organization, use of energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. 2. Identify functions of organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, ...
... Describe characteristics common to living things, including growth and development, reproduction, cellular organization, use of energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. 2. Identify functions of organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, ...