Take it Home Tuesday #8 Name
... 2) Describe one way that two or more body systems work together. ...
... 2) Describe one way that two or more body systems work together. ...
Cellular Organization and the Cell Cycle
... The rate at which food and oxygen are used up and waste products are produced depends on the cell’s volume (the amount of space it has inside). Therefore, for a cell to be most efficient, it wants as much surface area as possible, and as little volume as possible. Thus, it wants a high surface are ...
... The rate at which food and oxygen are used up and waste products are produced depends on the cell’s volume (the amount of space it has inside). Therefore, for a cell to be most efficient, it wants as much surface area as possible, and as little volume as possible. Thus, it wants a high surface are ...
Slide ()
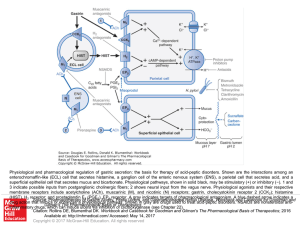
... 3 indicate possible inputs from postganglionic cholinergic fibers; 2 shows neural input from the vagus nerve. Physiological agonists and their respective membrane receptors include acetylcholine (ACh), muscarinic (M), and nicotinic (N) receptors; gastrin, cholecystokinin receptor 2 (CCK2); histamine ...
... 3 indicate possible inputs from postganglionic cholinergic fibers; 2 shows neural input from the vagus nerve. Physiological agonists and their respective membrane receptors include acetylcholine (ACh), muscarinic (M), and nicotinic (N) receptors; gastrin, cholecystokinin receptor 2 (CCK2); histamine ...
FORMATIVE Cell Test 1 Answers 2015
... Add more salt to the outside solution – and so make the [] gradient steeper ...
... Add more salt to the outside solution – and so make the [] gradient steeper ...
Organs systems – Plants Plant tissue and organs
... • ___________ (sing. stoma) are ______ in a leaf, mostly on the undersurface. • Each pore is surrounded by a pair of ________ _________. • Guard cells can change shape to _______ and _________ the stoma. • Guard cells control the movement of __________ ________, _________ and _________ _________ ...
... • ___________ (sing. stoma) are ______ in a leaf, mostly on the undersurface. • Each pore is surrounded by a pair of ________ _________. • Guard cells can change shape to _______ and _________ the stoma. • Guard cells control the movement of __________ ________, _________ and _________ _________ ...
Cells
... The flexible outer covering in ALL cells that contains tiny holes that allow important materials to enter, and wastes to leave the cell ...
... The flexible outer covering in ALL cells that contains tiny holes that allow important materials to enter, and wastes to leave the cell ...
Level Labelling the organelles of a eukaryotic cell
... A Level (or any other course for students aged 16-‐18) ...
... A Level (or any other course for students aged 16-‐18) ...
The drug colchicine inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. If you
... The cell membrane pinches off and splits into two daughter cells. ...
... The cell membrane pinches off and splits into two daughter cells. ...
Mitosis
... Sister chromatids- structures that contain identical copies of DNA Centromere: structure at the center of the chromosome where the sister chromatids are attached The centromere is important , it ensures that a complete copy of replicated DNA will be part of the daughter cells at the end of the cy ...
... Sister chromatids- structures that contain identical copies of DNA Centromere: structure at the center of the chromosome where the sister chromatids are attached The centromere is important , it ensures that a complete copy of replicated DNA will be part of the daughter cells at the end of the cy ...
Caylor 102 Biology Unit 3
... • As the cell gets larger, the surface area to volume ratio gets smaller • There are too many demands placed on the nucleus(specifically the DNA) • Too much difficulty moving things across the cell membrane • It takes too long for signaling proteins to travel the entire distance of the cell ...
... • As the cell gets larger, the surface area to volume ratio gets smaller • There are too many demands placed on the nucleus(specifically the DNA) • Too much difficulty moving things across the cell membrane • It takes too long for signaling proteins to travel the entire distance of the cell ...
Microtubules and Microfilaments
... membrane containing two phospholipid bilayers • Contains small nuclear pores – Allow substances to pass from the nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... membrane containing two phospholipid bilayers • Contains small nuclear pores – Allow substances to pass from the nucleus to cytoplasm ...
3.4-Active Transport
... AGAINST the concentration gradient (UPhill) – From low to high concentration ...
... AGAINST the concentration gradient (UPhill) – From low to high concentration ...
Questions
... Parasites adversely affect organisms by preventing their ability to maintain ___________ ...
... Parasites adversely affect organisms by preventing their ability to maintain ___________ ...
prokaryote and eukaryote
... • Has ribosomes but no other organelles. • Has cell wall – structure around cell membrane, provides structure and support. ...
... • Has ribosomes but no other organelles. • Has cell wall – structure around cell membrane, provides structure and support. ...
APB Unit 2 Outline - Westminster Public Schools Wiki
... Cells are the structural and functional units of life; cellular processes are based on physical and chemical changes. A. Chemistry of Life (Unit 1) B. Cells 1. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells What are their similarities and differences? ...
... Cells are the structural and functional units of life; cellular processes are based on physical and chemical changes. A. Chemistry of Life (Unit 1) B. Cells 1. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells What are their similarities and differences? ...
carson and gavy doc
... Another type of organism is a human organism. A human originates from a single cell, formed by an egg cell and a sperm cell; each gives the human half of the cell's genetic information. Like other complex organisms, people vary in size and shape, skin color, hair, facial features, ex cetera. But the ...
... Another type of organism is a human organism. A human originates from a single cell, formed by an egg cell and a sperm cell; each gives the human half of the cell's genetic information. Like other complex organisms, people vary in size and shape, skin color, hair, facial features, ex cetera. But the ...
The Cell
... for intercellular joining, cell-cell recognition, attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM). B. Peripheral (Glycocalyx): found on one side of membrane in gooey, carbohydrate-rich area at cell surface to provide highly specific biological markers for recognition. Membrane Junctions I. ...
... for intercellular joining, cell-cell recognition, attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM). B. Peripheral (Glycocalyx): found on one side of membrane in gooey, carbohydrate-rich area at cell surface to provide highly specific biological markers for recognition. Membrane Junctions I. ...
Biology Test
... 1. Label only 1 of the 3 diagrams using words from the word bank below. ( Artery mouth ...
... 1. Label only 1 of the 3 diagrams using words from the word bank below. ( Artery mouth ...
Rough ER Ribosome Protein
... a. The “distribution center” of the cell b. Made of many flattened sacks of membrane c. Proteins are sorted for export or use d. Vesicles bud off as transport boxes i. ...
... a. The “distribution center” of the cell b. Made of many flattened sacks of membrane c. Proteins are sorted for export or use d. Vesicles bud off as transport boxes i. ...
Can EVERY molecule pass through the cell membrane freely? Why
... Active Transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient. Molecules are moved from lower to higher concentration. It does require energy input from the cell. ...
... Active Transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient. Molecules are moved from lower to higher concentration. It does require energy input from the cell. ...
Cell Organelles
... • A cell is like a factory. It has many machines inside to make it work correctly. • The “machines” in a cell are called organelles ...
... • A cell is like a factory. It has many machines inside to make it work correctly. • The “machines” in a cell are called organelles ...
1. dia
... Cell is the central unit of biological organization: Cells are the basic units of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Only living cells can produce new cells. ...
... Cell is the central unit of biological organization: Cells are the basic units of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Only living cells can produce new cells. ...
Cell and Homeostasis
... organisms. However, the results of cell division are different depending on how many cells an organism has. Unicellular organisms use cell division to reproduce. In multicellular organisms, most cell division occurs in order to repair or renew old tissue. This renewal process is essentially continuo ...
... organisms. However, the results of cell division are different depending on how many cells an organism has. Unicellular organisms use cell division to reproduce. In multicellular organisms, most cell division occurs in order to repair or renew old tissue. This renewal process is essentially continuo ...
Summer Review Package: `14 -`15 PART I 1. Vocabulary – Please b
... (H) Eukaryotes copy DNA and are able to reproduce. (I) Prokaryotes do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. 7. What are the structures specialized for taking blood away from the heart called? (A) arteries (B) bronchioles (C) capillaries (D) veins 8. In the 1800s, scientists studied how fat-soluble subs ...
... (H) Eukaryotes copy DNA and are able to reproduce. (I) Prokaryotes do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. 7. What are the structures specialized for taking blood away from the heart called? (A) arteries (B) bronchioles (C) capillaries (D) veins 8. In the 1800s, scientists studied how fat-soluble subs ...