Synthesis, Targeting and Sorting STF - 1
... 7. (26 pts) The cells lining the digestive system of cnidarians (hydra, jellyfish, corals and their relatives) directly ingest and then internally digest unicellular prey. Curiously, some cnidaria (or coelenterata as they used to be called) have evolved mechanisms for forming a commensal relationshi ...
... 7. (26 pts) The cells lining the digestive system of cnidarians (hydra, jellyfish, corals and their relatives) directly ingest and then internally digest unicellular prey. Curiously, some cnidaria (or coelenterata as they used to be called) have evolved mechanisms for forming a commensal relationshi ...
Q1. The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from
... dots show the concentration of molecules. ...
... dots show the concentration of molecules. ...
Unit 2 - St. John Paul II Collegiate
... *Be able to identify the different types of cells Pg. 138, 139. The disadvantage of being unicellular -Unicellular organisms have to be able to move, eat, reproduce and respond to environments. Because they depend on cell membranes they can only live in watery, food rich environments. Multi-cellula ...
... *Be able to identify the different types of cells Pg. 138, 139. The disadvantage of being unicellular -Unicellular organisms have to be able to move, eat, reproduce and respond to environments. Because they depend on cell membranes they can only live in watery, food rich environments. Multi-cellula ...
Cellular Functions
... What do cells use to move substances from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration? ...
... What do cells use to move substances from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration? ...
Study Guide Answers
... 1. What is the smallest unit that can carry on all functions of life? cells 2. What is the major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Prokaryotes have no nucleus 3. Which organelle makes most of ATP during cellular ...
... 1. What is the smallest unit that can carry on all functions of life? cells 2. What is the major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Prokaryotes have no nucleus 3. Which organelle makes most of ATP during cellular ...
Study Guide
... 2. Controls what moves in and out of the nucleus 3. The sites of protein synthesis 4. Considered the roadways of the cell 5. The region inside the cell except for the nucleus 6. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 7. Site of photosynthesis in plants 8. Cont ...
... 2. Controls what moves in and out of the nucleus 3. The sites of protein synthesis 4. Considered the roadways of the cell 5. The region inside the cell except for the nucleus 6. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 7. Site of photosynthesis in plants 8. Cont ...
Body systems and cells
... I can set up the microscope correctly and peer assess another person in my class ...
... I can set up the microscope correctly and peer assess another person in my class ...
Cell Section 1
... -20 yrs later Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a microscope maker- looked at pond scum and called what he saw “animalcules – or little animals” – today they we call them protists- one celled organisms -also was the first to see bacteria -Father of Microbiology Cell Theory Based on the work of 3 scientists: Sc ...
... -20 yrs later Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a microscope maker- looked at pond scum and called what he saw “animalcules – or little animals” – today they we call them protists- one celled organisms -also was the first to see bacteria -Father of Microbiology Cell Theory Based on the work of 3 scientists: Sc ...
Body Systems Unit Review part 2
... The heart pumps blood, circulating it between the body heat and lungs. ORGANS: heart, blood vessels: artery, veins, capillaries, and bloodtechnically it’s a tissue! COMPARISON TO CELL FUNCTION: This system would be similar to the functions of a golgi body with in a cell identifying and delivering ma ...
... The heart pumps blood, circulating it between the body heat and lungs. ORGANS: heart, blood vessels: artery, veins, capillaries, and bloodtechnically it’s a tissue! COMPARISON TO CELL FUNCTION: This system would be similar to the functions of a golgi body with in a cell identifying and delivering ma ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... Chloroplast- converts energy from the sun into glucose and oxygen (these two things are used by living things to make ATP). Mitochondria- makes ATP through cellular respiration. ...
... Chloroplast- converts energy from the sun into glucose and oxygen (these two things are used by living things to make ATP). Mitochondria- makes ATP through cellular respiration. ...
Protists
... ____________ is a type of cell division which involves two cell divisions to produce four genetically distinct daughter cells. Ploidy: _______ Parent _______ each daughter cell Protists What is a clade? In what taxonomic level is it found? ...
... ____________ is a type of cell division which involves two cell divisions to produce four genetically distinct daughter cells. Ploidy: _______ Parent _______ each daughter cell Protists What is a clade? In what taxonomic level is it found? ...
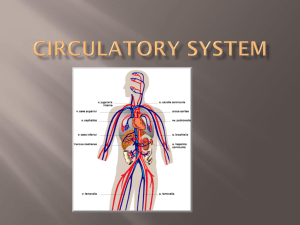
Circulatory System - Madison County Schools
... Arteries (Bright Red) Blood vessels that carry blood away Largest Artery is the Aorta Branch into small, flexible arteries then to capillaries. ...
... Arteries (Bright Red) Blood vessels that carry blood away Largest Artery is the Aorta Branch into small, flexible arteries then to capillaries. ...
Cell Theory and the Cell - The Naked Science Society
... Term “cell” was coined in 1665 by Robert Hooke when he looked at a slice of dried cork. He also observed that: 1. All living things are comprised of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest “living” unit in an organisms. 3. Cells come from previously existing cells. ...
... Term “cell” was coined in 1665 by Robert Hooke when he looked at a slice of dried cork. He also observed that: 1. All living things are comprised of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest “living” unit in an organisms. 3. Cells come from previously existing cells. ...
Organisms and Environments Test Review
... 17. Which Domain has organisms that can withstand harsh conditions? _______________ 18. How are organisms in Domain Eukarya different from those in Domain Bacteria? 19. What is the main organelle that a Eukaryotic cell has that a Prokaryotic Cell does not? ______________________ 20. Which Kingdom ha ...
... 17. Which Domain has organisms that can withstand harsh conditions? _______________ 18. How are organisms in Domain Eukarya different from those in Domain Bacteria? 19. What is the main organelle that a Eukaryotic cell has that a Prokaryotic Cell does not? ______________________ 20. Which Kingdom ha ...
Basic features of all cells
... of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration. • Facilitated diffusion: big and/or polar molecules (ions through channel proteins, sugars, amino acids by transmembrane transporters; aquaporins for facilitated diffusion of water). ...
... of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration. • Facilitated diffusion: big and/or polar molecules (ions through channel proteins, sugars, amino acids by transmembrane transporters; aquaporins for facilitated diffusion of water). ...
Cells Alive Activity
... your answers are neat and legible. You may use charts or pictures in order to answer the questions. ...
... your answers are neat and legible. You may use charts or pictures in order to answer the questions. ...
CHROMOSOMAL INSTABILITY AND CANCER CELL STEMNESS
... very frequent, while structural rearrangements affect almost every single chromosome. This challenging context provides excellent grounds to study telomere dysfunction driven CIN in a single cell basis. Many cancers are considered to be driven by cancer stem cells (CSCs) that may differentiate into ...
... very frequent, while structural rearrangements affect almost every single chromosome. This challenging context provides excellent grounds to study telomere dysfunction driven CIN in a single cell basis. Many cancers are considered to be driven by cancer stem cells (CSCs) that may differentiate into ...
EXCRETION
... The liver has many functions. One of them is to breakdown red blood cells. Within the red blood cell is a protein structure called hemoglobin. When hemoglobin breaks down it produces a pigment called urochrome. This yellow pigment is constantly filtered out of the blood as a waste product. Since red ...
... The liver has many functions. One of them is to breakdown red blood cells. Within the red blood cell is a protein structure called hemoglobin. When hemoglobin breaks down it produces a pigment called urochrome. This yellow pigment is constantly filtered out of the blood as a waste product. Since red ...
Part 2 Review - Manhasset Schools
... and a small piece is placed in a drop of water on a microscope slide. A cover slip is placed on top by touching it to the water at an angle, and then carefully placing it on the specimen, trying not to get air bubbles underneath. 2. The cells are examined under the light (compound) microscope. You s ...
... and a small piece is placed in a drop of water on a microscope slide. A cover slip is placed on top by touching it to the water at an angle, and then carefully placing it on the specimen, trying not to get air bubbles underneath. 2. The cells are examined under the light (compound) microscope. You s ...
Mitosis
... Mitosis Name two important functions for cell division? It enables multicellular organisms to develop from unicellular organisms. It allows cells to replace other cells that die off. There are other options as well. DNA molecules are made into chromosomes to make replication easier. True/False What ...
... Mitosis Name two important functions for cell division? It enables multicellular organisms to develop from unicellular organisms. It allows cells to replace other cells that die off. There are other options as well. DNA molecules are made into chromosomes to make replication easier. True/False What ...
2.1Cell Theory AT
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek documented unicellular organisms based on observations of protozoa [1673] and bacteria [1683] ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek documented unicellular organisms based on observations of protozoa [1673] and bacteria [1683] ...
The Cell Study Guide
... 1. Know the 3 parts of the cell theory and the scientists that contributed to it. Cell Organelles (section 3.2) 1. able to describe the internal structure of eukaryotic cells. 2. Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. 3. Know how organelles can work together as a system. Fo ...
... 1. Know the 3 parts of the cell theory and the scientists that contributed to it. Cell Organelles (section 3.2) 1. able to describe the internal structure of eukaryotic cells. 2. Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. 3. Know how organelles can work together as a system. Fo ...
Cheek Observation
... Cheek Cell Slide Preparation Obtain a clean slide. Place 1 drop of stain in the middle of the slide. Scrape cells from the inside of your cheek. Stir them in the stain. Add a cover slip. Sketch (½ page) a cell on high power. Label all visible structures to the best of your abilities. ...
... Cheek Cell Slide Preparation Obtain a clean slide. Place 1 drop of stain in the middle of the slide. Scrape cells from the inside of your cheek. Stir them in the stain. Add a cover slip. Sketch (½ page) a cell on high power. Label all visible structures to the best of your abilities. ...