From Neuroscience for Kids The human body is made up of trillions
... 1. Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body. 2. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. 3. Neurons contain some specialized structures (for example, ...
... 1. Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body. 2. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. 3. Neurons contain some specialized structures (for example, ...
human body systems- thesis
... Larynx – your “voicebox”, as air passes over your vocal chords, you speak Trachea – the “windpipe”, or what connects your pharynx to your lungs -- a piece of skin, called the epiglottis, covers the trachea when you swallow, preventing food from entering ...
... Larynx – your “voicebox”, as air passes over your vocal chords, you speak Trachea – the “windpipe”, or what connects your pharynx to your lungs -- a piece of skin, called the epiglottis, covers the trachea when you swallow, preventing food from entering ...
Eukaryotic Cell - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... • Heterochromatin: densely packed chromatin - indicates ...
... • Heterochromatin: densely packed chromatin - indicates ...
1) cells → tissues → organs → organ systems 2) tissues
... discover a basic similarity among organisms study the behavior of chordates develop techniques for growing plants in a laboratory 1) A ...
... discover a basic similarity among organisms study the behavior of chordates develop techniques for growing plants in a laboratory 1) A ...
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell
... Wakitani S et al. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine . 2007 ...
... Wakitani S et al. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine . 2007 ...
PDF - The Journal of Cell Biology
... ball of undifferentiated cells. But and I found it fascinating to see, first of at gastrulation, three new cell all, how little was known about the activtypes (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endo- ity of these factors and, second, how derm) emerge and begin to organize into much one could learn from doing ...
... ball of undifferentiated cells. But and I found it fascinating to see, first of at gastrulation, three new cell all, how little was known about the activtypes (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endo- ity of these factors and, second, how derm) emerge and begin to organize into much one could learn from doing ...
NAME - cloudfront.net
... Circle the letter of the answer that best completes the statement. 1. DNA that is spread out in a non-dividing cell is called _____________________. A. chromosomes B. chromatin 2. The two copies of each chromosome that are the same size, same shape, and carry genes for the same traits are called ___ ...
... Circle the letter of the answer that best completes the statement. 1. DNA that is spread out in a non-dividing cell is called _____________________. A. chromosomes B. chromatin 2. The two copies of each chromosome that are the same size, same shape, and carry genes for the same traits are called ___ ...
PDF File of Transcript for Dawn Tamarkin`s Case Story
... Now if this is not an onion cell but instead it's a cheek cell, there's no cell wall because animal cells don't have it and students can bend this the right way, and put the nucleus in, maybe even show that they've kind of bend the cell a little sticking out on the slide. And even have some bacteria ...
... Now if this is not an onion cell but instead it's a cheek cell, there's no cell wall because animal cells don't have it and students can bend this the right way, and put the nucleus in, maybe even show that they've kind of bend the cell a little sticking out on the slide. And even have some bacteria ...
Cell division (mitosis) lab
... DNA replication in eukaryotes is followed by the process called mitosis which assures that each daughter cell receives one copy of each of the replicated chromosomes. During the process of mitosis, the chromosomes pass through several stages known as prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. The ...
... DNA replication in eukaryotes is followed by the process called mitosis which assures that each daughter cell receives one copy of each of the replicated chromosomes. During the process of mitosis, the chromosomes pass through several stages known as prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. The ...
Course: 2000350 Anatomy and Physiology
... nonliving things in an area, such as plants, animals, water, soil, weather, landforms, and air. ...
... nonliving things in an area, such as plants, animals, water, soil, weather, landforms, and air. ...
AWAY - mshernandezscience
... 14. The function of the thyroid demonstrates that organ systems interact and depend on each other to function properly 15. Regulation among these three glands help to maintain homeostasis a. Thyroid b. Pituitary c. Hypothalamus 16. The role of the circulatory system in response to infection is to al ...
... 14. The function of the thyroid demonstrates that organ systems interact and depend on each other to function properly 15. Regulation among these three glands help to maintain homeostasis a. Thyroid b. Pituitary c. Hypothalamus 16. The role of the circulatory system in response to infection is to al ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Originated from the work of biologists Schleiden and Schwann in 1838-9 States that: All organisms are composed of cells German botanist Matthais Schleiden in 1838 German zoologist Theodor Schwann in 1839 All cells come only from preexisting cells – “Biogenesis” German physician Rudolph Virchow in 18 ...
... Originated from the work of biologists Schleiden and Schwann in 1838-9 States that: All organisms are composed of cells German botanist Matthais Schleiden in 1838 German zoologist Theodor Schwann in 1839 All cells come only from preexisting cells – “Biogenesis” German physician Rudolph Virchow in 18 ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... Leeuwenhoek improved lenses and drew observations • 1830’s – Robert Brown identified the nucleus ...
... Leeuwenhoek improved lenses and drew observations • 1830’s – Robert Brown identified the nucleus ...
Cell Organelles and their Functions
... There are more mitochondria in cells that have to perform lots of work, for example - your leg muscle cells. Other cells need less energy to do their work and have less mitochondria. Mitochondria is like a turtle’s stomach. ...
... There are more mitochondria in cells that have to perform lots of work, for example - your leg muscle cells. Other cells need less energy to do their work and have less mitochondria. Mitochondria is like a turtle’s stomach. ...
Cell Organelle Trading Cards
... the organelle on one side and information about it on the other. Then, you will compare the organelle to 3 other items. ...
... the organelle on one side and information about it on the other. Then, you will compare the organelle to 3 other items. ...
SALT AUGMENTS TH17 CELL RESPONSES IN ANCA
... positive cells infiltrating the kidney was analysed using FACS. The inflammatory infiltrate in renal biopsy tissue from patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome associated tubulointerstitial nephritis (pSS TIN) was isolated via laser microdissection. Fragments were digested into peptides and analyse ...
... positive cells infiltrating the kidney was analysed using FACS. The inflammatory infiltrate in renal biopsy tissue from patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome associated tubulointerstitial nephritis (pSS TIN) was isolated via laser microdissection. Fragments were digested into peptides and analyse ...
The Cell Membrane
... The cell membrane is permeable to some materials and impermeable to others. Permeable means “allowing passage,” and impermeable means “not allowing passage.” The cell membrane plays an important role in keeping harmful substances out of the cell and in removing wastes. Because it allows only certain ...
... The cell membrane is permeable to some materials and impermeable to others. Permeable means “allowing passage,” and impermeable means “not allowing passage.” The cell membrane plays an important role in keeping harmful substances out of the cell and in removing wastes. Because it allows only certain ...
CellReviewANS
... pores that allow materials to ...ribosomes are found on move in and out of the cell the rough ER ...newly made proteins move from the ribosomes to the ER where they may be ...
... pores that allow materials to ...ribosomes are found on move in and out of the cell the rough ER ...newly made proteins move from the ribosomes to the ER where they may be ...
Life is Cellular
... III. Cell Membrane A. Thin layer of lipids and proteins that separate cell contents B. Selectively Permeable ...
... III. Cell Membrane A. Thin layer of lipids and proteins that separate cell contents B. Selectively Permeable ...
Unit 3 Final Exam Scrambled
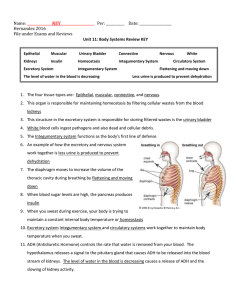
... 1. Several immovable joints are found in the human body. These joints are in the a. knee c. wrist b. skull d. knuckle 2. What is a typical blood pressure value for a young adult? a. 3/2 c. 120/80 b. 37ºC d. 80/120 3. As part of an exercise experiment, you measure pulse and blood pressure before exer ...
... 1. Several immovable joints are found in the human body. These joints are in the a. knee c. wrist b. skull d. knuckle 2. What is a typical blood pressure value for a young adult? a. 3/2 c. 120/80 b. 37ºC d. 80/120 3. As part of an exercise experiment, you measure pulse and blood pressure before exer ...
The Cell Cycle Control
... The results of fusing cells at two different phases of the cell cycle suggested that particular chemicals control the progression of phases. For example, when a cell in M phase was fused with one in any other phase, the nucleus from the latter cell immediately began mitosis. If the second cell was i ...
... The results of fusing cells at two different phases of the cell cycle suggested that particular chemicals control the progression of phases. For example, when a cell in M phase was fused with one in any other phase, the nucleus from the latter cell immediately began mitosis. If the second cell was i ...
1. Write scientific method down in order and describe each step
... WITHOUT energy • from high to low concentration (crowded to not crowded areas) • The 3 types are below ...
... WITHOUT energy • from high to low concentration (crowded to not crowded areas) • The 3 types are below ...
SBI3C, Rm - Holterman
... (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ln69k7LyTsU) Afterward, get yourself into a group of two (three max). One of you will complete the first table on their own sheet, and the other will complete the second table on their own sheet. Include the name of at least one example organism (Volvox algae, for in ...
... (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ln69k7LyTsU) Afterward, get yourself into a group of two (three max). One of you will complete the first table on their own sheet, and the other will complete the second table on their own sheet. Include the name of at least one example organism (Volvox algae, for in ...
Enzymes and CellMemb.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Enzyme K? Enzyme M? Enzyme L? 7. Which letter represents the activity of an enzyme that could be found in the stomach? 8. What happens to enzyme activity when the pH is higher or lower than the optimal pH? Why does this happen? 9. Match the structure with the correct letter from the diagram: _______ ...
... Enzyme K? Enzyme M? Enzyme L? 7. Which letter represents the activity of an enzyme that could be found in the stomach? 8. What happens to enzyme activity when the pH is higher or lower than the optimal pH? Why does this happen? 9. Match the structure with the correct letter from the diagram: _______ ...
Cell Part Functions
... Transports needed proteins and other substances (lipids) around inside the cell. If ribosomes are attached it is called rough ER. They sort proteins and other substances and package them into vesicles. The vesicles deliver the substances to areas inside the cell or to the membrane where they are rel ...
... Transports needed proteins and other substances (lipids) around inside the cell. If ribosomes are attached it is called rough ER. They sort proteins and other substances and package them into vesicles. The vesicles deliver the substances to areas inside the cell or to the membrane where they are rel ...