Cells
... have many fundamental similarities in their chemical composition and metabolic mechanisms. ...
... have many fundamental similarities in their chemical composition and metabolic mechanisms. ...
Micro Life Revision Powerpoint
... • What are antibiotics? • Why are human cells unharmed by antibiotics? An antibiotic is a poison that works to destroy bacterial cells while leaving human cells unharmed. Antibiotics destroy the cell wall of bacteria. As viruses have no cell wall, they have no effect on viruses. ...
... • What are antibiotics? • Why are human cells unharmed by antibiotics? An antibiotic is a poison that works to destroy bacterial cells while leaving human cells unharmed. Antibiotics destroy the cell wall of bacteria. As viruses have no cell wall, they have no effect on viruses. ...
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
... Read these passages from the text and answer the questions that follow. Two Types of Cells There is a basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and ...
... Read these passages from the text and answer the questions that follow. Two Types of Cells There is a basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and ...
XPO1 is selinexor`s prime target: validation by mutating cysteine 528
... It exports a broad range of different cargo proteins out of the cell’s nucleus to the cytoplasm. These cargo proteins include tumour suppressor and growth regulatory related proteins; therefore correct XPO1 function is key to normal cell homeostasis. In recent years, overexpression or dysfunction of ...
... It exports a broad range of different cargo proteins out of the cell’s nucleus to the cytoplasm. These cargo proteins include tumour suppressor and growth regulatory related proteins; therefore correct XPO1 function is key to normal cell homeostasis. In recent years, overexpression or dysfunction of ...
Circulatory Respiratory Muscular and Skeletal System Test Review
... Permeable means that substances can pass through 10. List the types of blood vessels. Arteries, capillaries, and veins 11. List the structures of the skeletal system. Bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. 12. What type of tissue is your heart made of that allows it to pump? Muscle tissue 13. Wha ...
... Permeable means that substances can pass through 10. List the types of blood vessels. Arteries, capillaries, and veins 11. List the structures of the skeletal system. Bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. 12. What type of tissue is your heart made of that allows it to pump? Muscle tissue 13. Wha ...
Biology Cells Notes
... personification of a cellular organelle. Explain the function of the organelle and be creative in the process. Ex: Mom! Something is wrong with me. This morning I woke up covered in bumps. Yesterday my skin was smooth and pretty, but today something has attached to me and caused me to be covered in ...
... personification of a cellular organelle. Explain the function of the organelle and be creative in the process. Ex: Mom! Something is wrong with me. This morning I woke up covered in bumps. Yesterday my skin was smooth and pretty, but today something has attached to me and caused me to be covered in ...
Introduction to Animal Organization and Physiology
... – An assembly of tissues integrated into a structure that carries out a specific function ...
... – An assembly of tissues integrated into a structure that carries out a specific function ...
'Helping the helpers' - a key for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease? (PDF File 72.3 KB)
... these cells can be better understood, it will assist in treatment of Alzheimer’s to delay onset of the disease or slow down its progression. The team will carry out two experiments. In the first, they will activate an inflammatory response in astroglial cell lines and monitor the release of glutathi ...
... these cells can be better understood, it will assist in treatment of Alzheimer’s to delay onset of the disease or slow down its progression. The team will carry out two experiments. In the first, they will activate an inflammatory response in astroglial cell lines and monitor the release of glutathi ...
HonoNameKEY Date Period Introduction to Living Things Notes
... Why can’t organisms just live forever? Over time there is damage to the DNA and cells (things wear out despite constant maintenance and repair). Organisms cannot always maintain homeostasis in all environmental conditions. If an organism cannot continue its metabolism and maintain homeostasis – its ...
... Why can’t organisms just live forever? Over time there is damage to the DNA and cells (things wear out despite constant maintenance and repair). Organisms cannot always maintain homeostasis in all environmental conditions. If an organism cannot continue its metabolism and maintain homeostasis – its ...
PE anti-mouse Ly6K Antibody
... *These products may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses (see the BioLegend Catalog or our website, www.biolegend.com/ordering#license). BioLegend products may not be transferred to third parties, resold, modified for resale, or used to manufacture commercial products, reverse engine ...
... *These products may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses (see the BioLegend Catalog or our website, www.biolegend.com/ordering#license). BioLegend products may not be transferred to third parties, resold, modified for resale, or used to manufacture commercial products, reverse engine ...
Cells Alive- Interactive Internet Lesson
... bacterial cell. Are any of the same parts found in eukaryotic cells? If so, name them_______________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________. Prokaryotes are bacteria ...
... bacterial cell. Are any of the same parts found in eukaryotic cells? If so, name them_______________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________. Prokaryotes are bacteria ...
LAB: CELL STUDIES This is a class set! Do ALL of this in your LAB
... LAB: CELL STUDIES This is a class set! Do ALL of this in your LAB book. The Cell Theory states that all living organisms are made of cells. It was only after microscopes were developed and we were able to view the universality of cells that this theory was accepted. Although cells are the building b ...
... LAB: CELL STUDIES This is a class set! Do ALL of this in your LAB book. The Cell Theory states that all living organisms are made of cells. It was only after microscopes were developed and we were able to view the universality of cells that this theory was accepted. Although cells are the building b ...
Cell Lab Report
... 3. What are three structures found in plant and animal cells? 4. In prokaryotes, plants, and fungi, what structure surrounds the cell membrane and provides cell support? Important Drawing Directions 1. For each specimen that you draw do not fill in the entire circle with cells. Just draw 4 cells for ...
... 3. What are three structures found in plant and animal cells? 4. In prokaryotes, plants, and fungi, what structure surrounds the cell membrane and provides cell support? Important Drawing Directions 1. For each specimen that you draw do not fill in the entire circle with cells. Just draw 4 cells for ...
YOUR AMAZING BODY
... The human digestive system is a series of organs and glands that processes food. In order to use the food you eat, your body has to break the food down into smaller molecules that it can process; it also has to get rid of waste. ...
... The human digestive system is a series of organs and glands that processes food. In order to use the food you eat, your body has to break the food down into smaller molecules that it can process; it also has to get rid of waste. ...
Biology Notes - Unit 3
... (b) Functions: controls the normal activities of the cell (c) Stores genes which help the ribosomes to make the right kinds of proteins (d) The genes are made of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and are located on the chromosomes (e) Chromosome are visible only in a dividing cell (f) They appear as chrom ...
... (b) Functions: controls the normal activities of the cell (c) Stores genes which help the ribosomes to make the right kinds of proteins (d) The genes are made of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and are located on the chromosomes (e) Chromosome are visible only in a dividing cell (f) They appear as chrom ...
Vascular Tissue - HCC Learning Web
... • Lateral meristems: allow the plant to increase in girth –Secondary growth: thickening of roots and shoots. • Produced by lateral meristems • Develop in slightly older regions of roots and shoots • Examples: vascular and cork cambium. ...
... • Lateral meristems: allow the plant to increase in girth –Secondary growth: thickening of roots and shoots. • Produced by lateral meristems • Develop in slightly older regions of roots and shoots • Examples: vascular and cork cambium. ...
Types of Cells
... • Cover, protect and line the body. Also allow for absorption in intestines/lungs ...
... • Cover, protect and line the body. Also allow for absorption in intestines/lungs ...
Two types of cells
... • They can be single celled (just one cell) or can make up more complex multi-cellular organisms. • All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic cells. ...
... • They can be single celled (just one cell) or can make up more complex multi-cellular organisms. • All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic cells. ...
Immunology - Bosna Sema
... Once time when bacteria find themselves inside phagocyte cells…there are some organelles that we call lysosomes. This little package will merge with bacteria and will dups. his contents into this pathogen and destroy it up. This is nonspecific immunity. It is called non-specific because they don’t r ...
... Once time when bacteria find themselves inside phagocyte cells…there are some organelles that we call lysosomes. This little package will merge with bacteria and will dups. his contents into this pathogen and destroy it up. This is nonspecific immunity. It is called non-specific because they don’t r ...
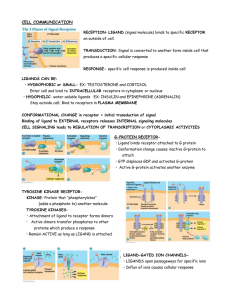
What to know Chap 11
... RECEPTION- LIGAND (signal molecule) binds to specific RECEPTOR on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERON ...
... RECEPTION- LIGAND (signal molecule) binds to specific RECEPTOR on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERON ...
Cells
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
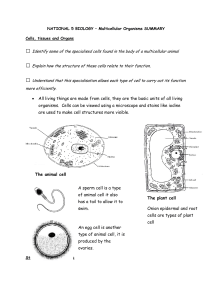
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the haemoglobin dissociates from the oxygen allowing it to be released. ...
... area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the haemoglobin dissociates from the oxygen allowing it to be released. ...