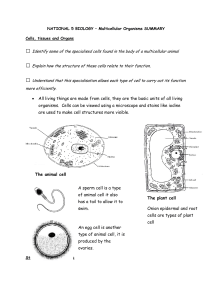
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the haemoglobin dissociates from the oxygen allowing it to be released. ...
... area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the haemoglobin dissociates from the oxygen allowing it to be released. ...
Cells
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
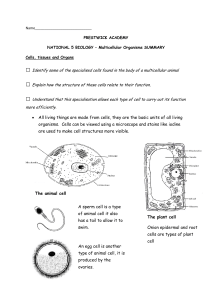
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the haemoglobin dissociates from the oxygen allowing it to be released. ...
... area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the haemoglobin dissociates from the oxygen allowing it to be released. ...
What is a Cell
... they can ________________ with the cell membrane and squirt the wastes outside. The cell sap vacuole in plants is much _________________ than animals. In addition to storing important substances, it also helps __________________ the plant. The ____________________of water filling the cell sap vacuol ...
... they can ________________ with the cell membrane and squirt the wastes outside. The cell sap vacuole in plants is much _________________ than animals. In addition to storing important substances, it also helps __________________ the plant. The ____________________of water filling the cell sap vacuol ...
Content Lesson Plan (45 minutes total)
... Aim: What differences can we observe between animal and plant cells? Q 1) What are the differences between animal and plant cells? Use diagram on projector or a picture on the board to identify differences. List these in a chart . Q 2) Why are some structures only in plant cells? What may they be us ...
... Aim: What differences can we observe between animal and plant cells? Q 1) What are the differences between animal and plant cells? Use diagram on projector or a picture on the board to identify differences. List these in a chart . Q 2) Why are some structures only in plant cells? What may they be us ...
The Cell - Structure - Jefferson County School Board
... SC.912.L.14.3 Compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.912.L.14.4 Compare and contrast structure and function of various types of microscopes. Cognitive Co ...
... SC.912.L.14.3 Compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.912.L.14.4 Compare and contrast structure and function of various types of microscopes. Cognitive Co ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Prokaryotic agar
... living things are made of one or more cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. All cells come from other cells. ...
... living things are made of one or more cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. All cells come from other cells. ...
1.2 Notes
... goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
... goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
Anatomy of a Cell
... Just as the body has organs that carry out different functions, each cell in the body has special structures that carry out particular functions. These structures are called organelles. Each organelle is surrounded by a membrane. The membrane keeps it separate from other cell components. An organell ...
... Just as the body has organs that carry out different functions, each cell in the body has special structures that carry out particular functions. These structures are called organelles. Each organelle is surrounded by a membrane. The membrane keeps it separate from other cell components. An organell ...
Name Period ______ Table of Contents Body System Page
... - Melanocytes are cells that produce the dark pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of skin ...
... - Melanocytes are cells that produce the dark pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of skin ...
1 Supplementary materials and methods Reagents and Western
... Suppl. Fig. 1. Mesangial cells and monocytes secrete YB-1 upon LPS stimulation Rat MC release YB-1 upon stimulation with PDGF-BB and LPS within 1 h (left panel). Quantification demonstrates that the secreted amount increases three-fold over constitutive release (right panel) (A.). Similarly MM6 cell ...
... Suppl. Fig. 1. Mesangial cells and monocytes secrete YB-1 upon LPS stimulation Rat MC release YB-1 upon stimulation with PDGF-BB and LPS within 1 h (left panel). Quantification demonstrates that the secreted amount increases three-fold over constitutive release (right panel) (A.). Similarly MM6 cell ...
BrainPOP for Metabolism and Mitosis
... 2. How do animals and humans obtain energy? 3. Once food is eaten, it goes through a process called ____________________. 4. What are the two categories of metabolism? ______________________ and _______________________ 5. ______________ reactions break down complex molecules in food into simple mole ...
... 2. How do animals and humans obtain energy? 3. Once food is eaten, it goes through a process called ____________________. 4. What are the two categories of metabolism? ______________________ and _______________________ 5. ______________ reactions break down complex molecules in food into simple mole ...
Chapter 03
... in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
... in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
Text Size: Question Spacing: Answer Layout: 7th Grade Science
... B) all cells have only one nucleus. D) only animals have cells. 2) What is the smallest unit that can carry on all functions of life? A) cells C) molecules B) elements D) organelles 3) New cells are created from A) matter. C) other cells. B) energy. D) non-living matter. ...
... B) all cells have only one nucleus. D) only animals have cells. 2) What is the smallest unit that can carry on all functions of life? A) cells C) molecules B) elements D) organelles 3) New cells are created from A) matter. C) other cells. B) energy. D) non-living matter. ...
Document
... Closure of Ca2+ channels in synaptic terminal Hair cell stereocilia bend as the movement of the basilar membrane displaces them in relation to the overlying tectorial membrane in which they are embedded. ...
... Closure of Ca2+ channels in synaptic terminal Hair cell stereocilia bend as the movement of the basilar membrane displaces them in relation to the overlying tectorial membrane in which they are embedded. ...
HW1HeLaCellsHW2014
... being treated, a doctor at John Hopkins Hospital collected a tissue sample, a collection of cells, from one of the tumors in Ms. Lacks’ body. Her cells were taken without her knowledge or consent. At the time, collecting tissue for research without permission was not uncommon. Ms. Lacks’ cells were ...
... being treated, a doctor at John Hopkins Hospital collected a tissue sample, a collection of cells, from one of the tumors in Ms. Lacks’ body. Her cells were taken without her knowledge or consent. At the time, collecting tissue for research without permission was not uncommon. Ms. Lacks’ cells were ...
Cell Lab Report
... 3. What are three structures found in plant and animal cells? 4. In prokaryotes, plants, and fungi, what structure surrounds the cell membrane and provides cell support? Important Drawing Directions 1. For each specimen that you draw do not fill in the entire circle with cells. Just draw 4 cells for ...
... 3. What are three structures found in plant and animal cells? 4. In prokaryotes, plants, and fungi, what structure surrounds the cell membrane and provides cell support? Important Drawing Directions 1. For each specimen that you draw do not fill in the entire circle with cells. Just draw 4 cells for ...
cell membranes
... –cellulose (plant cell wall compound)—most common CHO on planet –chitin (shells of bugs and some cells in fungi) ...
... –cellulose (plant cell wall compound)—most common CHO on planet –chitin (shells of bugs and some cells in fungi) ...
Mitosis Notes
... – In sexual reproduction, offspring are produced by the fusion of two sex cells – one from each of two parents. – The offspring produced inherit some genetic information from both parents, therefore they are genetically different. ...
... – In sexual reproduction, offspring are produced by the fusion of two sex cells – one from each of two parents. – The offspring produced inherit some genetic information from both parents, therefore they are genetically different. ...
me239 mechanics of the cell 1.2 introduction to the cell 1.2
... more than 50% of water. the cell membrane is semi-permeable allowing for a controlled exchange between intracellular and extracellular components and information. mechanisms of transport through the membrane • passive transport driven by gradients in concentration • active transport that does requir ...
... more than 50% of water. the cell membrane is semi-permeable allowing for a controlled exchange between intracellular and extracellular components and information. mechanisms of transport through the membrane • passive transport driven by gradients in concentration • active transport that does requir ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protests Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Packages proteins for t ...
... Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protests Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Packages proteins for t ...