Science Cumulative Review 1 Unicellular and Multicellular
... What is one example of a unicellular organism? a. Flower b. Bird c. Bacteria d. Cow What type of organism would be able to survive as a single cell? a. Algae b. Rabbit c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in ...
... What is one example of a unicellular organism? a. Flower b. Bird c. Bacteria d. Cow What type of organism would be able to survive as a single cell? a. Algae b. Rabbit c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in ...
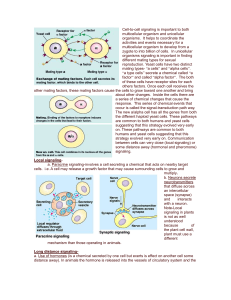
Long distance signaling
... Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organism and unicellular organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding differen ...
... Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organism and unicellular organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding differen ...
Biology SOL REVIEW
... pH because changes in pH cause changes in _______ conformation, resulting in a change in activity. ...
... pH because changes in pH cause changes in _______ conformation, resulting in a change in activity. ...
Inside Cells
... have an organization to them from organelle to cell to tissue to organ to organ system to whole organism and that all parts must work together for the whole organism to survive. • I will be able to identify key features that plant cells have and animal cells do not (e.g., cell wall and chloroplasts) ...
... have an organization to them from organelle to cell to tissue to organ to organ system to whole organism and that all parts must work together for the whole organism to survive. • I will be able to identify key features that plant cells have and animal cells do not (e.g., cell wall and chloroplasts) ...
Making New Cells: Mitosis - Social Circle City Schools
... Body Cells • Mitosis: process used to make new body cells • Body cells are cells found in the human body • Ex: Heart, lungs, skin, muscle, etc. • Human body has 46 chromosomes in each body cell ...
... Body Cells • Mitosis: process used to make new body cells • Body cells are cells found in the human body • Ex: Heart, lungs, skin, muscle, etc. • Human body has 46 chromosomes in each body cell ...
Cell Structure
... 2.) Chemosynthetic -simple nonliving chemical nutrients such as H2S, sulfur, and iron are consumed and made into living tissue; makes its own food • Heterotrophs: (unable to make own food) 1.) Ingestion: organism eats other organisms or their organic byproducts 2.) Absorption: produces enzymes that ...
... 2.) Chemosynthetic -simple nonliving chemical nutrients such as H2S, sulfur, and iron are consumed and made into living tissue; makes its own food • Heterotrophs: (unable to make own food) 1.) Ingestion: organism eats other organisms or their organic byproducts 2.) Absorption: produces enzymes that ...
Transport Systems and Solutions
... due to the movement of water into the cell Plants rely on hypotonic environments to get water into them and into their vacuoles. If plants are in a hypertonic environment they will wilt (known as plasmolysis). ...
... due to the movement of water into the cell Plants rely on hypotonic environments to get water into them and into their vacuoles. If plants are in a hypertonic environment they will wilt (known as plasmolysis). ...
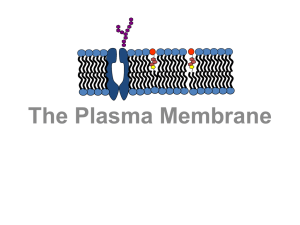
Plasma Membrane Notes (7.2)
... Selective Permeability Property of the membrane that allows certain materials to ____________ ____________ the cell while keeping others ____________ It also allows ____________ cells to perform different activities within the ____________ organism. Example: Human nerve cells respond to a cert ...
... Selective Permeability Property of the membrane that allows certain materials to ____________ ____________ the cell while keeping others ____________ It also allows ____________ cells to perform different activities within the ____________ organism. Example: Human nerve cells respond to a cert ...
Cell organelles
... Secretion vacuoles pinch off and fuse with cell membrane Cytoskeleton: Discovered in 1931 by Paul Wintrebert. 1. Intercellular proteins distributed inside cells help to give cell shape and movement. 2. Microtubules discovered in 1953 by De Robertis and Franchi. 3. Microfilaments/Actin discovered in ...
... Secretion vacuoles pinch off and fuse with cell membrane Cytoskeleton: Discovered in 1931 by Paul Wintrebert. 1. Intercellular proteins distributed inside cells help to give cell shape and movement. 2. Microtubules discovered in 1953 by De Robertis and Franchi. 3. Microfilaments/Actin discovered in ...
Topic One - OoCities
... The pump returns to its original shape waiting for another particle to bind. 1.4.7 Explain how vesicles are used to transport materials within a cell between the rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and plasma membrane. Proteins are transported inside the cell in vesicles. Proteins pro ...
... The pump returns to its original shape waiting for another particle to bind. 1.4.7 Explain how vesicles are used to transport materials within a cell between the rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and plasma membrane. Proteins are transported inside the cell in vesicles. Proteins pro ...
The Hierarchy of Structural Organization
... • Adaptations—features of an organism’s anatomy, physiology, or behavior that have evolved in response to these selection pressures and enable the organism to cope with the challenges of its environment – Model—animal species selected for research on a particular problem ...
... • Adaptations—features of an organism’s anatomy, physiology, or behavior that have evolved in response to these selection pressures and enable the organism to cope with the challenges of its environment – Model—animal species selected for research on a particular problem ...
Human Body Systems
... • Blood is made of 4 components (parts): 1. Plasma – liquid part of blood 2. Red blood cells – take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells 3. White blood cells – the body’s disease fighters (part of immune system) 4. Platelets – cell fragments used in forming blood clots (that make scabs) ...
... • Blood is made of 4 components (parts): 1. Plasma – liquid part of blood 2. Red blood cells – take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells 3. White blood cells – the body’s disease fighters (part of immune system) 4. Platelets – cell fragments used in forming blood clots (that make scabs) ...
A Tour of the Cell
... 1. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living things. 2. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. ...
... 1. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living things. 2. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. ...
Cells and Their Environment Diffusion: The movement of a
... free water molecules in the cytoplasm and in the fluid outside the cell. There are three possibilities for the direction of water movement: 1. Water move out. When water diffuses out of the cell, the cell shrinks. A solution that causes a cell to shrink because of osmosis is called a hypertonic solu ...
... free water molecules in the cytoplasm and in the fluid outside the cell. There are three possibilities for the direction of water movement: 1. Water move out. When water diffuses out of the cell, the cell shrinks. A solution that causes a cell to shrink because of osmosis is called a hypertonic solu ...
Read page108-153
... the body by eliminating waste matter. A. Kidneys excrete urine. B. Liver discharges bile. C. Skin eliminates perspiration. D. Large Intestine evacuates decomposed and undigested food. E. Lungs exhale carbon dioxide. ...
... the body by eliminating waste matter. A. Kidneys excrete urine. B. Liver discharges bile. C. Skin eliminates perspiration. D. Large Intestine evacuates decomposed and undigested food. E. Lungs exhale carbon dioxide. ...
Intro to animal structure and function powerpoint
... make up organ systems Most animals are composed of specialized cells organized into tissues that have different functions ...
... make up organ systems Most animals are composed of specialized cells organized into tissues that have different functions ...
Muscle Cells
... Multicellular plants also have cells with different jobs to do. These cells group together into tissues. One type of tissue delivers water, minerals, and nutrients to different parts of the plant. Some of its cells carry materials from the roots to the leaves. Others carry food made in the leaves to ...
... Multicellular plants also have cells with different jobs to do. These cells group together into tissues. One type of tissue delivers water, minerals, and nutrients to different parts of the plant. Some of its cells carry materials from the roots to the leaves. Others carry food made in the leaves to ...
Transport across the cell membrane
... Hypotonic: The solution has a HIGHER concentration of water than the concentration of water inside the cell therefore water will GO INTO the cell and the cell increases in size. Isotonic: The solution has an EQUAL concentration compared to the inside of the cell therefore no water would move in or ...
... Hypotonic: The solution has a HIGHER concentration of water than the concentration of water inside the cell therefore water will GO INTO the cell and the cell increases in size. Isotonic: The solution has an EQUAL concentration compared to the inside of the cell therefore no water would move in or ...
toward a `visible cell`… and beyond
... Visible CellTM Project is focused on the rapid imaging and reconstruction of whole mammalian cells at ~15-20 nm resolution using ET. This is accompanied by the development of efficient yet accurate mark-up of whole cell data, such that the 3D spatial coordinates and approximate volumes and membrane ...
... Visible CellTM Project is focused on the rapid imaging and reconstruction of whole mammalian cells at ~15-20 nm resolution using ET. This is accompanied by the development of efficient yet accurate mark-up of whole cell data, such that the 3D spatial coordinates and approximate volumes and membrane ...
ws flip cell parts - Renton School District
... 8. Nucleus contains ______________________ which are the instructions for making________. The nuclear envelope is a double membrane surrounding the nucleus. It has many _________________ for letting out genetic information. When the cell is making copies of itself, the DNA is wound up in thick ropy ...
... 8. Nucleus contains ______________________ which are the instructions for making________. The nuclear envelope is a double membrane surrounding the nucleus. It has many _________________ for letting out genetic information. When the cell is making copies of itself, the DNA is wound up in thick ropy ...