Name: Date: Period: _____ AP Unit 2 Review Packet: Cell Structure
... 14. Which type of microscope would a scientist use to study the internal structures of cells? Which type of microscope would as scientist use to study the external (3D) features of cells? ...
... 14. Which type of microscope would a scientist use to study the internal structures of cells? Which type of microscope would as scientist use to study the external (3D) features of cells? ...
Membrane Transport Powerpoint
... Since each substance requires a different Transport Protein – There are LOTS in the membrane of every Cell!! ...
... Since each substance requires a different Transport Protein – There are LOTS in the membrane of every Cell!! ...
Cell Functions
... Function: Support structure of cell and transport materials/organelles throughout the cell. The highway of the cell. Made of Microtubules (thin hollow cylinders) and Microfilaments (thin solid ...
... Function: Support structure of cell and transport materials/organelles throughout the cell. The highway of the cell. Made of Microtubules (thin hollow cylinders) and Microfilaments (thin solid ...
Multicellular Life
... – Adult stem cells – The primary role in a living organism is to maintain and repair the tissue in which they are found. – Where are adult stem cells found, and what do they normally do? – Adult stem cells have been identified in many organs and tissues, including brain, bone marrow, skeletal muscle ...
... – Adult stem cells – The primary role in a living organism is to maintain and repair the tissue in which they are found. – Where are adult stem cells found, and what do they normally do? – Adult stem cells have been identified in many organs and tissues, including brain, bone marrow, skeletal muscle ...
Cell Theory - PBSpaces.com Weblogs
... nucleus eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are extremely small. Their DNA floats in the cytoplasm, and they have no distinct* Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. internal parts. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, are made of only one cell. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleu ...
... nucleus eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are extremely small. Their DNA floats in the cytoplasm, and they have no distinct* Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. internal parts. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, are made of only one cell. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleu ...
Cell Analogy Project - Effingham County Schools
... Analogy (Webster’s): “A comparison between two things which are similar in some respects, but otherwise different. An explaining of something by comparing it point by point with something else.” ...
... Analogy (Webster’s): “A comparison between two things which are similar in some respects, but otherwise different. An explaining of something by comparing it point by point with something else.” ...
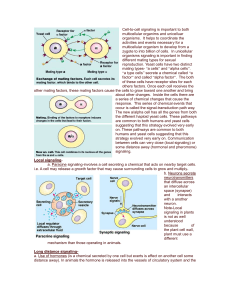
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
... Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and unicelluar organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding different ...
... Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and unicelluar organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding different ...
Cell Analogy Project 2
... a. You may create a 3-D model or a poster (at least 12 X 14) of the cartoon, videogame, or movie. b. This must be your own work, done by hand c. Each part must be visible and clearly labeled with both the real name of the object and the compared organelle. d. It must be neat, clear, and in color. e. ...
... a. You may create a 3-D model or a poster (at least 12 X 14) of the cartoon, videogame, or movie. b. This must be your own work, done by hand c. Each part must be visible and clearly labeled with both the real name of the object and the compared organelle. d. It must be neat, clear, and in color. e. ...
Cell Analogies Worksheet - Effingham County Schools
... Analogy (Webster’s): “A comparison between two things which are similar in some respects, but otherwise different. An explaining of something by comparing it point by point with something else.” ...
... Analogy (Webster’s): “A comparison between two things which are similar in some respects, but otherwise different. An explaining of something by comparing it point by point with something else.” ...
Content Domain 2: Organisms
... The mouse an owl eats would be a _________________. This relationship plus what the mouse eats could be shown in a ___________ ____________. If several food chains intertwine showing many feeding relationships and energy flow you would have a ____________ ______________. If the flow of energy is sho ...
... The mouse an owl eats would be a _________________. This relationship plus what the mouse eats could be shown in a ___________ ____________. If several food chains intertwine showing many feeding relationships and energy flow you would have a ____________ ______________. If the flow of energy is sho ...
Exam 1 Review - Iowa State University
... A) The genome of a prokaryote consists of a single linear strand of DNA contained in a welldefined membrane-bound nucleus. B) Prokaryotic chromosomes are also called plasmids. C) The genome of a prokaryote consists of a single linear strand of DNA contained in a welldefined membrane-bound nucleus. D ...
... A) The genome of a prokaryote consists of a single linear strand of DNA contained in a welldefined membrane-bound nucleus. B) Prokaryotic chromosomes are also called plasmids. C) The genome of a prokaryote consists of a single linear strand of DNA contained in a welldefined membrane-bound nucleus. D ...
Prokaryotic cells
... – Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell – Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the plasma membrane, (i.e., passive transport-diffusion, osmosis, facilitate diffusion; and active ...
... – Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell – Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the plasma membrane, (i.e., passive transport-diffusion, osmosis, facilitate diffusion; and active ...
Meiosis I
... Covered in this presentation was the cell cycle in detail. It was learned that the steps within this cycle are: • G1 phase - energy consuming process. • S phase - DNA duplication. • G2 Phase - growth and energy synthesis. • Mitosis - equal division of DNA. • Prophase - 2 centrosome move to opposite ...
... Covered in this presentation was the cell cycle in detail. It was learned that the steps within this cycle are: • G1 phase - energy consuming process. • S phase - DNA duplication. • G2 Phase - growth and energy synthesis. • Mitosis - equal division of DNA. • Prophase - 2 centrosome move to opposite ...
File
... then the solutions are isotonic to each other. • A solution that has the same salt concentration as the normal cells of the body and the blood. An isotonic beverage (such as Gatorade) may be drunk to replace the fluid and minerals that the body uses during physical activity. • An isotonic cellular e ...
... then the solutions are isotonic to each other. • A solution that has the same salt concentration as the normal cells of the body and the blood. An isotonic beverage (such as Gatorade) may be drunk to replace the fluid and minerals that the body uses during physical activity. • An isotonic cellular e ...
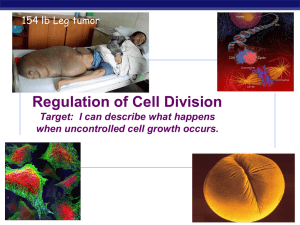
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... Target: I can describe what happens when uncontrolled cell growth occurs. ...
... Target: I can describe what happens when uncontrolled cell growth occurs. ...
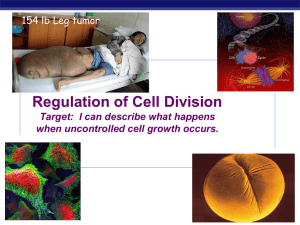
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... Target: I can describe what happens when uncontrolled cell growth occurs. ...
... Target: I can describe what happens when uncontrolled cell growth occurs. ...
SBI3C Exam Review
... relaxation phase in which blood enters the atria and flows in the ventricle = LUBB sound with the opening of the valve between the atria and ventricles. This is when the blood pressure is low. The systole is the contraction phase where the ventricles are filled with blood and pushed out with great ...
... relaxation phase in which blood enters the atria and flows in the ventricle = LUBB sound with the opening of the valve between the atria and ventricles. This is when the blood pressure is low. The systole is the contraction phase where the ventricles are filled with blood and pushed out with great ...
Why do cells need to divide?
... the cell pinches and divides the cytoplasm into two parts two identical separate cells are ...
... the cell pinches and divides the cytoplasm into two parts two identical separate cells are ...
Spontaneous Generation and the Discovery of the Cell
... Using the information you read in “The Debate Over Spontaneous Generation” and “Discovery of the Cell and Mitosis”, answer the following questions, and create a historical timeline. ...
... Using the information you read in “The Debate Over Spontaneous Generation” and “Discovery of the Cell and Mitosis”, answer the following questions, and create a historical timeline. ...
Require energy (ATP) - Olympic High School
... Describe what properties allow a molecule to pass through a phospholipid membrane and what properties prevent a molecule from passing through a phospholipid membrane. ...
... Describe what properties allow a molecule to pass through a phospholipid membrane and what properties prevent a molecule from passing through a phospholipid membrane. ...
Cell Specialization
... phase called GO. Depending on environmental signals, they may reenter the cell cycle or remain in GO permanently. A cell specializes while in interphase or GO. The process in which a cell becomes specialized is called differentiation and occurs when the cell selectively activates or inactivates spec ...
... phase called GO. Depending on environmental signals, they may reenter the cell cycle or remain in GO permanently. A cell specializes while in interphase or GO. The process in which a cell becomes specialized is called differentiation and occurs when the cell selectively activates or inactivates spec ...
Weekly PowerPoint
... 1. What do you think is going on inside of living cells? 2. What do they need to do that? Compare the following types of cells (not all cells look exactly the same! Note-they are not all magnified to the same scale, so even though they look like they are different sizes, it is impossible to tell fro ...
... 1. What do you think is going on inside of living cells? 2. What do they need to do that? Compare the following types of cells (not all cells look exactly the same! Note-they are not all magnified to the same scale, so even though they look like they are different sizes, it is impossible to tell fro ...
Nutrition
... Nutrition: is a process by which organisms acquire chemical substances (Nutrients) used in cellular activities such as metabolism and growth. Organisms differ in the use of particular elements, their source and chemical form. Microbial growth Microbial growth refers to both the increase in cell size ...
... Nutrition: is a process by which organisms acquire chemical substances (Nutrients) used in cellular activities such as metabolism and growth. Organisms differ in the use of particular elements, their source and chemical form. Microbial growth Microbial growth refers to both the increase in cell size ...
cell theory
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) • Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division) ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) • Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division) ...