Cell Wall Architecture Prerequisite for the Cell Division in the
... Most previous attempts to visualize the deposition of microfibrils have utilized the simple freeze fracture technique (Grout 1975, Willison and Cocking 1975, Willison and Grout 1978). Most of the figures in these reports shows microfibrils in close contact with plasma membrane, and the technique is ...
... Most previous attempts to visualize the deposition of microfibrils have utilized the simple freeze fracture technique (Grout 1975, Willison and Cocking 1975, Willison and Grout 1978). Most of the figures in these reports shows microfibrils in close contact with plasma membrane, and the technique is ...
Celltransport3
... random motion • Net diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (down or with the concentration gradient) ...
... random motion • Net diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (down or with the concentration gradient) ...
cell membrane transport
... Types of Solutions Cells can be found in 3 different types of solutions. Isotonic – when the concentrations are equal in and out of the cell Hypotonic – when there is a greater concentration outside the cell than inside the cell causing water to pass into the cell where it may burst Hypertoni ...
... Types of Solutions Cells can be found in 3 different types of solutions. Isotonic – when the concentrations are equal in and out of the cell Hypotonic – when there is a greater concentration outside the cell than inside the cell causing water to pass into the cell where it may burst Hypertoni ...
Sordaria Lab
... segregated during meiosis. This can be clearly visualized if the diploid nucleus is a hybrid for strains with two different spore coat colors. The wild-type strain (+) produces a dark spore, while mutant-tan (tn) or gray (g) strains produce lighter-colored spores. If crossing-over does not occur, th ...
... segregated during meiosis. This can be clearly visualized if the diploid nucleus is a hybrid for strains with two different spore coat colors. The wild-type strain (+) produces a dark spore, while mutant-tan (tn) or gray (g) strains produce lighter-colored spores. If crossing-over does not occur, th ...
Seminar Paper - LENS - The University of Auckland
... The Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations reports that 923 million people worldwide were undernourished in 2007. Just under a quarter of these people were from the Asia‐Pacific region, excluding India and China. Over a quarter of the total were in India (FAO, ...
... The Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations reports that 923 million people worldwide were undernourished in 2007. Just under a quarter of these people were from the Asia‐Pacific region, excluding India and China. Over a quarter of the total were in India (FAO, ...
Packet 18- Kidneys
... On the luminal (aka “apical”) membrane (touching tubule lumen) A. SGLT transporters… Na+ comes into the cell (down the conc gradient) and brings glucose with it! 5. On the basolateral membrane (touching the interstitial fluid): A. NaK Pump!!! (3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in…)…uses ATP B. Maintains the Na+ c ...
... On the luminal (aka “apical”) membrane (touching tubule lumen) A. SGLT transporters… Na+ comes into the cell (down the conc gradient) and brings glucose with it! 5. On the basolateral membrane (touching the interstitial fluid): A. NaK Pump!!! (3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in…)…uses ATP B. Maintains the Na+ c ...
An Adaptive Multiple Access Protocol for Broadcast Channels
... Another factor that influence handoff Area and shape of the cell An ideal situation is to have the cell configuration match the velocity of the MSs and to have a larger boundary where the handoff rate is minimal The mobility of an individual MS is difficult to predict Each MS having a different ...
... Another factor that influence handoff Area and shape of the cell An ideal situation is to have the cell configuration match the velocity of the MSs and to have a larger boundary where the handoff rate is minimal The mobility of an individual MS is difficult to predict Each MS having a different ...
Molecular identification of 26 syntaxin genes and
... *Corresponding author: Roland Kissmehl, [email protected] ...
... *Corresponding author: Roland Kissmehl, [email protected] ...
Stem Cells – general characteristic and sources
... Most primitive stem cell of the adult mammalian is the zygote, which is the result of the fusion of two haploid cells during fertilization. The zygote, as a totipotent stem cell, is able to give rise to both the embryo and the placenta. The “artificial” counterpart of the totipotent zygote is referr ...
... Most primitive stem cell of the adult mammalian is the zygote, which is the result of the fusion of two haploid cells during fertilization. The zygote, as a totipotent stem cell, is able to give rise to both the embryo and the placenta. The “artificial” counterpart of the totipotent zygote is referr ...
Cell Membrane
... Selective permeability enables a cell to maintain homeostasis in spite of unpredictable, changing conditions outside the cell. Because a cell needs to maintain certain conditions to carry out its functions, it must control the import and export of certain molecules and ions. Thus, even if ion conc ...
... Selective permeability enables a cell to maintain homeostasis in spite of unpredictable, changing conditions outside the cell. Because a cell needs to maintain certain conditions to carry out its functions, it must control the import and export of certain molecules and ions. Thus, even if ion conc ...
Plant Stem Cell Niches: Standing the Test of Time
... dent just after the first division of the cap stem cells. Loss of function in the the quiescent center, and (3) generate a zygote into a smaller apical cell and a PIN genes that drive basal auxin trans- basipetal auxin gradient. Using an auxin larger basal cell (Friml et al., 2003). Using port or di ...
... dent just after the first division of the cap stem cells. Loss of function in the the quiescent center, and (3) generate a zygote into a smaller apical cell and a PIN genes that drive basal auxin trans- basipetal auxin gradient. Using an auxin larger basal cell (Friml et al., 2003). Using port or di ...
CELL STRUCTURE_2012
... Simple diffusion of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration ...
... Simple diffusion of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration ...
Slide 1 - Yengage
... • The secretory component is a polypeptide synthesized by epithelial cells that provide the passage for IgA to the mucosal surface. • It also protects IgA from being degraded in intestinal tract. In serum some IgA exists as monomeric H2L2. ...
... • The secretory component is a polypeptide synthesized by epithelial cells that provide the passage for IgA to the mucosal surface. • It also protects IgA from being degraded in intestinal tract. In serum some IgA exists as monomeric H2L2. ...
Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated
... between lysosomes (LAMP11, LC3–) and autolysosomes (LAMP11, LC31) After 4 h of starvation, most, if not all, lysosomes coalesced into enlarged autolysosomes (Fig. 1d). After 8 h of starvation, we saw LAMP1-positive tubular structures extending from autolysosomes (Fig. 1d). After 12 h of starvation, ...
... between lysosomes (LAMP11, LC3–) and autolysosomes (LAMP11, LC31) After 4 h of starvation, most, if not all, lysosomes coalesced into enlarged autolysosomes (Fig. 1d). After 8 h of starvation, we saw LAMP1-positive tubular structures extending from autolysosomes (Fig. 1d). After 12 h of starvation, ...
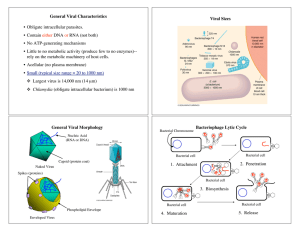
General Viral Characteristics • Obligate intracellular parasites
... Infections where viruses are not detectable for long periods of time but then manifest as a disease. Trigger for disease manifestation is usually a stressor (infection with another microbe, injury, psychological stress) of the infected person. Latent infections may be lysogenic or extrachromosomal. ...
... Infections where viruses are not detectable for long periods of time but then manifest as a disease. Trigger for disease manifestation is usually a stressor (infection with another microbe, injury, psychological stress) of the infected person. Latent infections may be lysogenic or extrachromosomal. ...
The tRNA methyltransferase Dnmt2 is required foraccurate
... (Goll et al, 2006) were backcrossed into the C57BL/6 background for more than 10 generations, thus establishing a homogeneous genetic background for the evaluation of specific aberrant phenotypes. The resulting mice were viable and fertile with no overt phenotypic abnormalities. However, a detailed ...
... (Goll et al, 2006) were backcrossed into the C57BL/6 background for more than 10 generations, thus establishing a homogeneous genetic background for the evaluation of specific aberrant phenotypes. The resulting mice were viable and fertile with no overt phenotypic abnormalities. However, a detailed ...
Oriented Asymmetric Divisions That Generate the
... markers for specific stages and cell types become available. Pavement cells make up most of the surface area of a mature epidermis. Large cells (greater than ⵑ400 m2 in area) were not observed to divide and were scored as pavement cells. These cells were often shaped like jigsaw puzzle pieces with ...
... markers for specific stages and cell types become available. Pavement cells make up most of the surface area of a mature epidermis. Large cells (greater than ⵑ400 m2 in area) were not observed to divide and were scored as pavement cells. These cells were often shaped like jigsaw puzzle pieces with ...
Zinc Transporter of Arabidopsis thaliana AtMTP1 is Localized
... gradient centrifugation (Fig. 2). AtMTP1 protein was recovered in fractions 9–13 together with the vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit a (VHA-a). VHA-a is mainly localized to vacuolar membranes, although a part of VHA-a protein was detected in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and other endomembranes (Sze et al ...
... gradient centrifugation (Fig. 2). AtMTP1 protein was recovered in fractions 9–13 together with the vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit a (VHA-a). VHA-a is mainly localized to vacuolar membranes, although a part of VHA-a protein was detected in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and other endomembranes (Sze et al ...
The following images will be similar to images you will
... The following images and questions will be similar to images you will see on the lab practical next class period. ...
... The following images and questions will be similar to images you will see on the lab practical next class period. ...
The following images will be similar to images you will see on the
... The following images and questions will be similar to images you will see on the lab practical next class period. ...
... The following images and questions will be similar to images you will see on the lab practical next class period. ...
Cells Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Life - Eukaryotes
... not all bacteria are dangerous or disease causing (MH - the adult human in addition bacteria to the skin surface and lining of the respiratory/digestive tract, also has intestines contains trillions of bacteria made up from hundreds of species and thousands of subspecies) biochemically diverse simpl ...
... not all bacteria are dangerous or disease causing (MH - the adult human in addition bacteria to the skin surface and lining of the respiratory/digestive tract, also has intestines contains trillions of bacteria made up from hundreds of species and thousands of subspecies) biochemically diverse simpl ...
studies on the intracellular digestive process in mammalian tissue
... the DNA-protein coacervates as a marker permitted a study of the various stages of the intracellular digestive process which will be described in this report. The role of the dense bodies in intracellular digestion is also demonstrated by labeling them with a different colloidal metal (saccharated i ...
... the DNA-protein coacervates as a marker permitted a study of the various stages of the intracellular digestive process which will be described in this report. The role of the dense bodies in intracellular digestion is also demonstrated by labeling them with a different colloidal metal (saccharated i ...