MsEnod12A Expression Is Linked to Meristematic Activity
... major types of nodule differentiation, the indeterminate and determinate nodule types. For development of indeterminate nodules, such as observed on alfalfa and pea, cortical cell divisions are initiated in the inner cortex. A persistent meristem develops at the distal nodule end, generating a gradi ...
... major types of nodule differentiation, the indeterminate and determinate nodule types. For development of indeterminate nodules, such as observed on alfalfa and pea, cortical cell divisions are initiated in the inner cortex. A persistent meristem develops at the distal nodule end, generating a gradi ...
Reviews
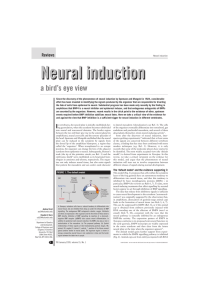
... Since the discovery of the phenomenon of neural induction by Spemann and Mangold in 1924, considerable effort has been invested in identifying the signals produced by the organizer that are responsible for diverting the fate of cells from epidermal to neural. Substantial progress has been made only ...
... Since the discovery of the phenomenon of neural induction by Spemann and Mangold in 1924, considerable effort has been invested in identifying the signals produced by the organizer that are responsible for diverting the fate of cells from epidermal to neural. Substantial progress has been made only ...
Reperfusion of ischemic myocardium: Ultrastructural and
... From the large number of dogs used in this experimental series, only three for each ischemic interval (each interval being defined as one group) will be described here. The experiments presented were deliberately selected from each group for their special and very typical features representative of ...
... From the large number of dogs used in this experimental series, only three for each ischemic interval (each interval being defined as one group) will be described here. The experiments presented were deliberately selected from each group for their special and very typical features representative of ...
Structural Investigations of Liposomes: Effect of Phospholipid
... with the aqueous phase whereas the hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains interact with each other. Characteristics of the particular phospholipid, or combination of phospholipids, also contribute to the type of supramolecular structure. For example, the charge of head group can contribute to ionic repulsio ...
... with the aqueous phase whereas the hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains interact with each other. Characteristics of the particular phospholipid, or combination of phospholipids, also contribute to the type of supramolecular structure. For example, the charge of head group can contribute to ionic repulsio ...
The AP-3 adaptor complex is required for vacuolar function
... mutant background, we observed swelling and vacuolization of PVC compartments visualized by PVC markers, such as GFP-RABF2b [34] (Figure 2E and 2F). Moreover, the swollen PVC phenotype in the pat4 mutant resembled the effect of wortmannin on the PVC morphology [10]. Taken together, these results ind ...
... mutant background, we observed swelling and vacuolization of PVC compartments visualized by PVC markers, such as GFP-RABF2b [34] (Figure 2E and 2F). Moreover, the swollen PVC phenotype in the pat4 mutant resembled the effect of wortmannin on the PVC morphology [10]. Taken together, these results ind ...
Functional unit of RNA polymerase II
... CTD are conserved between yeast and mammals. In fact, all metazoans, fungi, and green plants examined to date, as well as the nearest protistan relatives of these multicellular groups, contain a tandemly repeated CTD. In contrast, the RNAP II largest subunits from many other eukaryotic organisms hav ...
... CTD are conserved between yeast and mammals. In fact, all metazoans, fungi, and green plants examined to date, as well as the nearest protistan relatives of these multicellular groups, contain a tandemly repeated CTD. In contrast, the RNAP II largest subunits from many other eukaryotic organisms hav ...
2386 East Heritage Way, Suite B, Salt Lake City, Utah 84109 USA
... local swelling of the ORS that houses a significant fraction of skin epithelial stem cells (Fig. 1A; Paus and Cotsarelis 1999; Fuchs et al. 2001; Millar 2002). Anagen reentry requires the action of a papilla-derived signal (Hardy 1992) that causes bulge epithelial stem cells to proliferate, migrate ...
... local swelling of the ORS that houses a significant fraction of skin epithelial stem cells (Fig. 1A; Paus and Cotsarelis 1999; Fuchs et al. 2001; Millar 2002). Anagen reentry requires the action of a papilla-derived signal (Hardy 1992) that causes bulge epithelial stem cells to proliferate, migrate ...
TEF30 interacts with photosystem II monomers and is involved in the
... Downloaded from on June 15, 2017 - Published by www.plantphysiol.org Copyright © 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
... Downloaded from on June 15, 2017 - Published by www.plantphysiol.org Copyright © 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
October 9, 2009 - Northwestern University
... band were able to induce RIG-I ATPase activity (Fig. 2C). Comparable results were observed with ss2.2s RNA. Together, these results showed that the immunostimulatory activity of RNA produced by IVT resulted exclusively from unexpected, potentially base-paired RNA species. It has been described that ...
... band were able to induce RIG-I ATPase activity (Fig. 2C). Comparable results were observed with ss2.2s RNA. Together, these results showed that the immunostimulatory activity of RNA produced by IVT resulted exclusively from unexpected, potentially base-paired RNA species. It has been described that ...
Functional Characterization of the spf/ash Splicing Variation in OTC
... amino acids extra) which is degraded rapidly and is inactive [10]. Presumably, the 90% decrease in transcripts detected as Otc mRNA results from other aberrant splicing events possibly causing a frameshift and a premature termination codon and are degraded by the nonsense mediated decay (NMD) mechan ...
... amino acids extra) which is degraded rapidly and is inactive [10]. Presumably, the 90% decrease in transcripts detected as Otc mRNA results from other aberrant splicing events possibly causing a frameshift and a premature termination codon and are degraded by the nonsense mediated decay (NMD) mechan ...
Designing logical codon reassignment
... and UAA over the endogenous amino acids and tRNAs. Enhanced selectivity has been achieved by transferring an aaRS/tRNA pair from another kingdom to the organism of interest, and subsequent aaRS evolution to acquire enhanced selectivity for the desired UAA. Today, over 150 non-canonical amino acids h ...
... and UAA over the endogenous amino acids and tRNAs. Enhanced selectivity has been achieved by transferring an aaRS/tRNA pair from another kingdom to the organism of interest, and subsequent aaRS evolution to acquire enhanced selectivity for the desired UAA. Today, over 150 non-canonical amino acids h ...
Dynamics of Tubulovesicular Recycling Endosomes in Hippocampal
... the dynamics of the endosomal system in neurons. Here we describe two distinct classes of syntaxin 13-labeled endosomes: round– oval stationary organelles and highly mobile tubulovesicular structures. The behavior of these organelles suggests the presence of a dynamic population of endosomes that tr ...
... the dynamics of the endosomal system in neurons. Here we describe two distinct classes of syntaxin 13-labeled endosomes: round– oval stationary organelles and highly mobile tubulovesicular structures. The behavior of these organelles suggests the presence of a dynamic population of endosomes that tr ...
Cardosin A Molecular Determinants and Biosynthetic Pathways
... and it allowed to conclude that the protein’s expression did not retrieved any phenotype to the cells or individuals. However, experiments conducted in BY-2 cells revealed to be inconclusive since cardosin A expression in this system is not predictable. The data obtained along this work using severa ...
... and it allowed to conclude that the protein’s expression did not retrieved any phenotype to the cells or individuals. However, experiments conducted in BY-2 cells revealed to be inconclusive since cardosin A expression in this system is not predictable. The data obtained along this work using severa ...
Mechanisms for the Carcinostatic Activity of Se
... Initiation of cancer is caused by a carcinogen, a foreign chemical, a natural metabolite, or radiation such as xrays and UV-light and pollutants such as caused by smoking. Initiators cause genetic damage that results in mutations of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that may lead to cancer. Selenite, sele ...
... Initiation of cancer is caused by a carcinogen, a foreign chemical, a natural metabolite, or radiation such as xrays and UV-light and pollutants such as caused by smoking. Initiators cause genetic damage that results in mutations of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that may lead to cancer. Selenite, sele ...
Murine Regulatory T Cells Contain Hyperproliferative and Death
... with different concentrations of an anti-CD3 Ab for 72 h. After cell surface staining for CD4 and CD8 as well as fixable Live/ Dead staining for dead cells, cultured cells were intracellularly stained for Foxp3. Comparison between total CD4+Foxp3+ Treg and CD4+Foxp32 Tcon revealed much weaker prolif ...
... with different concentrations of an anti-CD3 Ab for 72 h. After cell surface staining for CD4 and CD8 as well as fixable Live/ Dead staining for dead cells, cultured cells were intracellularly stained for Foxp3. Comparison between total CD4+Foxp3+ Treg and CD4+Foxp32 Tcon revealed much weaker prolif ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... out, di¡erences in the bio¢lms formed by the Gramnegative species E. cloacae and P. aeruginosa might have caused di¡erences in accessibility to phage. In removal of bacteria from stainless steel surfaces with listeriaphage, combinations of two phage or a phage in combination with quaternary ammonium ...
... out, di¡erences in the bio¢lms formed by the Gramnegative species E. cloacae and P. aeruginosa might have caused di¡erences in accessibility to phage. In removal of bacteria from stainless steel surfaces with listeriaphage, combinations of two phage or a phage in combination with quaternary ammonium ...
Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways
... of inflammatory signaling has been attributed to its deubiquitinase activity toward ubiquitinated TRAF2, TRAF3 and TRAF6 (ref. 37). Such data support the hypothesis that TRAF ubiquitination is an important factor in TRAF-mediated signaling. Nevertheless, precise genetic experiments, probably involvi ...
... of inflammatory signaling has been attributed to its deubiquitinase activity toward ubiquitinated TRAF2, TRAF3 and TRAF6 (ref. 37). Such data support the hypothesis that TRAF ubiquitination is an important factor in TRAF-mediated signaling. Nevertheless, precise genetic experiments, probably involvi ...
Gametogenesis: Conversion of Germ Cells Into Male and Female
... Occasionally nondisjunction occurs during mitosis (mitotic nondisjunction) in an embryonic cell during the earliest cell divisions. Such conditions produce mosaicism, with some cells having an abnormal chromosome number and others being normal. Affected individuals may exhibit few or many of the cha ...
... Occasionally nondisjunction occurs during mitosis (mitotic nondisjunction) in an embryonic cell during the earliest cell divisions. Such conditions produce mosaicism, with some cells having an abnormal chromosome number and others being normal. Affected individuals may exhibit few or many of the cha ...
Review Catecholamines, cardiac natriuretic peptides and
... therapeutic use. The concept of the endocrine heart was later enriched by the identification of a growing number of cardiac hormonal substances involved in organ modulation under normal and stress-induced conditions. Recently, chromogranin A (CgA), a major constituent of the secretory granules, and ...
... therapeutic use. The concept of the endocrine heart was later enriched by the identification of a growing number of cardiac hormonal substances involved in organ modulation under normal and stress-induced conditions. Recently, chromogranin A (CgA), a major constituent of the secretory granules, and ...
Assembling Neural Crest Regulatory Circuits into a Gene
... Neural crest cells form over a lengthy period of time during development that starts at gastrulation and extends into late organogenesis. This process is initiated by a combination of inductive signals emanating from environing tissues, such as the underlying mesoderm or adjacent neural and non-neur ...
... Neural crest cells form over a lengthy period of time during development that starts at gastrulation and extends into late organogenesis. This process is initiated by a combination of inductive signals emanating from environing tissues, such as the underlying mesoderm or adjacent neural and non-neur ...
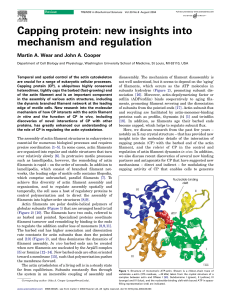
Capping protein: new insights into mechanism
... the dynamic branched filament network at the leading edge of motile cells. New research into the molecular mechanism of how CP interacts with the actin filament in vitro and the function of CP in vivo, including discoveries of novel interactions of CP with other proteins, has greatly enhanced our un ...
... the dynamic branched filament network at the leading edge of motile cells. New research into the molecular mechanism of how CP interacts with the actin filament in vitro and the function of CP in vivo, including discoveries of novel interactions of CP with other proteins, has greatly enhanced our un ...
Graded maternal short gastrulation protein contributes to embryonic
... (Araujo and Bier, 2000; Twombly et al., 1996) where they function to pattern structures of the chorion (Araujo and Bier, 2000; Deng and Bownes, 1997; Peri and Roth, 2000; Twombly et al., 1996) as well as the embryonic DV axis (Araujo and Bier, 2000). With respect to its DV patterning role, genetic e ...
... (Araujo and Bier, 2000; Twombly et al., 1996) where they function to pattern structures of the chorion (Araujo and Bier, 2000; Deng and Bownes, 1997; Peri and Roth, 2000; Twombly et al., 1996) as well as the embryonic DV axis (Araujo and Bier, 2000). With respect to its DV patterning role, genetic e ...
Glutamate Decreases Mitochondrial Size and Movement in Primary
... generate ATP and ROS. Mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles that are capable of replicating their own genome, synthesizing proteins, and undergoing fission and fusion, and presumably degradation too (for review, see Scheffler, 1999). It is widely believed (although not necessarily proven) that ...
... generate ATP and ROS. Mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles that are capable of replicating their own genome, synthesizing proteins, and undergoing fission and fusion, and presumably degradation too (for review, see Scheffler, 1999). It is widely believed (although not necessarily proven) that ...
the Early Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Engrailed-2
... number of key limitations with prostate specific antigen (PSA), currently the standard detection test, has justified evaluation of new biomarkers. We have assessed the diagnostic potential of Engrailed-2 (EN2) protein, a homeodomain-containing transcription factor expressed in PC cell lines and secr ...
... number of key limitations with prostate specific antigen (PSA), currently the standard detection test, has justified evaluation of new biomarkers. We have assessed the diagnostic potential of Engrailed-2 (EN2) protein, a homeodomain-containing transcription factor expressed in PC cell lines and secr ...