Mitosis
... • nuclear membrane starts to form around each gp of daughter chromosomes • cell appears to have 2 nuclei (nucleus) ...
... • nuclear membrane starts to form around each gp of daughter chromosomes • cell appears to have 2 nuclei (nucleus) ...
10-2 Cell Division lecture notes
... _______________________________________________________________________ Chromosomes: Genetic material (DNA) is usually in ____________________________ Before cell division,_______________________________________________________ Each chromosomes makes__________________________________________________ ...
... _______________________________________________________________________ Chromosomes: Genetic material (DNA) is usually in ____________________________ Before cell division,_______________________________________________________ Each chromosomes makes__________________________________________________ ...
Cell Review
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
2nd Nine Weeks Science Benchmark Study Guide
... What process uses the plant food, _________, and breaks it apart to release energy in the form of ATP? _______________ Write the equation ...
... What process uses the plant food, _________, and breaks it apart to release energy in the form of ATP? _______________ Write the equation ...
Cancer Guided Notes
... ______________________: stops tumor growth _____________________: corrects mistakes in DNA made during replication ...
... ______________________: stops tumor growth _____________________: corrects mistakes in DNA made during replication ...
Week 18 - Crossroads Academy
... Some practical applications of the concepts: (try to answer these on your own by Thursday, Jan. 12th. Please rewrite the question followed by your answer neatly on a separate sheet of paper) 1) How does prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA structure differ? 2) What is the difference between rough ER and s ...
... Some practical applications of the concepts: (try to answer these on your own by Thursday, Jan. 12th. Please rewrite the question followed by your answer neatly on a separate sheet of paper) 1) How does prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA structure differ? 2) What is the difference between rough ER and s ...
Chap 19 - Iowa State University
... anterior end and they later act as _________ causing development of anterior end of the embryo. ...
... anterior end and they later act as _________ causing development of anterior end of the embryo. ...
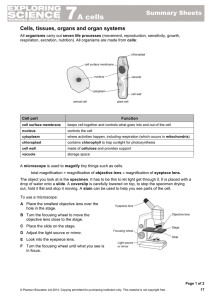
7A cells
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
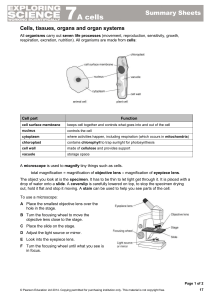
KS3 Science
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
Objectives - Cengage Learning
... Understand the basic tenets of the cell theory. Understand the essential structure and function of the cell membrane. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. Describe the organelles associated with ...
... Understand the basic tenets of the cell theory. Understand the essential structure and function of the cell membrane. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. Describe the organelles associated with ...
Cells - Hazlet.org
... forms two new cells. This process is called mitosis. What is a reason that human skin cells frequently undergo mitosis? ...
... forms two new cells. This process is called mitosis. What is a reason that human skin cells frequently undergo mitosis? ...
Cells - BrainPOP
... 4. Which of the following is a type of cell organelle? a. Membrane b. Cytoplasm c. DNA d. Peroxysome 5. The majority of a cell's interior is comprised of: a. Cytoplasm b. Nuclei c. Mitochondria d. Ribosomes ...
... 4. Which of the following is a type of cell organelle? a. Membrane b. Cytoplasm c. DNA d. Peroxysome 5. The majority of a cell's interior is comprised of: a. Cytoplasm b. Nuclei c. Mitochondria d. Ribosomes ...
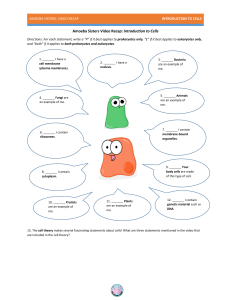
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Introduction to Cells
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
Meisosis ppt
... • Cells that have the normal number of chromosomes are called “Diploid” • Cells that have ½ the normal number of chromosomes are called “Haploid” • Meiosis results in 4 Haploid cells that are genetically different from each other (and remember the parent cell was diploid) ...
... • Cells that have the normal number of chromosomes are called “Diploid” • Cells that have ½ the normal number of chromosomes are called “Haploid” • Meiosis results in 4 Haploid cells that are genetically different from each other (and remember the parent cell was diploid) ...
Robert Hooke
... states that the basic units of living organisms structure are all cells. • Matthias was a professor at universities of Jena • He concluded that all plants were made of cells • Matthias concluded (as seen in the quote below) that all cells come from another cell before them • He also discovered t ...
... states that the basic units of living organisms structure are all cells. • Matthias was a professor at universities of Jena • He concluded that all plants were made of cells • Matthias concluded (as seen in the quote below) that all cells come from another cell before them • He also discovered t ...
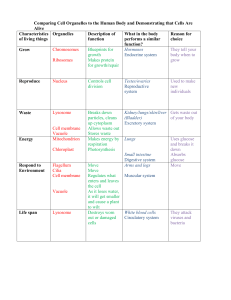
Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and
... Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and Demonstrating that Cells Are Alive Characteristics Organelles Description of What in the body Reason for of living things function performs a similar choice function? Chromosomes Blueprints for Hormones They tell your Grow growth Endocrine system body ...
... Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and Demonstrating that Cells Are Alive Characteristics Organelles Description of What in the body Reason for of living things function performs a similar choice function? Chromosomes Blueprints for Hormones They tell your Grow growth Endocrine system body ...
Slide () - Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research
... From: Biotechnology in the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Foundations and Future of Hair Cell Regeneration J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2011;54(6):1709-1731. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2011/10-0149) ...
... From: Biotechnology in the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Foundations and Future of Hair Cell Regeneration J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2011;54(6):1709-1731. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2011/10-0149) ...
The Cell Overview - Bulldogbiology.com
... Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He also predicted that cells come from other cells. ...
... Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He also predicted that cells come from other cells. ...