Cells Dictionary (Answers) Word Definition Carbohydrates Lipids
... Stands for deoxyribonucleic acid It holds the code for every cell in your body Shape is called a double helix DNA is the instruction manual for an organism The order of our DNA determines what and who we are ...
... Stands for deoxyribonucleic acid It holds the code for every cell in your body Shape is called a double helix DNA is the instruction manual for an organism The order of our DNA determines what and who we are ...
Levels of Cellular Organization - Concordia Shanghai Teacher
... a. organ systems, organs, tissues, cells b. tissues, cells, organs, organ systems c. cells, tissues, organ systems, organs d. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems ...
... a. organ systems, organs, tissues, cells b. tissues, cells, organs, organ systems c. cells, tissues, organ systems, organs d. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems ...
Cells
... Tissues are groups of cells working together to perform a certain job. Organs are groups of tissue that perform a certain function. Organs working together to carry out a certain life function are an organ system. An Organism is any organized body or system conceived of as analogous to a living bein ...
... Tissues are groups of cells working together to perform a certain job. Organs are groups of tissue that perform a certain function. Organs working together to carry out a certain life function are an organ system. An Organism is any organized body or system conceived of as analogous to a living bein ...
Lesson Plan
... a. Explain the characteristics of life as indicated by cellular processes including i. Homeostasis ii. Energy transfers and transformation iii. Transportation of molecules iv. Disposal of wastes v. Synthesis of new molecules Learning Objectives: At the conclusion of this lesson, students will be abl ...
... a. Explain the characteristics of life as indicated by cellular processes including i. Homeostasis ii. Energy transfers and transformation iii. Transportation of molecules iv. Disposal of wastes v. Synthesis of new molecules Learning Objectives: At the conclusion of this lesson, students will be abl ...
Cell Organelles
... Cell Wall • Found in plant and bacterial cells • Rigid, protective barrier • Located outside of the cell membrane • Made of cellulose in ...
... Cell Wall • Found in plant and bacterial cells • Rigid, protective barrier • Located outside of the cell membrane • Made of cellulose in ...
3/1 Spirochetes and Mycoplasma
... Treponema T. pallidum most significant-syphilis Only found in humans Cannot use light microscope Syphilis Primary-lesions at site of inoculation and some lymph node involvement Secondary-flu-like symptoms, more wide spread lymp node involvement and lesions over the body Tertiary or late stage-any bo ...
... Treponema T. pallidum most significant-syphilis Only found in humans Cannot use light microscope Syphilis Primary-lesions at site of inoculation and some lymph node involvement Secondary-flu-like symptoms, more wide spread lymp node involvement and lesions over the body Tertiary or late stage-any bo ...
1. Which organelles are most closely associated with the process of
... 2. Centrioles are normally present in the (1) cytoplasm of onion cells (2) cytoplasm of cheek cells (3) nuclei of liver cells (4) nuclei of bean cells ...
... 2. Centrioles are normally present in the (1) cytoplasm of onion cells (2) cytoplasm of cheek cells (3) nuclei of liver cells (4) nuclei of bean cells ...
Tissue - scienceathawthorn
... relationships of function are most commonly used. For example the urinary system comprises organs that work together to produce, store, and carry urine. Usually there is a main tissue and sporadic tissues. The main tissue is the one that is unique for the specific organ. For example, main tissue in ...
... relationships of function are most commonly used. For example the urinary system comprises organs that work together to produce, store, and carry urine. Usually there is a main tissue and sporadic tissues. The main tissue is the one that is unique for the specific organ. For example, main tissue in ...
Cell - WordPress.com
... -They are found free-floating in the cytoplasm throughout the cell or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum ...
... -They are found free-floating in the cytoplasm throughout the cell or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum ...
Cells - Biloxi Public Schools
... thick, gel-like fluid “cell-liquid” cell organelles float in the cytoplasm ...
... thick, gel-like fluid “cell-liquid” cell organelles float in the cytoplasm ...
Tenlie Mourning November 20,2010 Investigation 5 Homeostasis is
... concentration inside the cell, the cell is in a hypotonic environment. At this point, water will diffuse inside the cell until equilibrium is reached. When the concentration of solute molecules is higher inside the cell, the cell is in a hypertonic environment. In this case, water will diffuse out u ...
... concentration inside the cell, the cell is in a hypotonic environment. At this point, water will diffuse inside the cell until equilibrium is reached. When the concentration of solute molecules is higher inside the cell, the cell is in a hypertonic environment. In this case, water will diffuse out u ...
Biology 1406 - HCC Learning Web
... 5. (P. 7-9) Living things interact with and draw sustenance from their environment. All living things depend on each other for food which supplies energy and material nutrients. Living things use the energy in their environment to create orderly processes for themselves and return disorder to their ...
... 5. (P. 7-9) Living things interact with and draw sustenance from their environment. All living things depend on each other for food which supplies energy and material nutrients. Living things use the energy in their environment to create orderly processes for themselves and return disorder to their ...
The Cell Theory Notes
... 11. Unicellular organisms are composed of ___________________________ cell. 12. Multicellular organisms are made up of ___________________________cells. ...
... 11. Unicellular organisms are composed of ___________________________ cell. 12. Multicellular organisms are made up of ___________________________cells. ...
5-1
... Consist of 4 phases: G1 Most of the cells growth and activity S Chromosome replication takes place G2 Final preparations for cell division M Cell Divison takes place (Mitosis) Cell Division is the process in which the cell divides into two ...
... Consist of 4 phases: G1 Most of the cells growth and activity S Chromosome replication takes place G2 Final preparations for cell division M Cell Divison takes place (Mitosis) Cell Division is the process in which the cell divides into two ...
Notes – Chapter 5
... A. Anton von Leeuwenhoek invented the first Microscope in the 17th century. He used it to become the first person to observe and describe microscopic organisms and living cells. B. Robert Hooke used the microscope to describe the empty chambers of cork as “Cells”. Hooke was the first person to use t ...
... A. Anton von Leeuwenhoek invented the first Microscope in the 17th century. He used it to become the first person to observe and describe microscopic organisms and living cells. B. Robert Hooke used the microscope to describe the empty chambers of cork as “Cells”. Hooke was the first person to use t ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy - RIDDELL
... membrane made up of cellulose. This helps the plant cell to accept large amounts of liquid through osmosis, without being destroyed. An animal cell does not have this cell wall, too much fluid would cause it the cell to pop. Plant cells also are different from animal cells because they have chloropl ...
... membrane made up of cellulose. This helps the plant cell to accept large amounts of liquid through osmosis, without being destroyed. An animal cell does not have this cell wall, too much fluid would cause it the cell to pop. Plant cells also are different from animal cells because they have chloropl ...
04_Clicker_Questions
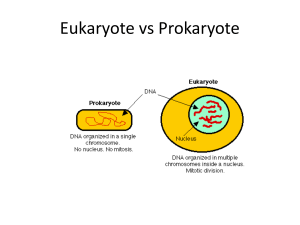
... Eukaryotes have the interior of the cell divided by internal membranes into specialized compartments. ...
... Eukaryotes have the interior of the cell divided by internal membranes into specialized compartments. ...
cell theory - Valhalla High School
... Cell Theory Timeline • 1839 - Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann create cell theory. The theory states that all living things are made up of one or more cells. Schleiden publishes his cell theory applying it to plants, while Schwann publishes his applied to animals. ...
... Cell Theory Timeline • 1839 - Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann create cell theory. The theory states that all living things are made up of one or more cells. Schleiden publishes his cell theory applying it to plants, while Schwann publishes his applied to animals. ...
Cells
... cell. Types of organelles: Ribosome are organelles which participate in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion, the power plants of the cell, are organelles that produce energy. Lysosomes are organelles that contain enzymes that aid in the digestion. ...
... cell. Types of organelles: Ribosome are organelles which participate in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion, the power plants of the cell, are organelles that produce energy. Lysosomes are organelles that contain enzymes that aid in the digestion. ...
Chapter #12 The Cell Cycle
... 2. The ability of an organism to procreate has cellular basis. 3. Rudolf Virchow put it this way: “Where a cell exists, there must have been a preexisting cell.” He summarized this concept with the Latin axiom, “Omnis cellula e cellula,” meaning “Every cell from a cell.” 4. The continuity of life is ...
... 2. The ability of an organism to procreate has cellular basis. 3. Rudolf Virchow put it this way: “Where a cell exists, there must have been a preexisting cell.” He summarized this concept with the Latin axiom, “Omnis cellula e cellula,” meaning “Every cell from a cell.” 4. The continuity of life is ...
Chapter 3, Section 1 - Rock Hill High School
... – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
1.immune system notes
... multiplying to kill it. This process is so immediate & explosive that the pathogen is killed before you know you are sick. Memory cells make you immune to that pathogen ...
... multiplying to kill it. This process is so immediate & explosive that the pathogen is killed before you know you are sick. Memory cells make you immune to that pathogen ...