Chapter 9 PPT
... The time interval during which the velocity changes from its initial to final values is assumed to be short The interaction forces are assumed to be much greater than any external forces present ...
... The time interval during which the velocity changes from its initial to final values is assumed to be short The interaction forces are assumed to be much greater than any external forces present ...
Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [Exercise 0010
... (a) Express N̂ using X̂n . Using theorems on adding independent random variables find hN i and Var(N ). (b) Find the probability function f (N ) using combinatorial considerations. Calculate from it hL̂i and V ar(L). (c) Assume |(V /V0 ) − 21 | 1, and treat N as a continuous random variable. Apprx ...
... (a) Express N̂ using X̂n . Using theorems on adding independent random variables find hN i and Var(N ). (b) Find the probability function f (N ) using combinatorial considerations. Calculate from it hL̂i and V ar(L). (c) Assume |(V /V0 ) − 21 | 1, and treat N as a continuous random variable. Apprx ...
simulating fritz haber`s ammonia synthesis with thermodynamic
... Lappeenranta University of Technology • 53851 Lappeenranta, Finland n 1909, Fritz Haber succeeded in synthesizing ammonia from hydrogen and atmospheric nitrogen. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918. He presented the original experimental results in his Nobel lecture in 1920. This pap ...
... Lappeenranta University of Technology • 53851 Lappeenranta, Finland n 1909, Fritz Haber succeeded in synthesizing ammonia from hydrogen and atmospheric nitrogen. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918. He presented the original experimental results in his Nobel lecture in 1920. This pap ...
An engine operates with 1 mol
... The work done by the system is the area enclosed by the cycle, where we assume that we start with the isothermal expansion. It is only in this expansion that heat is extracted from a reservoir. There is no heat transfer in the adiabatic expansion or compression. Thus we would completely convert heat ...
... The work done by the system is the area enclosed by the cycle, where we assume that we start with the isothermal expansion. It is only in this expansion that heat is extracted from a reservoir. There is no heat transfer in the adiabatic expansion or compression. Thus we would completely convert heat ...
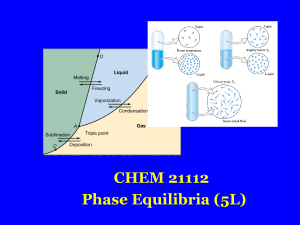
Thermodynamics and Phase Diagrams
... Sometimes metastable states can be very short-lived, or at other times they can exist almost indefinitely. These are explained by the free-energy hump between the metastable and equilibrium states in Fig. 3.1. In general, higher free-energy humps, or energy barriers, lead to slower transformation ra ...
... Sometimes metastable states can be very short-lived, or at other times they can exist almost indefinitely. These are explained by the free-energy hump between the metastable and equilibrium states in Fig. 3.1. In general, higher free-energy humps, or energy barriers, lead to slower transformation ra ...
Pressure Data - Moore Chemistry
... The Temperature – Volume Relationship : Charles’ Law Jacques Charles (1746-1823) was the scientist who developed the scientific law that relates temperature of a gas to its volume. As the temperature of a gas increases, its volume increases and as the temperature of a gas decreases, its volume d ...
... The Temperature – Volume Relationship : Charles’ Law Jacques Charles (1746-1823) was the scientist who developed the scientific law that relates temperature of a gas to its volume. As the temperature of a gas increases, its volume increases and as the temperature of a gas decreases, its volume d ...
Notes Sheet - mychemcourse
... Substances react according to definite ratios of numbers of particles (atoms, ions, formula units, or molecules). The following balanced chemical equation shows that two atoms of aluminum react with three molecules of iodine to form two formula units of aluminum iodide. 2Al(s) + 3I2(s) 2AlI3(s) If ...
... Substances react according to definite ratios of numbers of particles (atoms, ions, formula units, or molecules). The following balanced chemical equation shows that two atoms of aluminum react with three molecules of iodine to form two formula units of aluminum iodide. 2Al(s) + 3I2(s) 2AlI3(s) If ...
Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics
... ⎛ ∂ ln Ω ⎞ ⎛ ∂ ln Ω ⎞ ln Ω E − Ei , N − N j , = ln Ω ( E, N ) − ⎜ ...
... ⎛ ∂ ln Ω ⎞ ⎛ ∂ ln Ω ⎞ ln Ω E − Ei , N − N j , = ln Ω ( E, N ) − ⎜ ...