Free Energy - Wunder Chem
... by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively) the signs of both Ho and So, and calculation or estimation of Go when needed. LO 5.14 The student is able to determine whether a chemical or physical process is thermodynamically favorable by calculating the change in standard Gibbs free e ...
... by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively) the signs of both Ho and So, and calculation or estimation of Go when needed. LO 5.14 The student is able to determine whether a chemical or physical process is thermodynamically favorable by calculating the change in standard Gibbs free e ...
File
... by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively) the signs of both Ho and So, and calculation or estimation of Go when needed. LO 5.14 The student is able to determine whether a chemical or physical process is thermodynamically favorable by calculating the change in standard Gibbs fre ...
... by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively) the signs of both Ho and So, and calculation or estimation of Go when needed. LO 5.14 The student is able to determine whether a chemical or physical process is thermodynamically favorable by calculating the change in standard Gibbs fre ...
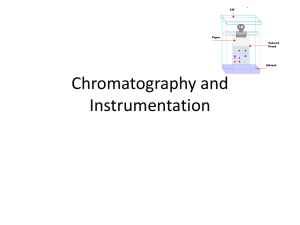
Chromatography and Instrumentation
... phase and mobile phase, the components of the mixture which have a better affinity with the mobile phase will move more easily with the water than those that have a better affinity with the stationary phase ...
... phase and mobile phase, the components of the mixture which have a better affinity with the mobile phase will move more easily with the water than those that have a better affinity with the stationary phase ...
Molecular dynamics algorithms and hydrodynamic screening
... different thermodynamic ensemble, which may be more suitable for the system in consideration. Sometimes, however, one is simply forced to introduce such modifications to overcome the inherent instability of microcanonical MD algorithms, which is due to the discretization errors induced by the finite ...
... different thermodynamic ensemble, which may be more suitable for the system in consideration. Sometimes, however, one is simply forced to introduce such modifications to overcome the inherent instability of microcanonical MD algorithms, which is due to the discretization errors induced by the finite ...
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I (01:160:327) SYLLABUS AND GENERAL
... statistical thermodynamics, and kinetics, which you should be able to apply in future studies and in your career in science or a related field. be able to apply your knowledge of thermodynamics/kinetics to physical transformations, chemical reactions, phase and chemical equilibria, and solutions. ha ...
... statistical thermodynamics, and kinetics, which you should be able to apply in future studies and in your career in science or a related field. be able to apply your knowledge of thermodynamics/kinetics to physical transformations, chemical reactions, phase and chemical equilibria, and solutions. ha ...
Chapter 4 The First Law - Physics | Oregon State University
... state defined as in Eq.4.5. Moreover, state variables are not independent and can be functionally expressed in terms of other state variables. Usually only a few are needed to completely specify any state of a system. The precise number required is the content of an important theorem which is stated ...
... state defined as in Eq.4.5. Moreover, state variables are not independent and can be functionally expressed in terms of other state variables. Usually only a few are needed to completely specify any state of a system. The precise number required is the content of an important theorem which is stated ...
THERMODYNAMICS. Elements of Physical Chemistry. By P. Atkins
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
THERMODYNAMICS. Elements of Physical Chemistry. By P. Atkins
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
Statistics_Probability
... without distinguishing them from one another is called macrostate of the system. For example, if four particles are to be distributed in two compartments without distinguishing among the particles, then there are five possible macrostates. If n particles are to be distributed in 2 compartments. The ...
... without distinguishing them from one another is called macrostate of the system. For example, if four particles are to be distributed in two compartments without distinguishing among the particles, then there are five possible macrostates. If n particles are to be distributed in 2 compartments. The ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics
... The ideas and methods developed in this course find very broad application, not only within physics, but in biology, geology, chemistry, astronomy, engineering, computer science/artificial intelligence/information technology, finance, philosophy, etc. Indeed one of the central reasons why a physics deg ...
... The ideas and methods developed in this course find very broad application, not only within physics, but in biology, geology, chemistry, astronomy, engineering, computer science/artificial intelligence/information technology, finance, philosophy, etc. Indeed one of the central reasons why a physics deg ...